Transmission Control Module (TCM)
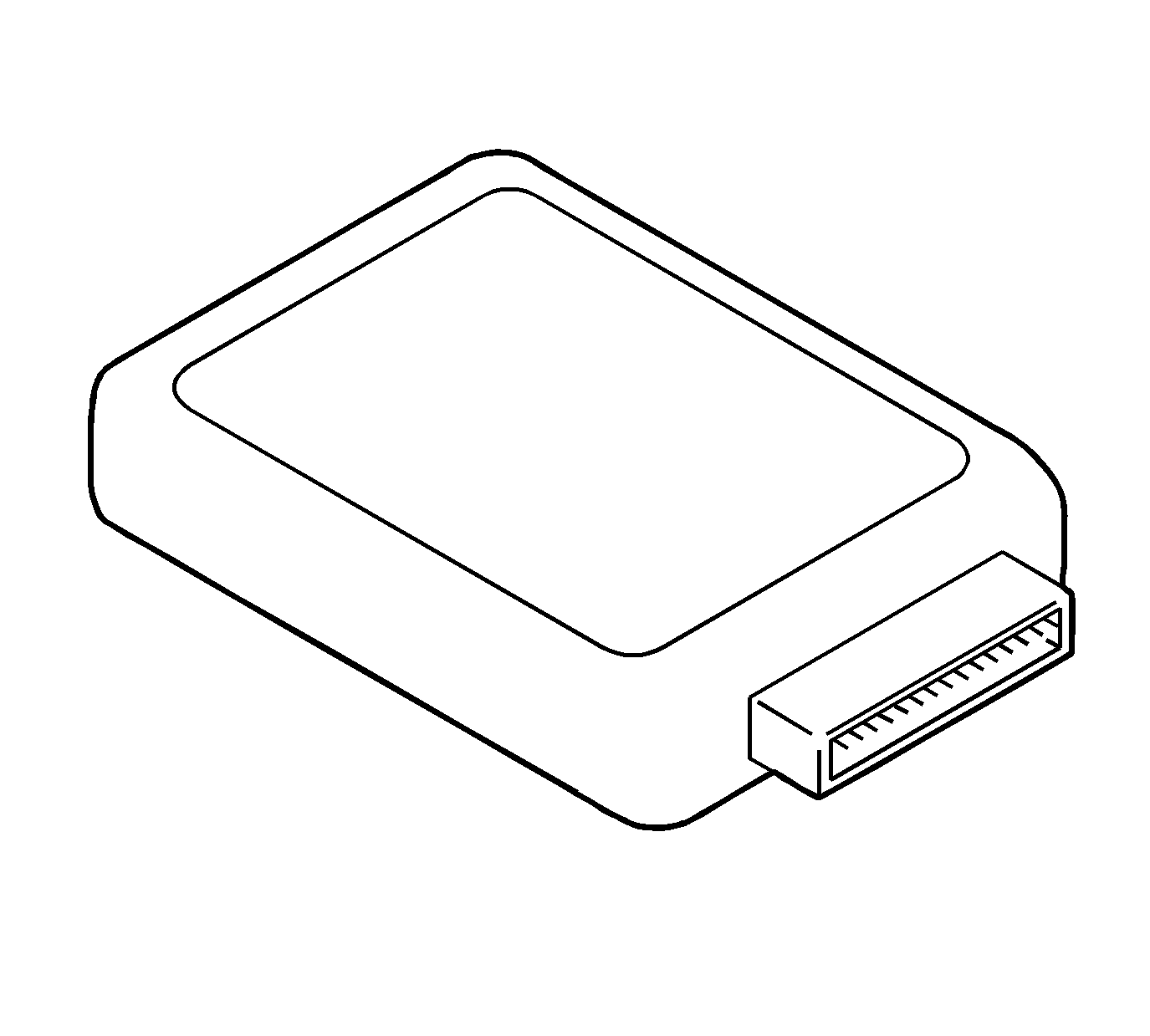
The electronic control system for the automatic transmission provides extremely precise control to make smooth shifting in all driving situations. Engine torque, clutch engagement, oil pressure, shifting time, shift timing and other factors are controlled by signals from the TCM in accordance with vehicle condition. The electronic control system is also equipped with a self diagnosis system which diagnosis malfunctions of electronically controlled components. The TCM receives the signal from each sensor and then sends the control signal to the transmission and the engine to make precise operation.
The TCM controls the operation of the clutches and brakes based on the shift pattern for each driving mode, Economy, Power, Winter. When shifting the transmission, the engine torque is controlled and the hydraulic pressure in the transmission is controlled to make smooth shifting in all driving situations.
The electronic shift system consists of the following components:
| • | TCM |
| • | 2-3/3-4 Shift Solenoid (S1) |
| • | 1-2/3-4 Shift Solenoid (S2) |
| • | Line Pressure Control Solenoid (SLT) |
| • | Lockup Control Solenoid (SLU) |
| • | Neutral Switching Solenoid |
| • | Transmission Input Speed Sensor (ISS) |
| • | Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS) |
| • | Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor |
| • | Park/Neutral Position Switch |
Shift Solenoid (S1, S2)
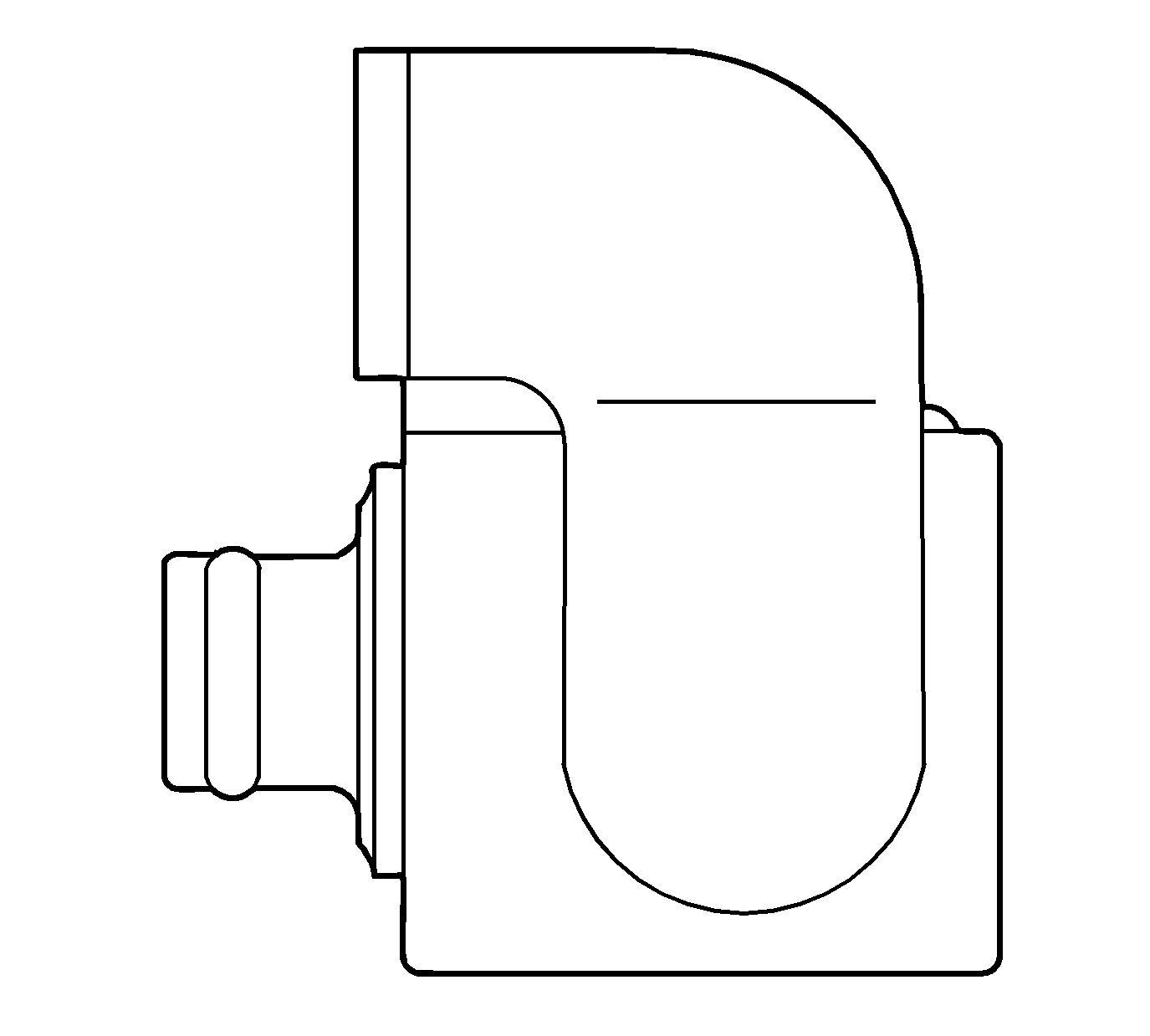
The shift solenoids reside directly in the transmission valve body. The shift solenoids are normally closed and are energized, turned ON, by the TCM supplying voltage to the solenoids. Coil resistance is 11-15 ohm at 20°C (68°F).
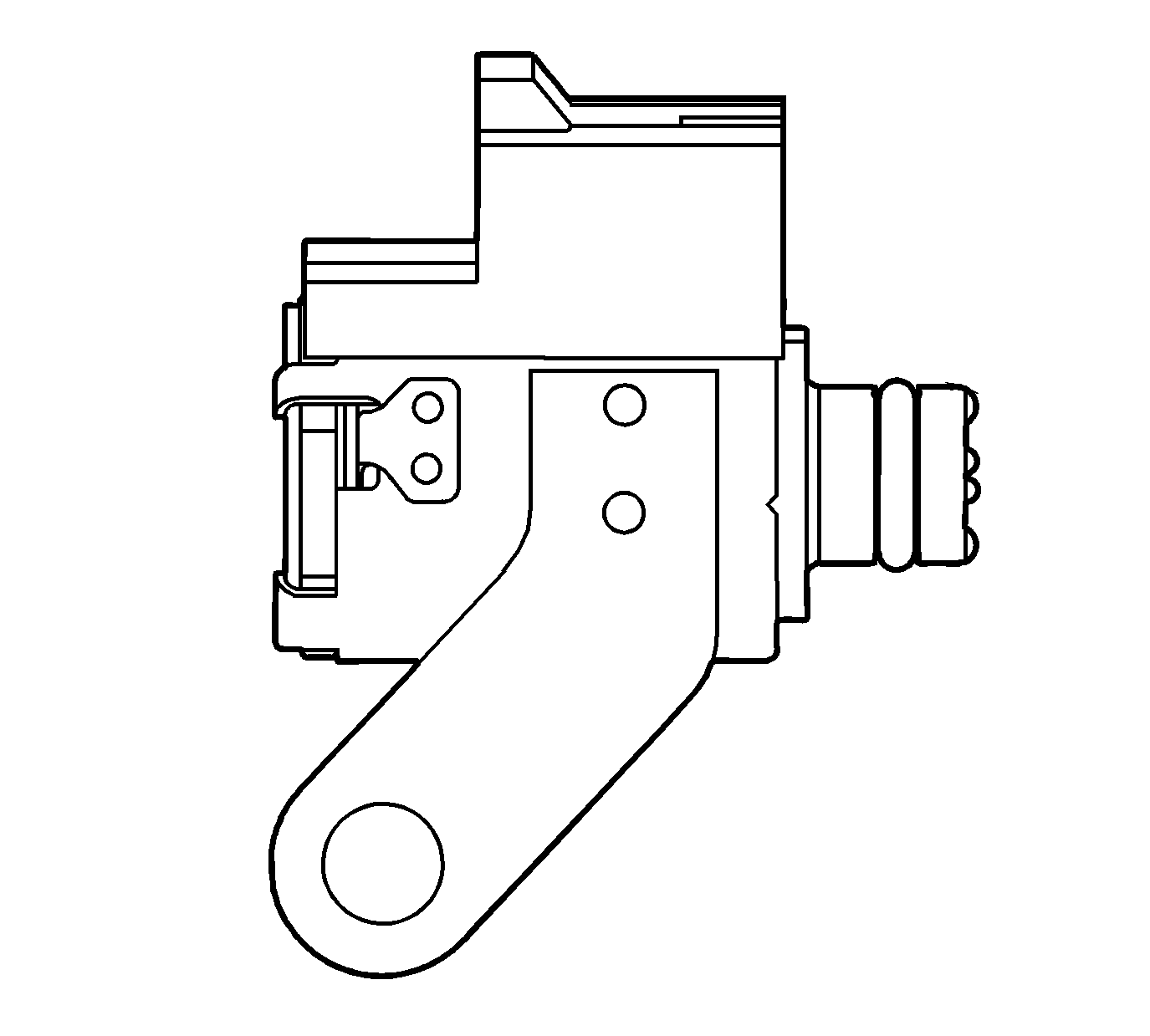
Line Pressure Control Solenoid (SLT)
The line pressure control solenoid resides directly in the transmission valve body. The solenoid controls transmission line pressure based on the current flow through its coil windings. The TCM supplies and monitors the current to the solenoid. Coil resistance is 3.2-3.8 ohm at 20°C (68°F).
Duty Cycle, Frequency and Current Flow
A "duty cycle" may be defined as the percentage of time current is flowing through a solenoid coil during each cycle. The number of cycles that occur within a specified amount of time, usually measured in seconds, is called "frequency". Typically, the operation of an electronically controlled pulse width modulated solenoid is explained in terms of duty cycle and frequency.
Lockup Control Solenoid (SLU)

The lockup control solenoid resides directly in the transmission valve body. The solenoid controls transmission lockup pressure based on the current flow through its coil windings. The TCM supplies and monitors the current to the solenoid. Coil resistance is 5.0-5.6 ohm at 20°C (68°F).
Duty Cycle, Frequency and Current Flow
A "duty cycle" may be defined as the percentage of time current is flowing through a solenoid coil during each cycle. The number of cycles that occur within a specified amount of time, usually measured in seconds, is called "frequency". Typically, the operation of an electronically controlled pulse width modulated solenoid is explained in terms of duty cycle and frequency.
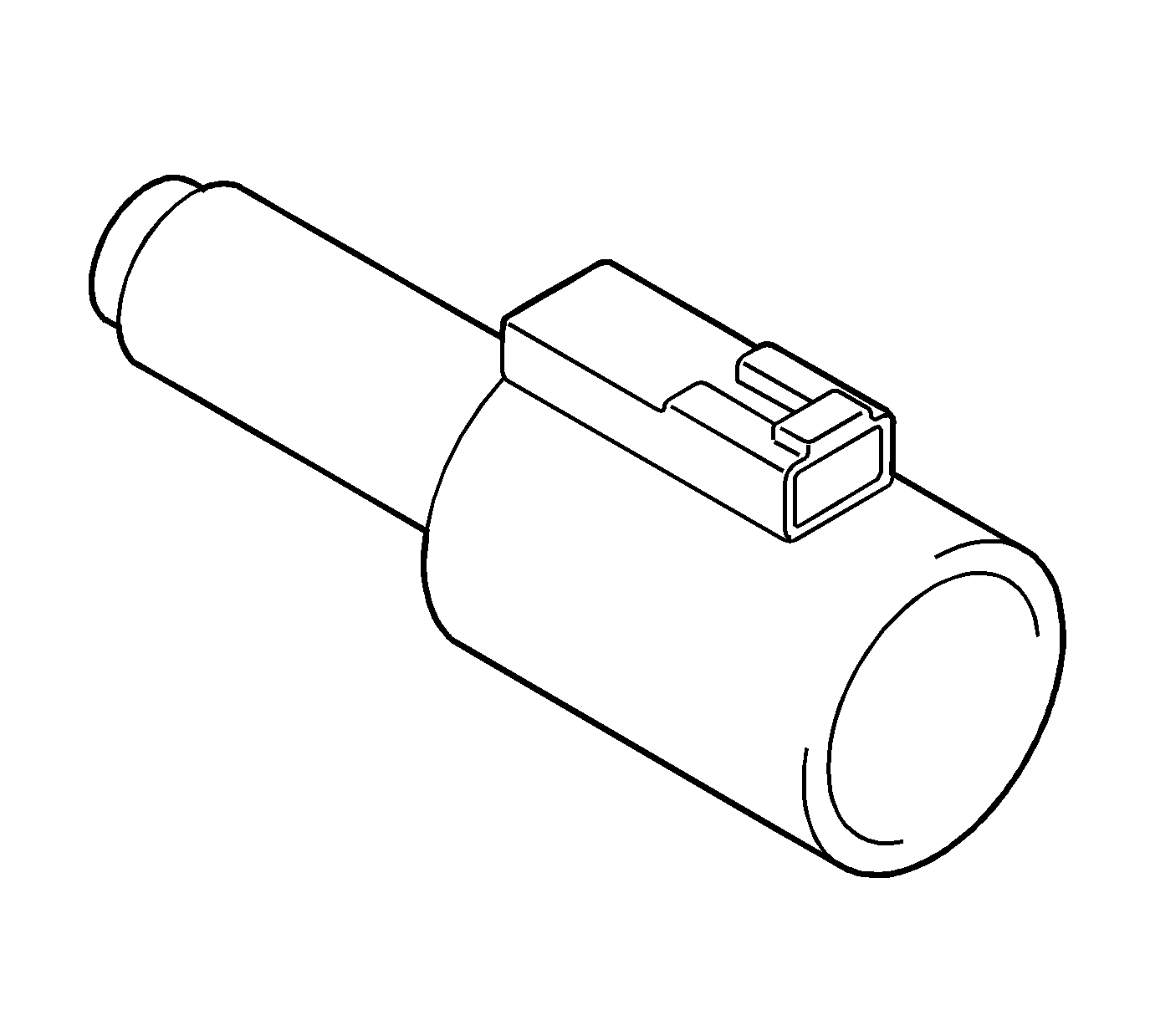
Neutral Switching Solenoid
The neutral switching solenoid resides directly in the transmission valve body. The solenoid is normally open and is energized, turned ON, by the TCM supplying voltage to the solenoid. Coil resistance is 12-16 ohm at 20°C (68°F).
Transmission Input Speed Sensor (ISS)
The ISS is a magnetic pick-up type sensor. It produces 20 pulses for each C1 cylinder revolution.
Transmission Output Speed Sensor (OSS)

The OSS is a magnetic pick-up type sensor. It produces 12 pulses for each output shaft revolution.
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Sensor
The TFT sensor is part of the automatic transmission wiring harness assembly. The TFT sensor is an analog type, which changes value based on temperature. The sensor has a negative-temperature coefficient. This means that as the temperature increases, the resistance decreases, and as the temperature decreases the resistance increases. The TCM supplies a 5-volt reference signal to the sensor and measures the voltage drop in the circuit. When the transmission fluid is cold the sensor resistance is high and the TCM detects high signal voltage. As the fluid temperature warms to a normal operating temperature, the resistance becomes less and the signal voltage decreases. Resistance is 5800-7090 ohm at 10°C (50°F) and 105-117 ohm at 145°C (293°F).
Park/Neutral Position Switch
The park/neutral position switch is a sliding contact switch attached to the manual shift detent lever assembly outside the transmission case. The four inputs to the TCM from the park/neutral position switch indicate which position is selected by the transmission selector lever. This information is used for engine controls as well as determining the transmission shift patterns. The four input parameters represented are A, B, C, and PA.
