For 1990-2009 cars only
Useful information about a tire is molded into its sidewall. The examples below show a typical passenger car tire and a compact spare tire sidewall.
Passenger Car Tire Example
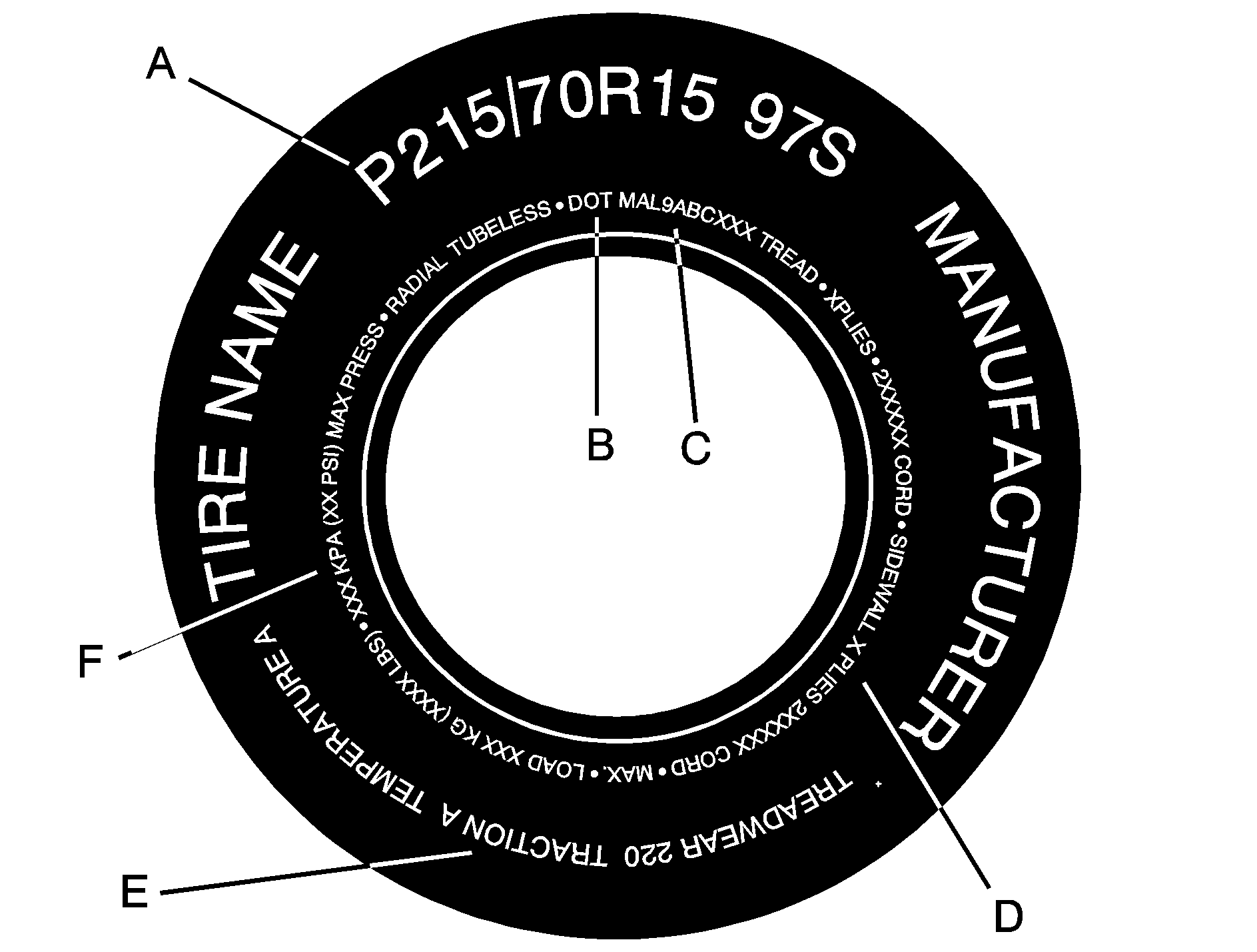
(A) Tire Size : The tire size is a combination of letters and numbers used to define a particular tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type and service description. See the "Tire Size" illustration later in this section for more detail.
(B) DOT (Department of Transportation) : The Department of Transportation (DOT) code indicates that the tire is in compliance with the U.S. Department of Transportation Motor Vehicle Safety Standards.
(C) Tire Identification Number (TIN) : The letters and numbers following DOT code are the Tire Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture.
(D) Tire Ply Material : The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(E) Uniform Tire Quality Grading (UTQG) : Tire manufacturers are required to grade tires based on three performance factors: treadwear, traction and temperature resistance. For more information see Uniform Tire Quality Grading .
(F) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit : Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load. For information on recommended tire pressure see Inflation - Tire Pressure and Loading the Vehicle .
Compact Spare Tire Example
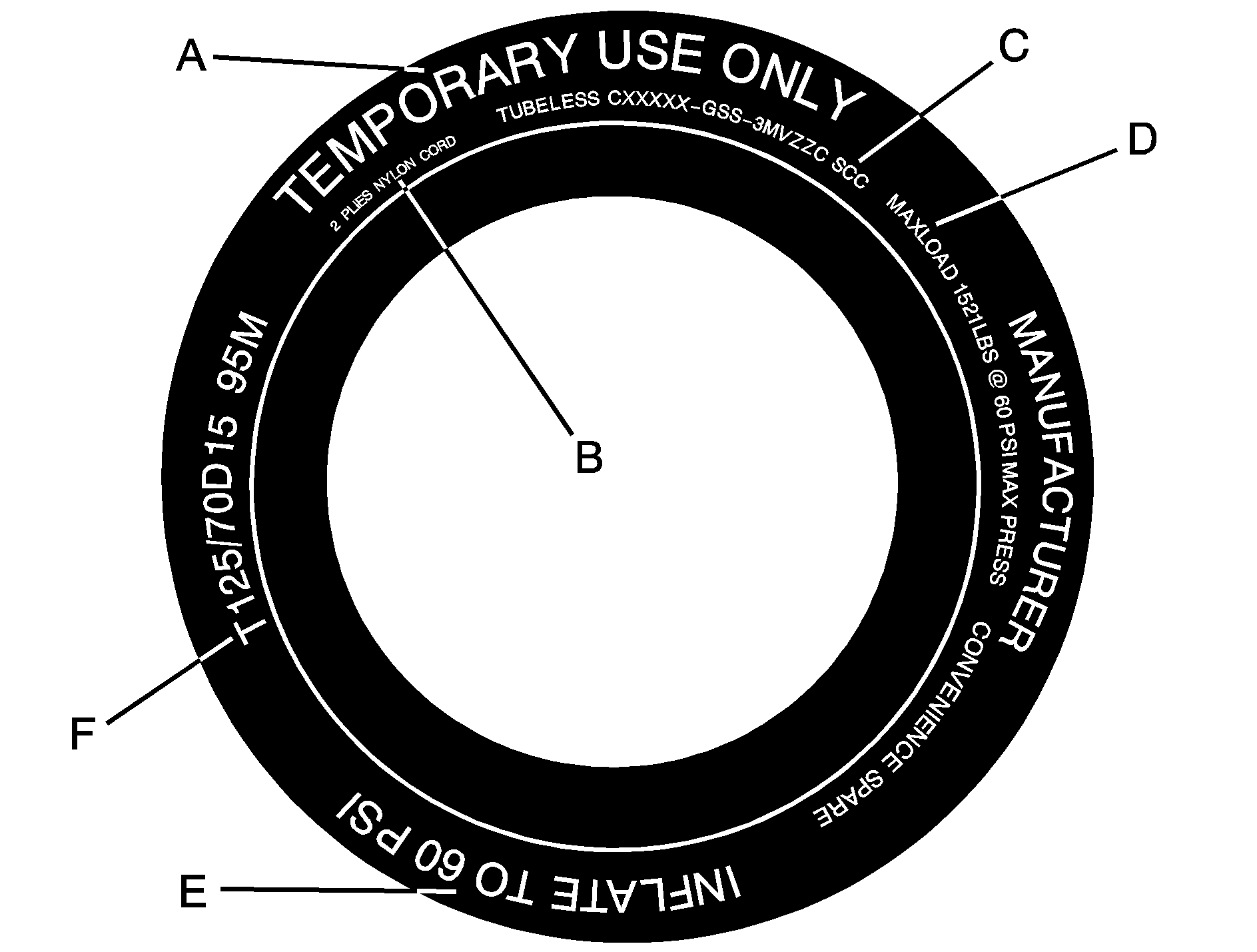
(A) Temporary Use Only : The compact spare tire or temporary use tire has a tread life of approximately 3,000 miles (5 000 km) and should not be driven at speeds over 65 mph (105 km/h). The compact spare tire is for emergency use when a regular road tire has lost air and gone flat. See Compact Spare Tire and If a Tire Goes Flat .
(B) Tire Ply Material : The type of cord and number of plies in the sidewall and under the tread.
(C) Tire Identification Number (TIN) : The Tire Identification Number (TIN). The TIN shows the manufacturer and plant code, tire size, and date the tire was manufactured. The TIN is molded onto both sides of the tire, although only one side may have the date of manufacture.
(D) Maximum Cold Inflation Load Limit : Maximum load that can be carried and the maximum pressure needed to support that load. See Compact Spare Tire and Loading the Vehicle .
(E) Tire Inflation : The temporary use tire or compact spare tire should be inflated to 60 psi (420 kPa). For more information on tire pressure and inflation see Inflation - Tire Pressure .
(F) Tire Size : A combination of letters and numbers define a tire's width, height, aspect ratio, construction type and service description. The letter T as the first character in the tire size means the tire is for temporary use only.
Tire Size
The following illustration shows an example of a typical passenger car tire size.
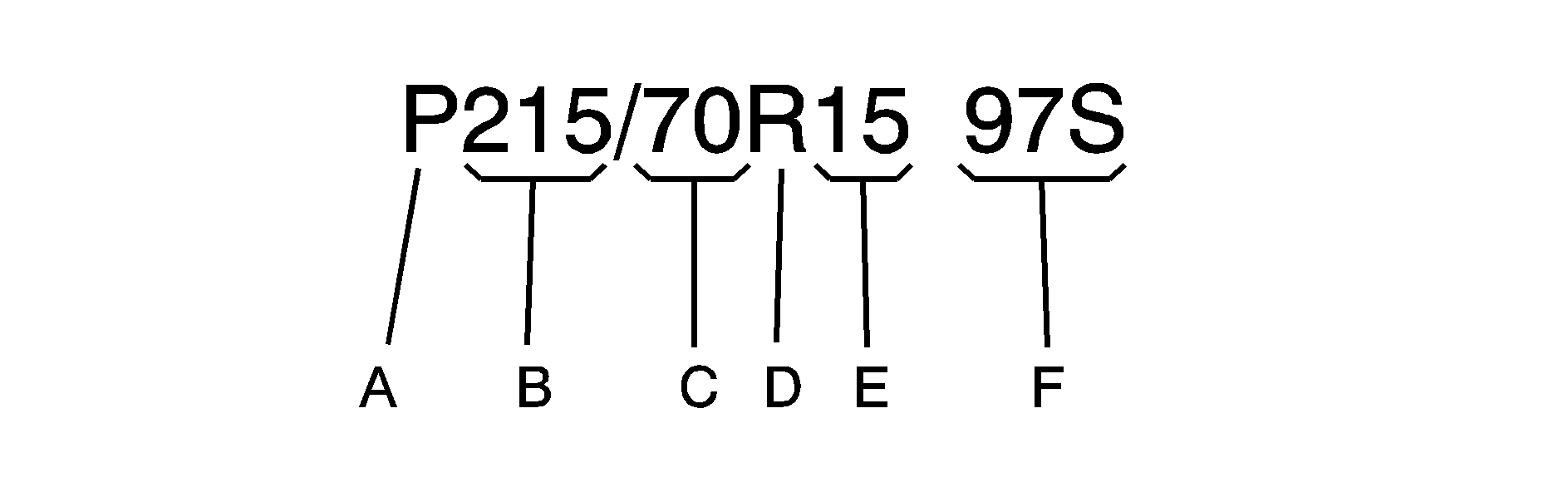
(A) Passenger (P-Metric) Tire : The United States version of a metric tire sizing system. The letter P as the first character in the tire size means a passenger vehicle tire engineered to standards set by the U. S. Tire and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width : The three-digit number indicates the tire section width in millimeters from sidewall to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio : A two-digit number that indicates the tire height-to-width measurements. For example, if the tire size aspect ratio is 70, as shown in item C of the illustration, it would mean that the tire's sidewall is 70% as high as it is wide.
(D) Construction Code : A letter code is used to indicate the type of ply construction in the tire. The letter R means radial ply construction; the letter D means diagonal or bias ply construction; and the letter B means belted-bias ply construction.
(E) Rim Diameter : Diameter of the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description : These characters represent the load index and speed rating of the tire. The load index represents the load carry capacity a tire is certified to carry. The speed rating is the maximum speed a tire is certified to carry a load.
