Tools Required
| • | J 43290 Fuel Tank Siphon Hose Assembly in Cautions and Notices. |
| • | Fuel Flow/Pressure Test Adapter |
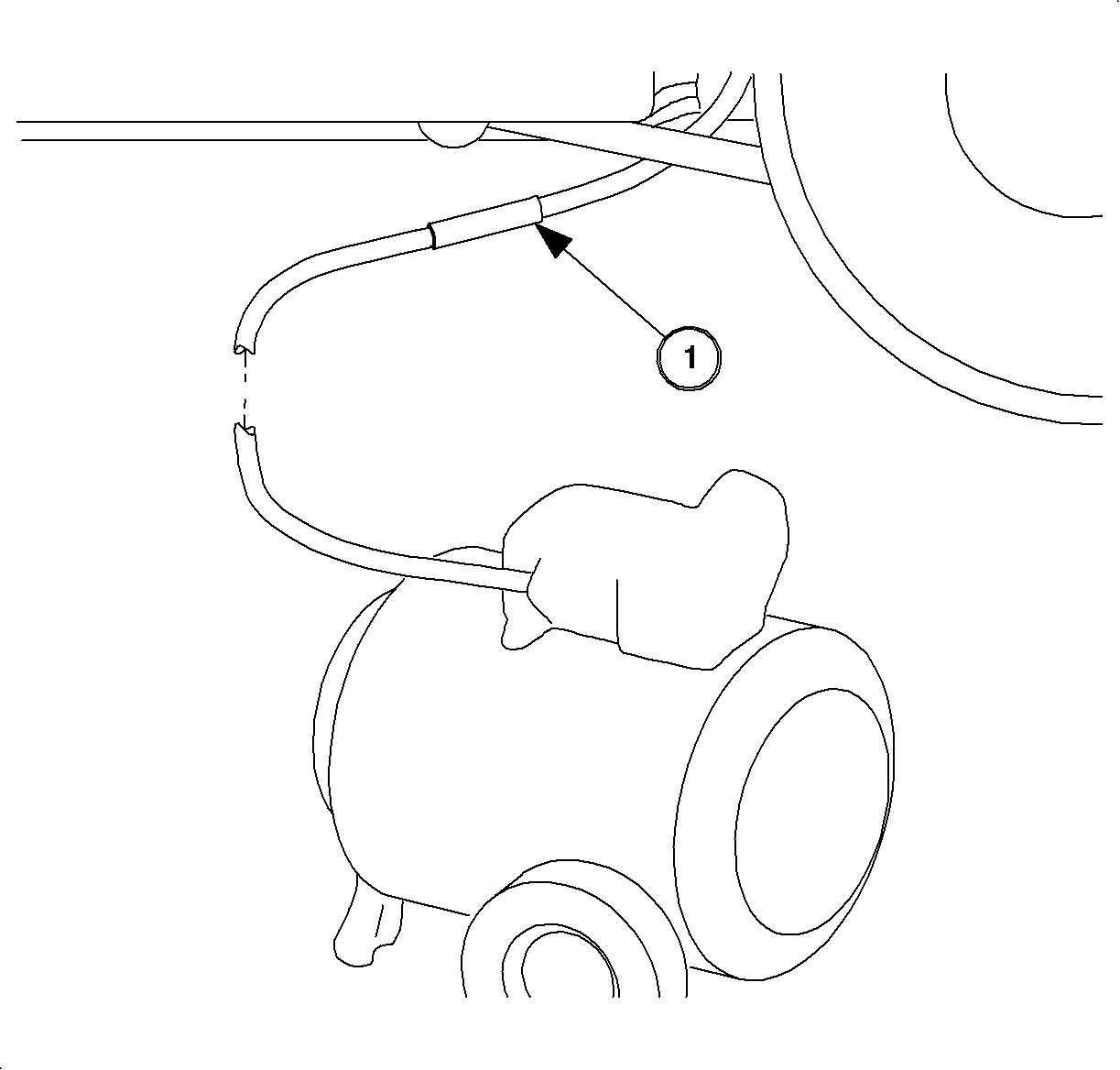
If fuel pump is inoperative, the tank can be drained by siphoning from the tank. A suitable means is through the fuel filler pipe with the correct type and stiffness of tubing as used with the J 43290 .
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Open the fuel filler door and remove the gas cap.
- Insert the siphon hose guide/funnel into fuel filler pipe.
- Insert the J 43290 into the guide funnel and into the fuel filler pipe. Some resistance may be encountered when the tip of the siphon hose reaches the inlet check valve. Repeated probing may be necessary to slide the hose tip through the check valve cage.
- Begin the fuel siphoning process. Place the fuel into an approved fuel container.
- Remove the siphon hose from the fuel filler pipe after the draining is complete.
Caution: Refer to Gasoline/Gasoline Vapors Caution in the Preface section.
Notice: Do not attempt to insert any other type of siphon hose or tube into the fuel filler pipe. The design of the inlet check valve restricts insertion of a hose and, most importantly, prevents removal of this hose. If the siphon hose becomes stuck in the check valve, the fuel filler pipe will not be able to be removed from the fuel tank without damage to the fill pipe or fuel tank.
Important: The siphon hose will reach the bottom of tank within about 10 inches of the end fitting, and tag. When connecting the siphon hose to another length of hose connected to fuel drain tanker, DO NOT insert siphon hose into fill pipe funnel past the tag at the fitting end. If inserted too far, the upper portion of the siphon hose may pass through the check valve cage and then jam on attempted removal.
Caution: Refer to Relieving Fuel Pressure Caution in the Preface section.
Important: The fuel flow rate from the siphon hose will range from 0.3 gal/min up to 1 gal/min, depending on whether it is gravity siphoned or with an air-powered pump.
For any operation requiring removal of the fuel tank, there should be no more than 11.4 liters (3 gallons) of fuel remaining. This minimizes the weight of the assembly and eases handling. The fuel level can be determined by reading the fuel level gage. A reading below 1/4 full indicates that no more than 11.4 liters (3 gallons) are remaining.
Using the Fuel Pump
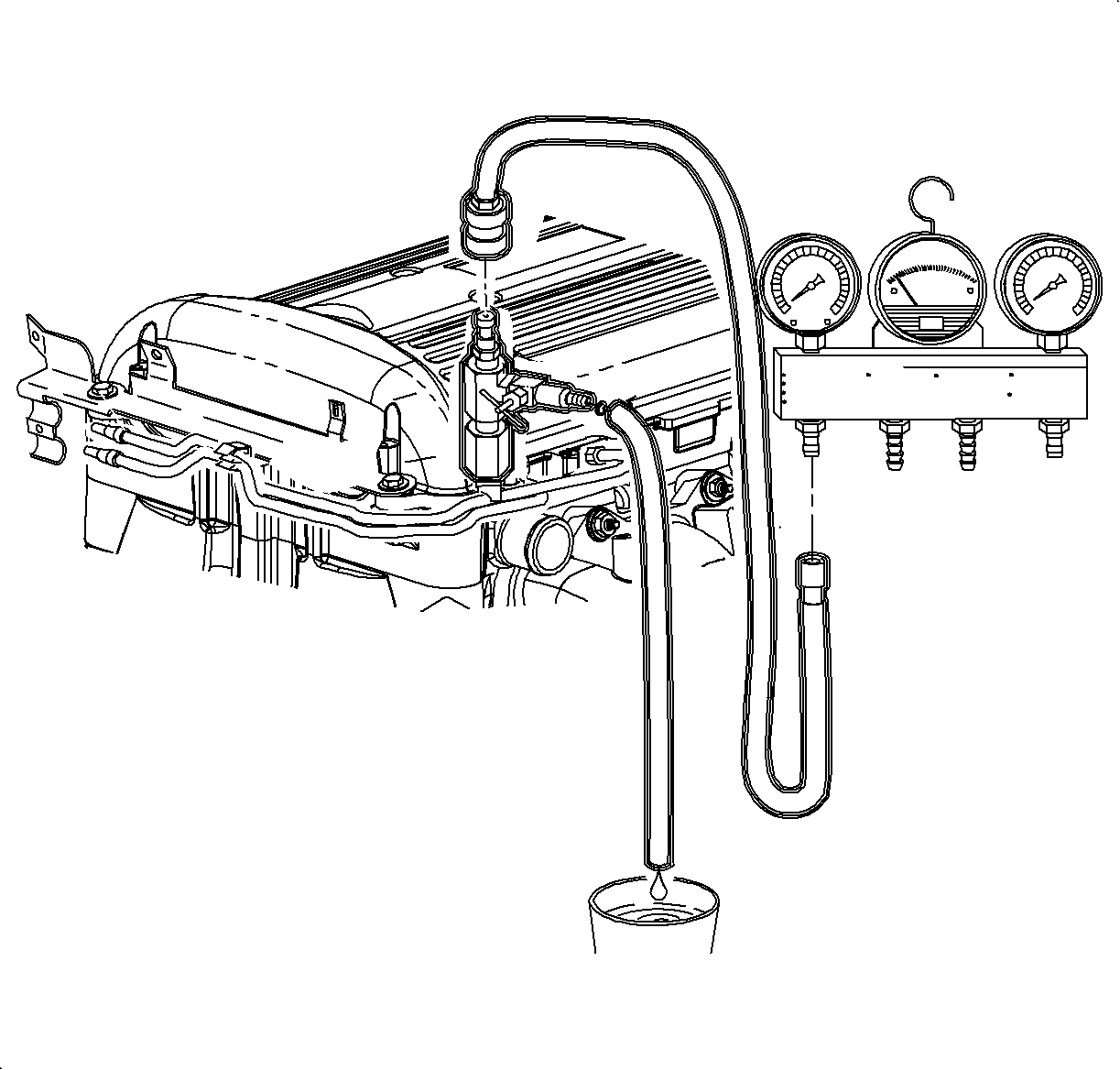
Using the fuel pump to drain the tank is the easiest procedure if the pump is operable. The fuel can be pumped out with the vehicle on the ground or on the hoist.
On the Ground
- Relieve the fuel system pressure. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis .
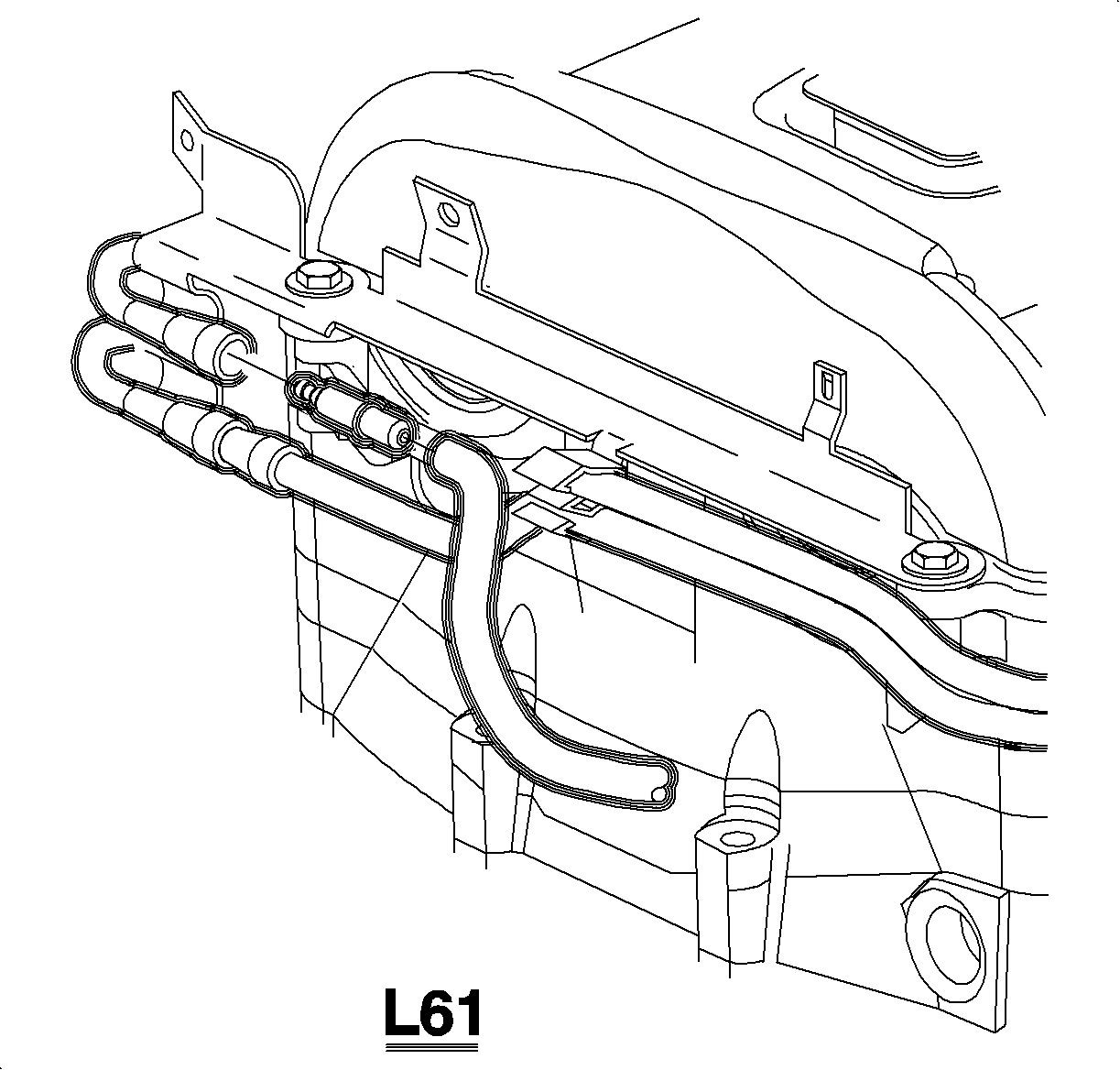
- Disconnect the fuel feed line at the fuel rail and install a 3/8 in x 1/4 in quick connect from the into fuel feed line.
- Connect a suitable drain hose to the other end of the adapter and connect the drain hose into a certified fuel handling cart.
- Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and turn the ignition ON.
- Energize the fuel pump using the scan tool. Refer to Energizing Fuel Pump in this section.
- Pump out the fuel until no more than 1/4 tank remains.
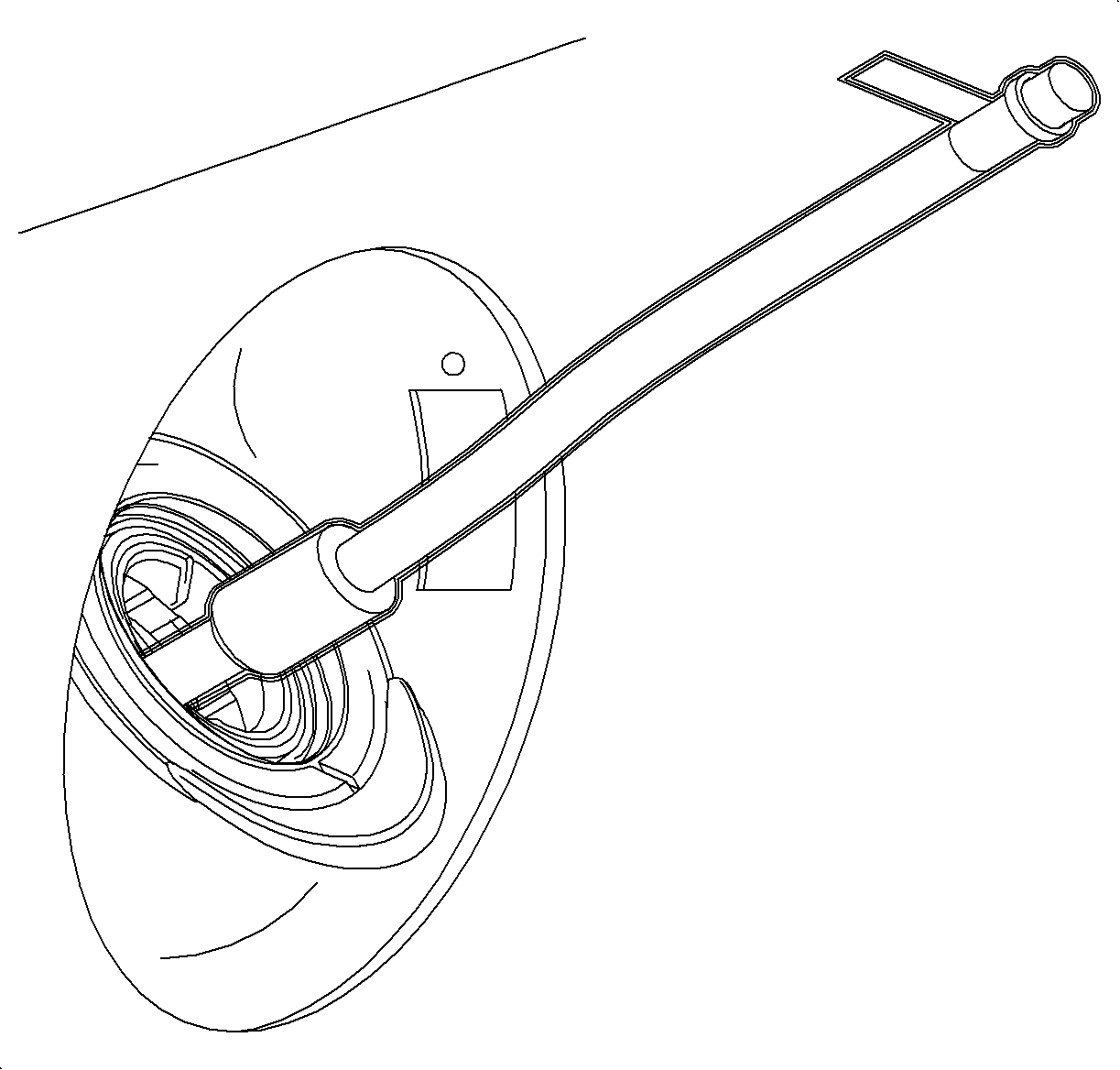
On the Hoist
- Connect a scan tool to the vehicle diagnostic connector and turn the ignition ON.
- Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis .
- Raise the vehicle on a hoist to a comfortable working height, keeping the scan tool outside of the vehicle and accessible from under the car.
- Disconnect the fuel feed line at the outlet to filter 3/8 in. line.
- Install a 3/8 in. x 1/4 in. quick connect 1 adapter from the into the fuel feed line.
- Connect a suitable drain hose to the other end of the adapter, and connect the drain hose to a certified fuel handling cart.
- Energize the fuel pump using the scan tool. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis .
- Pump out the fuel until no more than 1/4 tank remains.