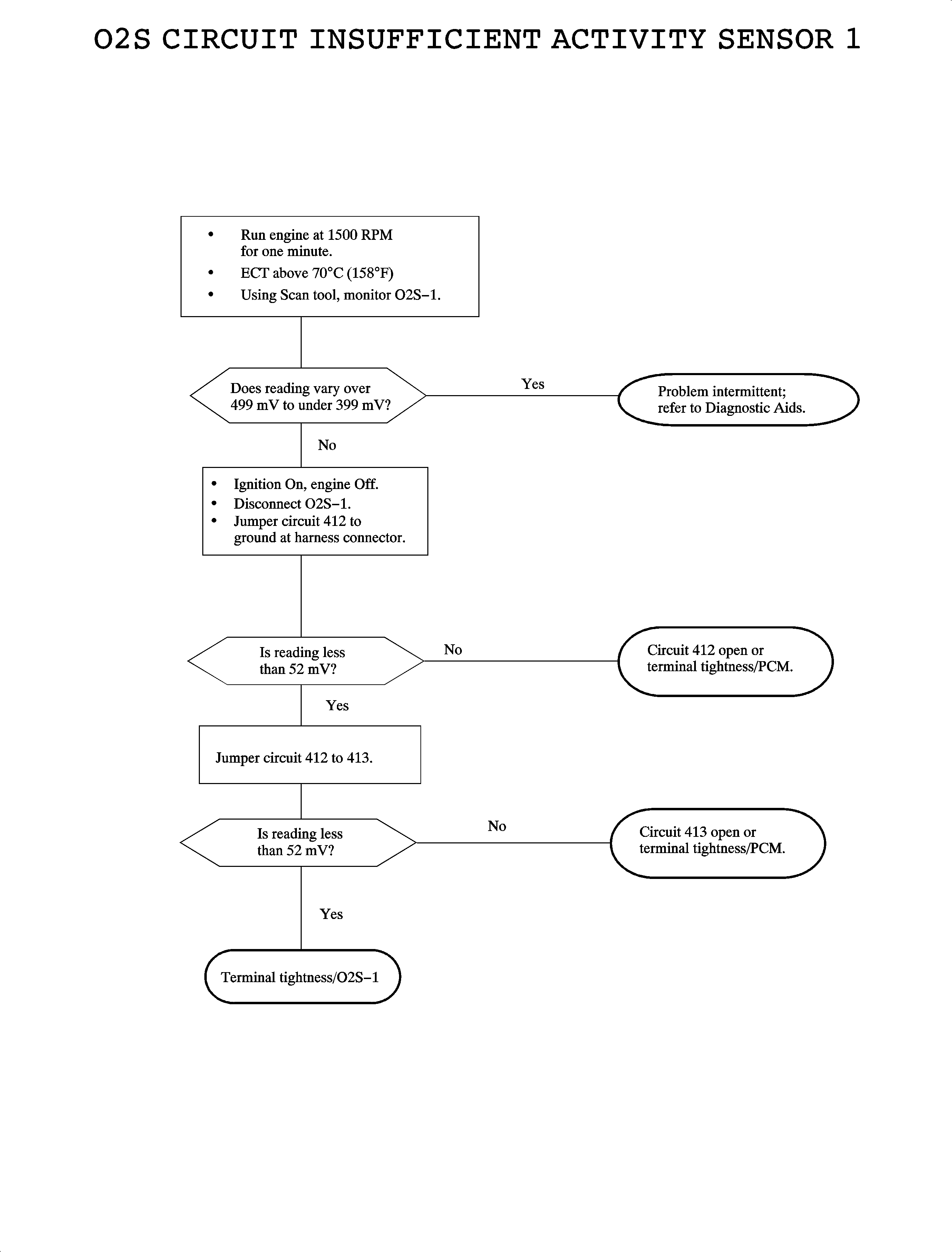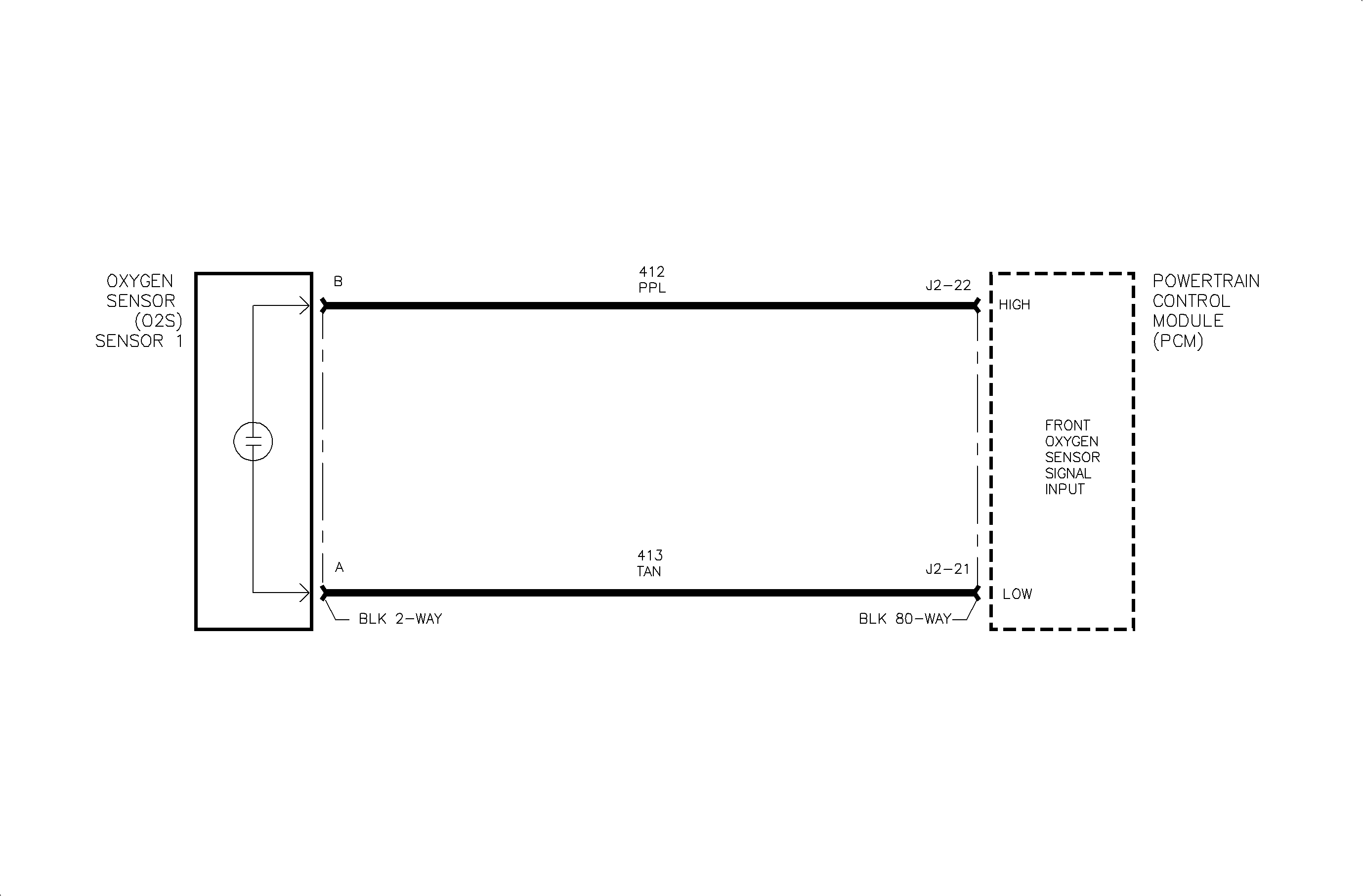
Circuit Description
The oxygen sensor (O2S-1) is an electrical source that responds to oxygen content in the exhaust manifold. When the sensor reaches approximately 316°C (600°F), it produces a voltage based on the difference in oxygen between the atmosphere and the exhaust gas. The PCM sends a bias voltage (399-499 mV) on the signal line, which is pulled up through high resistance. When the O2S-1 is cold, it produces no voltage and has extremely high internal resistance. The internal resistance of the sensor is much greater than the resistance of the bias pull-up resistor. However, when the sensor heats up, it produces voltage that overrides the bias voltage. This voltage is read by the PCM to determine a rich/lean O2S-1 signal used to adjust the injector pulse width. under normal conditions, low sensor voltage means high oxygen content/lean air-fuel mixture and vice versa. Normal sensor readings will fluctuate between 10 mV and 1065 mV. DTC P0134 will set when the O2S-1 signal is inactive.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0134 will set if O2S-1 is inactive (voltage is not fluctuating outside the 399-499 mV range) when:
| • | Condition exists for longer than 2 minutes and 5 seconds. |
| • | Engine run time is greater than 30 seconds |
| • | ECT is greater than 75°C (167°F) for at least 20 seconds |
| • | No CKP, ECT, EVAP fuel injector, fuel tank pressure, fuel trim, IAT idle speed, MAP, misfire, PCM internal fault, or TP sensor DTCs have been set. |
DTC P0134 diagnostic runs continuously once the above conditions have been met.
P0134 is a (type B) DTC
Diagnostic Aids
To locate an intermittent problem, use the scan tool to monitor the O2S-1 voltage with engine at normal operating temperature.
Bias voltage (399-499 mV) will appear on the scan tool if the circuit 412 or 413 is open.
Normal scan tool readings in a closed loop will show O2S-1 voltage varying between 10 mV and 1065 mV.
DTC P0134