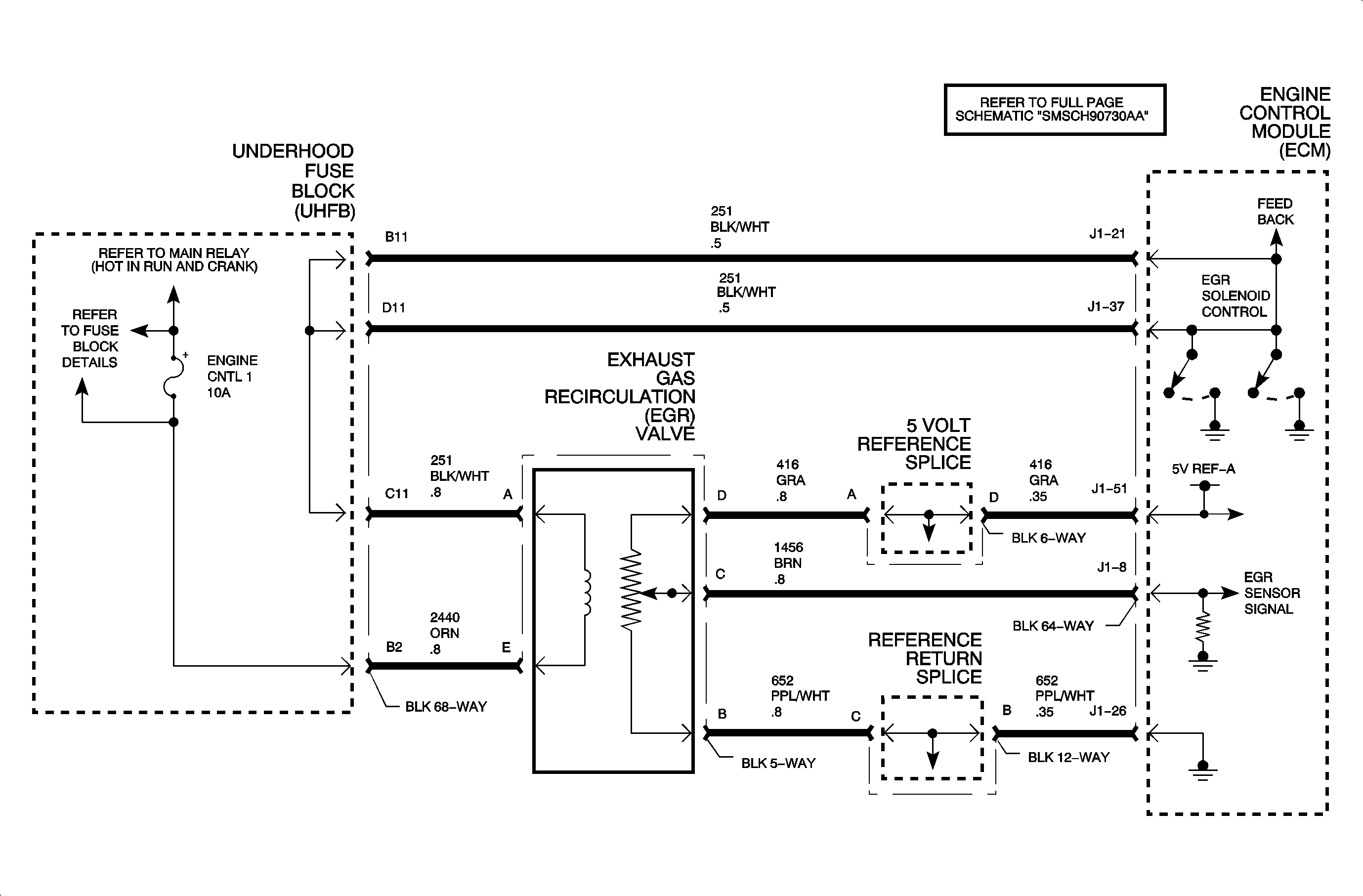
Circuit Description
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve consists of a pintle valve, which moves by the use of an internal solenoid, and an internal position sensor, potentiometer, used to determine pintle valve position. The engine control module (ECM) controls the solenoid by supplying it ground whenever exhaust gas needs to be recirculated into the intake manifold. The ECM monitors the EGR solenoid and position sensor circuit for correct voltage levels at certain times. The ECM also monitors the flow rate of exhaust gas through the EGR valve by using the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor. After certain conditions have been met, the ECM will compare the MAP sensor signal voltage change and its steady state value to a modeled MAP sensor signal value after the EGR valve has been commanded ON. This once per ignition cycle test is based off of the narrow engine speed and load range listed under DTC parameters. DTC P0402 sets when the MAP sensor signal voltage changes or its steady state value is above a certain threshold, indicating too much change in intake manifold pressure, when the EGR valve is commanded to a certain duty cycle.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Accumulated air mass is more than 0.5 kg. |
| • | The EGR valve is commanded to 60 percent duty cycle. |
| • | The engine speed is between 1,600-2,200 RPM and is steady. |
| • | Engine load is between 35-65 percent. |
| • | Altitude is less than 2750 meters (9,023 feet). |
| • | The EGR flow test can take between 4-9 seconds to run. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0402 will set if the ECM determines EGR flow to be excessive by comparing the MAP sensor signal voltage change along with a steady state value to a modeled value when:
| • | The condition exists for longer than 9 seconds continuously or for a total of 9 seconds up to 3 independent tests. |
| • | The EGR solenoid is commanded to a 60 percent duty cycle. |
| • | The engine speed is between 1,600-2,200 RPM. |
| • | The engine load is between 35-65 percent. |
| • | The engine load change rate is less than 0.35 percent. |
| • | The accumulated air mass is greater than 0.5 kg since engine start. |
| • | The altitude is less than 2 750 meters (9,023 ft). |
DTC P0402 diagnostic runs once per ignition cycle up to 9 seconds once the above conditions have been met. However, the diagnostic may take only 3 seconds to pass.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The control module stores this information in the Freeze Frame/Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | A vacuum restriction to the MAP sensor--A skewed MAP sensor reading can cause the ECM to read incorrect MAP changes during the EGR flow test. |
| • | An engine that is running poorly due to a mechanical condition such as worn piston rings, worn camshaft, etc.--These types of conditions can cause low engine vacuum and thus can cause a less than expected MAP changes during the flow test. |
| • | Excessive back pressure in the exhaust system may cause this DTC to set. This condition can cause low engine vacuum and thus can cause a less than expected MAP changes during the EGR flow test. Possible causes of this could be a restriction in the exhaust system or non original equipment manufacture (OEM) exhaust parts. |
| • | Exhaust system leaks can cause an insufficient amount of EGR flow through the EGR valve. This condition can cause a less than expected MAP changes due to insufficient exhaust back pressure. possible causes of this could be a leaking exhaust system, a leaking EGR pipe or non OEM exhaust parts. |
| • | A restriction in the intake manifold such as carbon deposits and casting flash |
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the diagnostic table.
-
MAP sensor, EGR control, and EGR position sensor faults must be diagnosed first. A skewed MAP sensor reading or EGR position sensor reading could cause this DTC to set.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics | ||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Is DTC P0107, P0108, P0403, P0405, P0406, P0409, P0489, P0490, P1403, P1405, or P1406 also set? | -- | Go to Step 3 | ||
3 | Inspect for a vacuum leak between the EGR valve and the intake manifold. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 4 |
4 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 5 |
5 | Inspect the EGR tube for leaks. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 6 |
6 | Inspect the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor and gasket for vacuum leaks. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 7 |
7 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 8 |
8 | Inspect the exhaust system for leaks, restrictions, and for modification of original equipment manufacture (OEM) parts. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 9 |
9 |
Important: Do not insert test equipment probes into any connector or fuse block terminal. The diameter of the test probes will deform most terminals. A deformed terminal can cause a poor connection, which can result in system failures. Always use the J 43907 Connector Test Adapter Kit in order to frontprobe terminals. Do not use paper clips or other substitutes as they can damage terminals and cause incorrect measurements.
Is the calculated resistance more than the specified value? | 200 ohms | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 10 |
10 |
Is the calculated resistance more than the specified value? | 5 ohms | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 11 |
11 |
Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 4.82 V | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 14 |
12 | Test the 5-volt reference circuit of the EGR position sensor for resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 15 |
13 | Test the low reference circuit of the EGR position sensor for resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 15 |
14 | Test the signal circuit of the EGR position sensor for resistance. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 15 |
15 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the ECM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 18 |
16 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the EGR valve. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs . Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 17 |
17 | Replace the EGR valve. Refer to Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- |
18 | Replace the engine control module (ECM). Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 19 | -- |
19 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 20 |
20 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |
