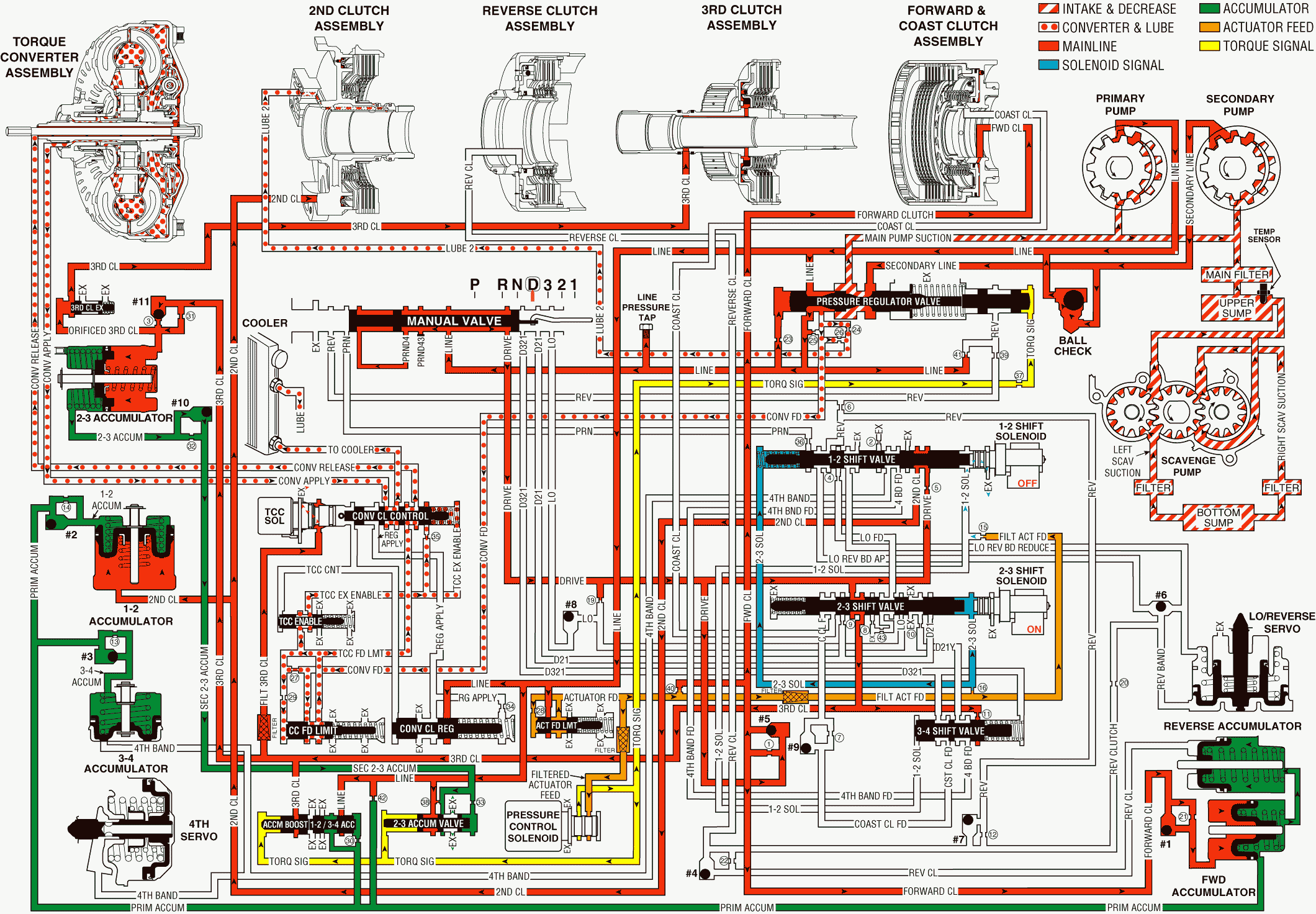
As the speed of the vehicle increases, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) receives input signals from various engine and transmission sensors. The PCM uses this data to energize the 2-3 shift solenoid (SS) valve in order to shift the transmission into third gear at the appropriate time.
Third Clutch Applies
2-3 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve
The PCM energizes (turns ON) the 2-3 SS valve. The PCM blocks the exhaust of the 2-3 SS valve fluid to create high pressure in the 2-3 SS valve passage. High fluid pressure from the 2-3 SS valve moves the 2-3 shift valve into the upshifted position.
2-3 Shift Valve
High fluid pressure from the 2-3 SS valve holds the 2-3 shift valve in the upshifted position. The 2-3 shift valve allows drive fluid to pass between two valve lands and enter the third clutch circuit. Third clutch fluid is then routed to the third clutch piston, and the fluid applies the clutch. In addition, third clutch fluid is routed to the following components:
| • | Checkball #11 |
| • | 2-3 Accumulator Piston |
| • | Third Clutch Exhaust Valve |
| • | Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid Valve |
| • | 3-4 Shift Valve |
#11 Checkball (Third Clutch, Orificed Third Clutch)
The #11 checkball is located in the case cover. Third clutch pressure seats the checkball, which routes fluid through orifice #31, where the fluid enters the orificed third clutch circuit. Orificed third clutch fluid is also routed to the 2-3 accumulator valve, to the 1-2 & 3-4 accumulator valve, and to the TCC solenoid valve.
2-3 Shift Accumulation
2-3 Accumulator Piston
Orificed third clutch pressure actuates the 2-3 accumulator piston, which cushions the apply of the third clutch. The 2-3 accumulator fluid acts on the spring side of the piston, and the fluid is forced back through its circuit to checkball #10.
#10 Checkball (2-3 Accumulator, Secondary 2-3 Accumulator)
The #10 checkball is located in the case cover. This checkball is unseated by 2-3 accumulator fluid, allowing fluid to enter the secondary 2-3 accumulator circuit. Secondary 2-3 accumulator fluid is then routed to the 2-3 accumulator valve.
2-3 Accumulator Valve
Biased by spring force and torque signal on one end, the 2-3 accumulator valve regulates the exhaust of 2-3 accumulator fluid during a 2-3 shift.
Third Clutch Exhaust Valve
Orificed third clutch fluid pressure shifts the exhaust valve against spring force. The valve allows orificed third clutch fluid to enter the third clutch circuit, where the fluid applies the third clutch.
Overdrive Range, Third Gear