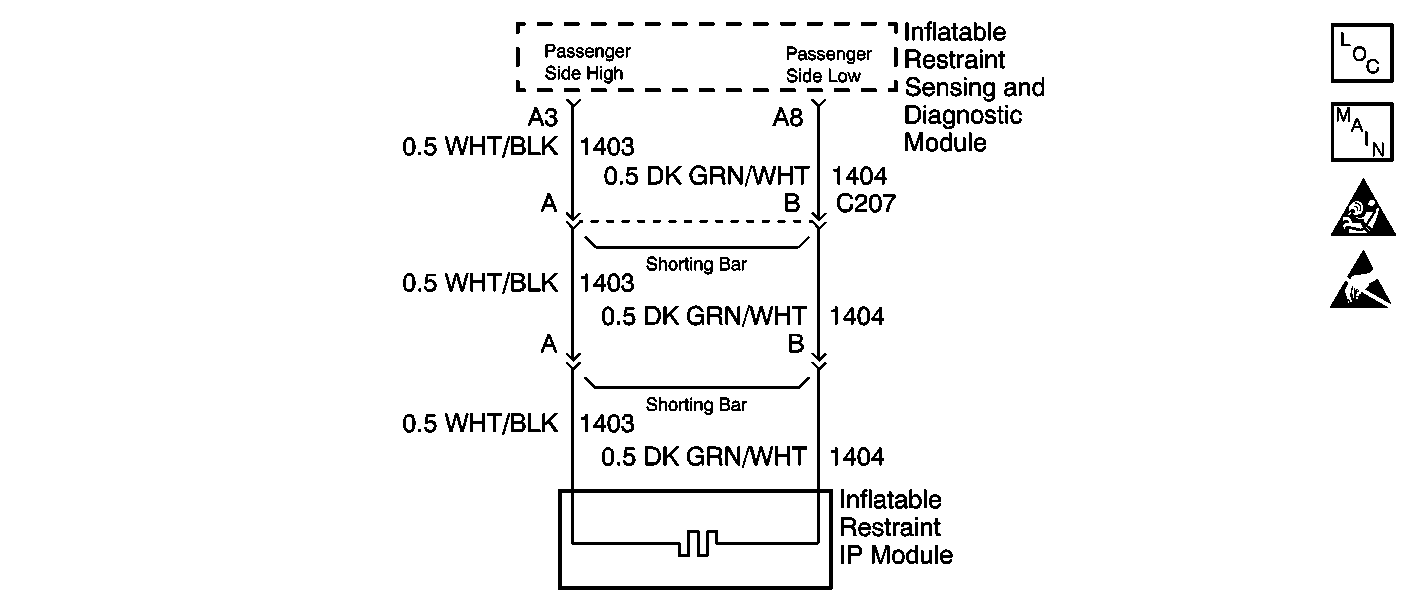
Circuit Description
When you first turn ON the ignition, the inflatable restraint sensing and diagnostic module (SDM) performs tests to diagnose critical malfunctions within itself. Then the SDM performs the following continuous diagnostic tests on the deployment loops:
| • | Deployment loop voltage out of range test |
| • | Deployment loop resistance measurement test |
If the voltage out of range test detects a short to voltage condition, the resistance measurement test for that deployment loop will not be performed.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Deployment loop voltage out of range test - Ignition voltage is within the normal operating voltage range.
Deployment loop resistance measurement test:
| • | Ignition voltage is within the normal operating voltage range. |
| • | Passenger frontal deployment loop is not shorted to voltage. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Deployment loop voltage out of range test - Passenger frontal high terminal A3 is more than 6 volts for 300 milliseconds.
Deployment loop resistance measurement test - Passenger frontal high terminal A3 of is less than 2 volts AND passenger frontal deployment loop resistance is less than 6 ohms for 300 milliseconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The SDM commands ON the AIR BAG warning lamp via Class 2 serial data.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition responsible for setting the DTC no longer exists, and the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function is used. |
| • | A history DTC will clear once 255 malfunction free ignition cycles have occurred. |
Diagnostic Aids
A short to voltage or a short to ground condition in the inflatable restraint IP module deployment loop can cause an intermittent condition. Inspect the passenger frontal high and passenger frontal low circuits carefully for cutting or chafing. Wiring pigtail damage requires replacement of the inflatable restraint IP module.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step checks the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector at the base of the steering column.
-
This step isolates the malfunction to one side of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector at the base of the steering column .
-
This step checks the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector at the IP module.
-
This step determines if there is a short to ground or a short to voltage in either the passenger frontal high or passenger frontal low circuits or if there is a malfunctioning inflatable restraint IP module.
-
This step checks to see if there is a short to ground in the passenger frontal high circuit.
-
This step checks to see if there is a short to ground in the passenger frontal low circuit.
-
This step checks to see if there is a short to voltage in the passenger frontal high circuit.
-
This step determines if there is a short to voltage in the passenger frontal low circuit or if there is a malfunctioning SDM.
-
This step clears all SIR and all communication DTCs.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the SIR Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||
Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. Does either the component or harness side of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector at the base of the steering column exhibit signs of corrosion, terminal damage, or poor connections? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | |||||||
3 | If the harness side of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector is damaged, replace the harness side of the connector. Refer to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 16 | -- | ||||||
4 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this DTC is current? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||
5 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this DTC is current? | -- | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||
Does either the component or harness side of the inflatable restraint IP module yellow 2-way connector at the IP module exhibit any signs of corrosion, terminal damage, or poor connections? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 | |||||||
7 |
Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
Does the scan tool indicate that this DTC is current? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 10 | |||||||
9 |
Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
10 |
Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
Does the resistance measure less than the specified value? | OL | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 13 | |||||||
12 | Locate and repair the short to ground in the passenger frontal high circuit. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
Use the DMM the measure the resistance between the passenger frontal low circuit and a known good ground. Does the resistance measure less than the specified value? | OL | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 15 | |||||||
14 | Locate and repair the short to ground in the passenger frontal low circuit. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
Does the voltage measure less than the specified value? | 1 V | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 16 | |||||||
16 | Locate and repair the short to voltage in the passenger frontal high circuit. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
Use the DMM to measure the voltage between the passenger frontal low circuit and a known good ground. Does the voltage measure less than the specified value? | 1 V | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 18 | |||||||
18 | Locate and repair the short to voltage in the passenger frontal low circuit. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
19 |
Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||
Did you complete the action? | -- | -- |
