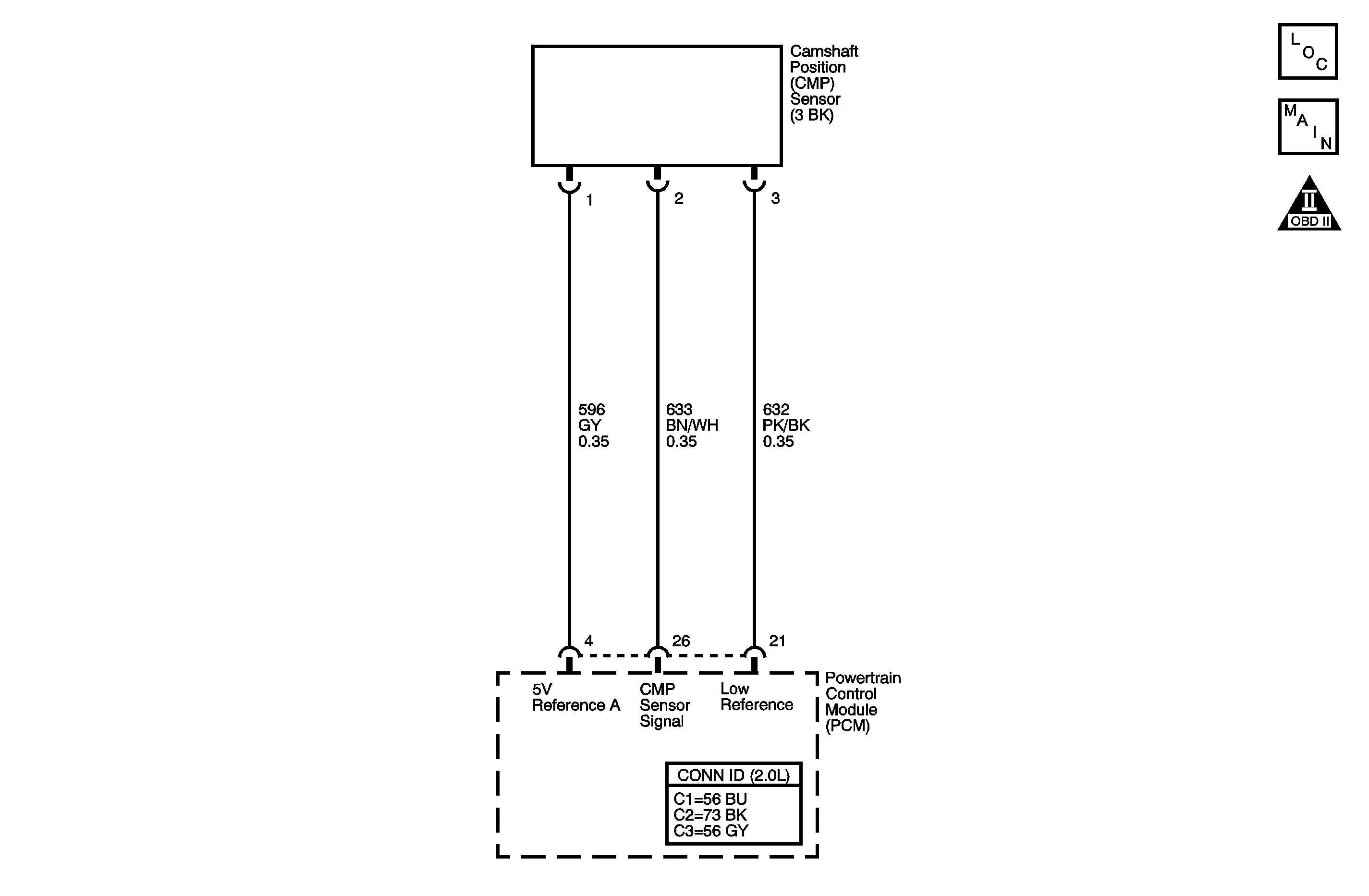
Circuit Description
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor provides the powertrain control module (PCM) with a signal representing the camshaft's rotational position. The CMP sensor is a hall effect switch that works in conjunction with a 4X reluctor wheel. The reluctor wheel consists of 4 pairs of rising and falling edges that are differently spaced. The CMP sensor produces a magnetic field. When the camshaft rotates, and the reluctor wheel edge passes by the CMP sensor, there is a change in the magnetic field. The PCM views each transition from low to high as one signal. The PCM receives 4 signals per camshaft revolution. The CMP sensor has the following circuits:
| • | A 5-volt circuit |
| • | A low reference circuit |
| • | A signal circuit |
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the CMP sensor on the 5-volt reference circuit, and provides a low reference circuit. The CMP sensor provides a 4X signal to the PCM on the signal circuit. If the PCM detects extra or missing CMP sensor signal transitions within a certain number of crankshaft revolutions, DTC P0340 will set.
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC P0340 Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Circuit
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0315, P0335, and P0336 are not set. |
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) is more than 45 kPa. |
| • | This DTC runs continuously. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM does not detect the signal of the CMP sensor for 3 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls Connector End Views or Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views | ||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle in Vehicle DTC Information | ||||||||
2 |
Does the CMP Sensor parameter increment? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||
3 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||
4 |
Is the voltage within the specified range? | 4.8-5.2 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||
5 | Measure the voltage from the 5-volt reference circuit of the CMP sensor to a good ground. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 4.8-5.2 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||
6 | Measure the resistance of the low reference circuit of the CMP sensor with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 12 | ||||||||
7 | Measure the resistance of the 5-volt reference circuit of the CMP sensor with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 11 | ||||||||
8 |
Does the CMP sensor parameter increment? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 13 | ||||||||
9 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||
10 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||
11 | Test the 5-volt reference circuit of the CMP sensor for one of the following conditions:
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||
12 | Test the low reference circuit of the CMP sensor for an open or high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||
13 | Test the signal circuit of the CMP sensor for one of the following conditions:
Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||
14 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the CMP sensor. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 16 | ||||||||
15 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the powertrain control module (PCM). Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 17 | ||||||||
16 | Replace the CMP sensor. Refer to Camshaft Position Sensor Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 18 | -- | ||||||||
17 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Control Module References in Computer/Integrating Systems for replacement, setup, and programming. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 18 | -- | ||||||||
18 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||
19 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle in Vehicle DTC Information | System OK | ||||||||
