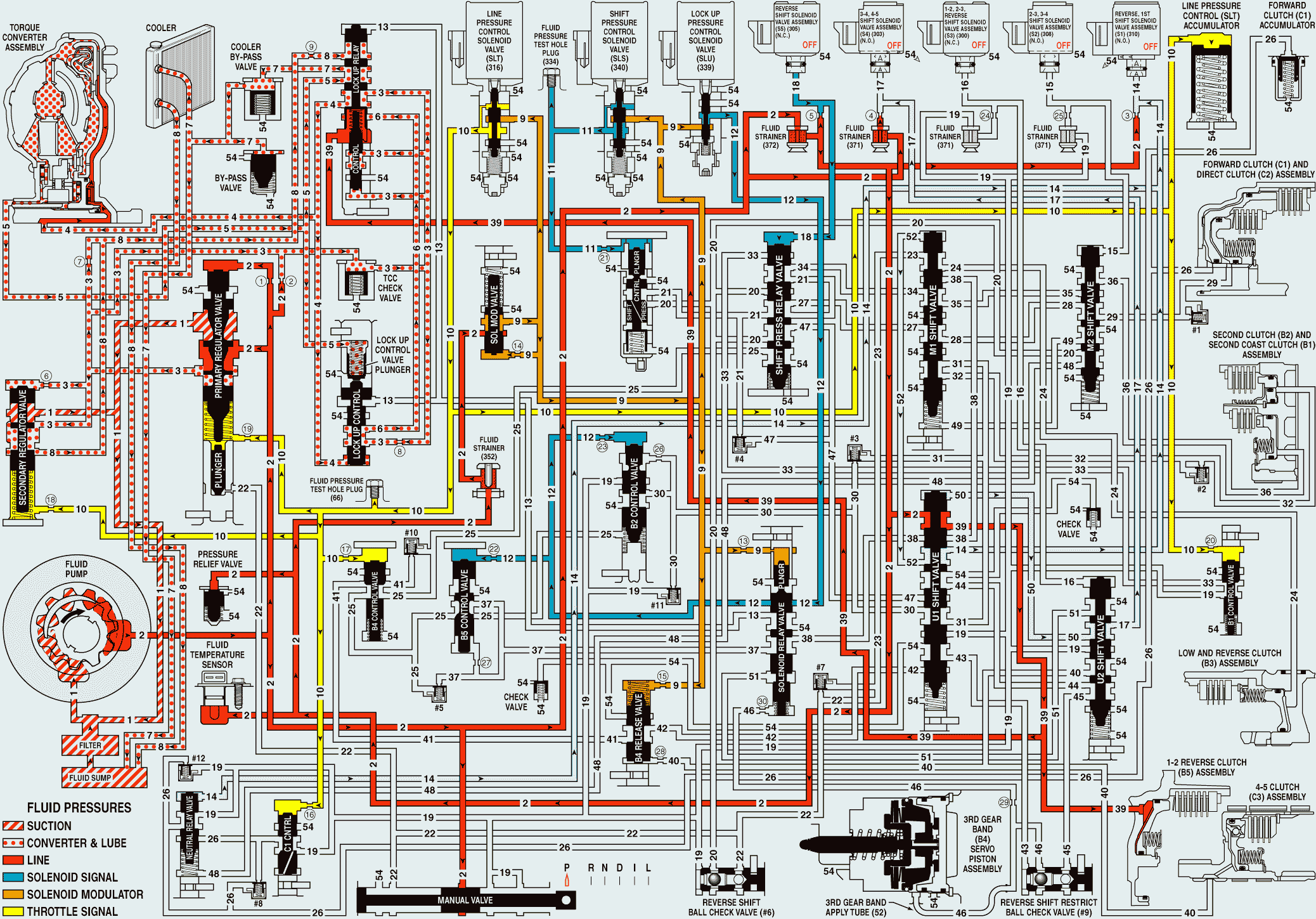
With the gear selector lever in the PARK (P) position and the engine running, the line pressure from the fluid pump assembly is directed to various components in the control valve body assembly and the transmission case assembly.
FLUID PRESSURE DIRECTED IN PREPARATION FOR A SHIFT
Manual Valve
Mechanically controlled by the gear selector lever, the manual valve is in the PARK (P) position and prevents line (2) pressure from the primary regulator valve from entering the drive (19) and reverse (22) fluid circuits.
Reverse, 1st Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Assembly (S1)
Line (2) fluid passes through orifice #3 into the S1 signal (14) fluid circuit in preparation for a shift. The normally open reverse, 1st SS valve assembly is OFF, allowing any fluid pressure in the S1 signal (14) fluid circuit to exhaust through the solenoid.
3-4, 4-5 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Assembly (S4)
Line (2) fluid passes through orifice #4 into the S4 signal (17) fluid circuit in preparation for a shift. The normally open 3-4, 4-5 SS valve assembly is OFF, allowing any fluid pressure in the S4 signal (17) fluid circuit to exhaust through the solenoid.
Reverse Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Assembly (S5)
Line (2) fluid passes through orifice #5 into the S5 signal (18) fluid circuit. The normally closed reverse SS valve assembly is OFF, causing fluid pressure to build-up in the S5 signal (18) fluid circuit.
Shift Pressure Relay Valve
S5 signal (18) fluid is routed to the shift pressure relay valve and applies the valve against spring force.
1-2 REVERSE CLUTCH (B5) APPLIES
U1 Shift Valve
Line (2) fluid is also routed to the U1 shift valve and passes through the valve into the 1-2 reverse clutch (39) fluid circuit.
1-2 Reverse Clutch (B5) Assembly
1-2 reverse clutch (39) fluid enters the automatic transmission case cover assembly and moves the 1-2 reverse clutch piston against spring force to apply the 1-2 reverse clutch plates. In PARK range, the 1-2 reverse clutch has no effect. However, when REVERSE or a forward range is selected, only one apply device has to be energized, which helps create a smooth starting motion.
FLUID PRESSURE DIRECTED TO PREVENT TCC APPLY
Lock Up Relay Valve
1-2 reverse clutch (39) fluid is also routed to the lock up relay valve. Here it assists converter feed (3) fluid pressure and spring force to hold the valve in the released position, thus preventing torque converter clutch apply.
PASSAGES
- SUCTION
- LINE
- CONVERTER FEED
- RELEASE
- APPLY
- EXHAUST ENABLE
- COOLER
- LUBE
- SOLENOID MODULATOR
- THROTTLE SIGNAL (SLT)
- SHIFT CONTROL (SLS)
- LOCK UP CONTROL (SLU)
- TCC SIGNAL
- S1 SIGNAL
- S2 SIGNAL
- S3 SIGNAL
- S4 SIGNAL
- S5 SIGNAL
- DRIVE
- DRIVE OR REVERSE
- REGULATED DRIVE OR REVERSE
- REVERSE
- REVERSE CLUTCH
- LOW AND REVERSE CLUTCH
- REVERSE CONTROL
- FORWARD CLUTCH
- DIRECT CLUTCH FEED 1
- DIRECT CLUTCH FEED 2
- DIRECT CLUTCH
- B2 CONTROL 1
- B2 CONTROL 2
- SECOND CLUTCH
- B1 CONTROL 1
- B1 CONTROL 2
- B1 CONTROL 3
- SECOND COAST CLUTCH
- B5 CONTROL 1
- B5 CONTROL 2
- 1-2 REVERSE (B5) CLUTCH
- 4-5 CLUTCH
- B4 CONTROL
- B4 RELEASE
- SERVO RELEASE
- SERVO FEED
- SERVO APPLY
- 3RD GEAR BAND APPLY
- PN12345
- PRN15
- 234NCON
- 345 ENABLE
- 45 ENABLE
- REVERSE INHIBIT
- VENT
- EXHAUST
- SUMP
- VOID
- TORQUE CONVERTER SEAL DRAINBACK
Park - Engine Running