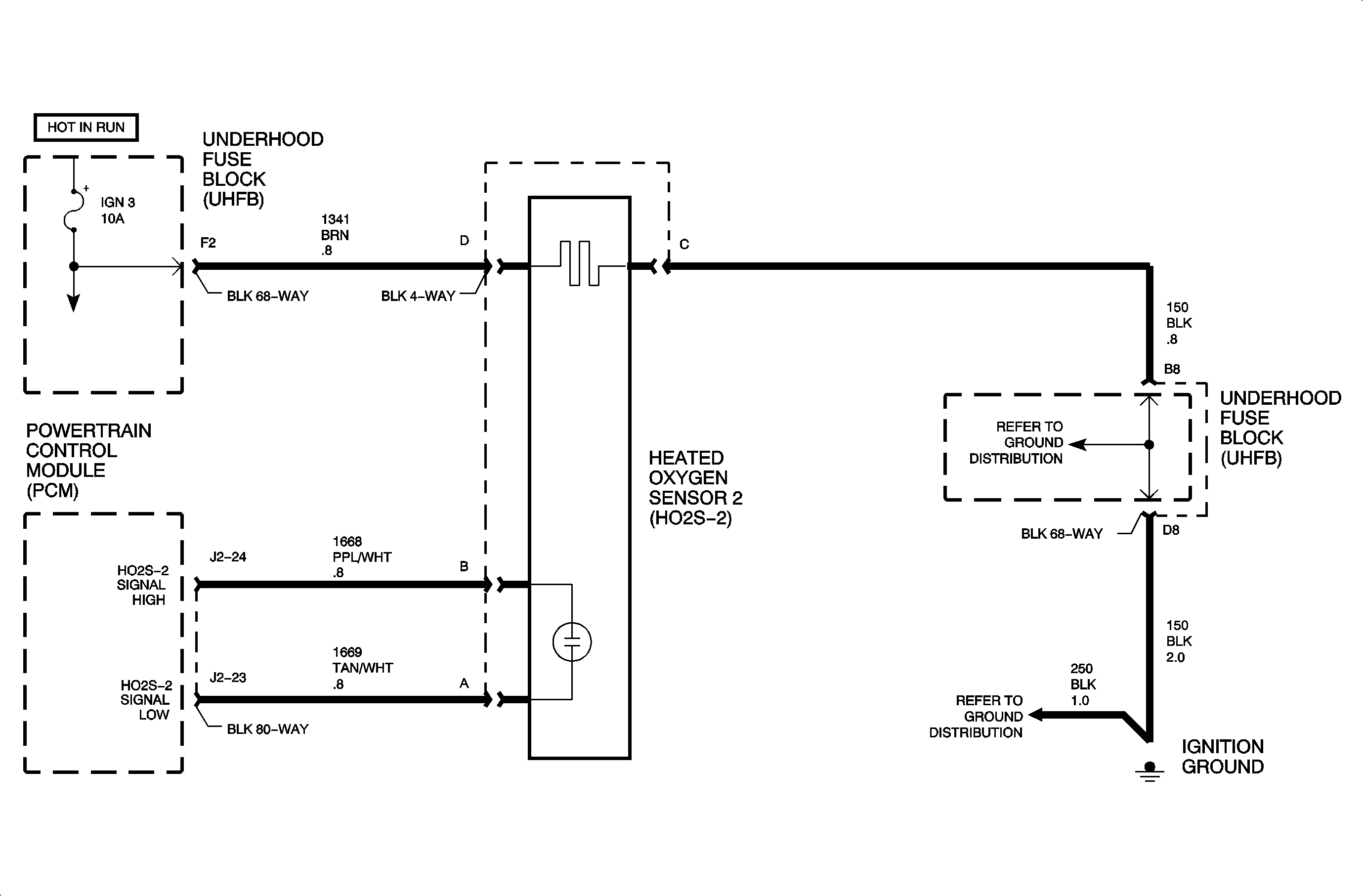
The heated oxygen sensor (H02S-2) is an electrical source that responds to oxygen content out of the catalytic converter. When the sensor reaches approximately 316°C (600°F), it produces a voltage based on the difference in oxygen between the atmosphere and exhaust gas. The PCM sends a bias voltage (425-460 mV) on the signal line, which is pulled up through high resistance. When the HO2S-2 is cold, it produces no voltage and has extremely high internal resistance. The internal resistance of the sensor is much greater than the resistance of the bias pull-up resistor. However, when the sensor heats up, it produces voltage that overrides the bias voltage. This voltage is read by the PCM to determine the efficiency of the catalytic converter. Under normal conditions, low sensor voltage means high oxygen content/lean air-fuel mixture and vice versa. Normal sensor readings at steady cruise with a properly functioning catalytic converter will be around 500-800 mV. DTC P1138 sets when the HO2S-2 signal voltage is too high during deceleration or fuel cut-off mode.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P1138 will set if H02S-2 signal voltage is greater than 650 mV in decel fuel cut-off mode or fuel cut-off mode when:
| • | The condition exists for longer than 6 seconds out of a 10 second test. |
| • | The vehicle must be in DFCO or FCO mode for 6 seconds (auto) and 10 seconds (manual) to start the test. |
| • | The loop status is closed. |
| • | The fuel level is greater than 10 percent. |
| • | No CKP, ECT, EVAP, fuel injector, fuel tank pressure, fuel trim, IAT, idle speed, MAP, misfire, PCM internal fault, or TP DTCs have been set. |
DTC P1138 diagnostic runs continuously once the above conditions have been met.
DTC P1138 is a type B DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
If DTC P0138 is also set, diagnose that DTC first. A short to voltage on circuit 1668 may set DTC P1138.
Replace the HO2S-2.
