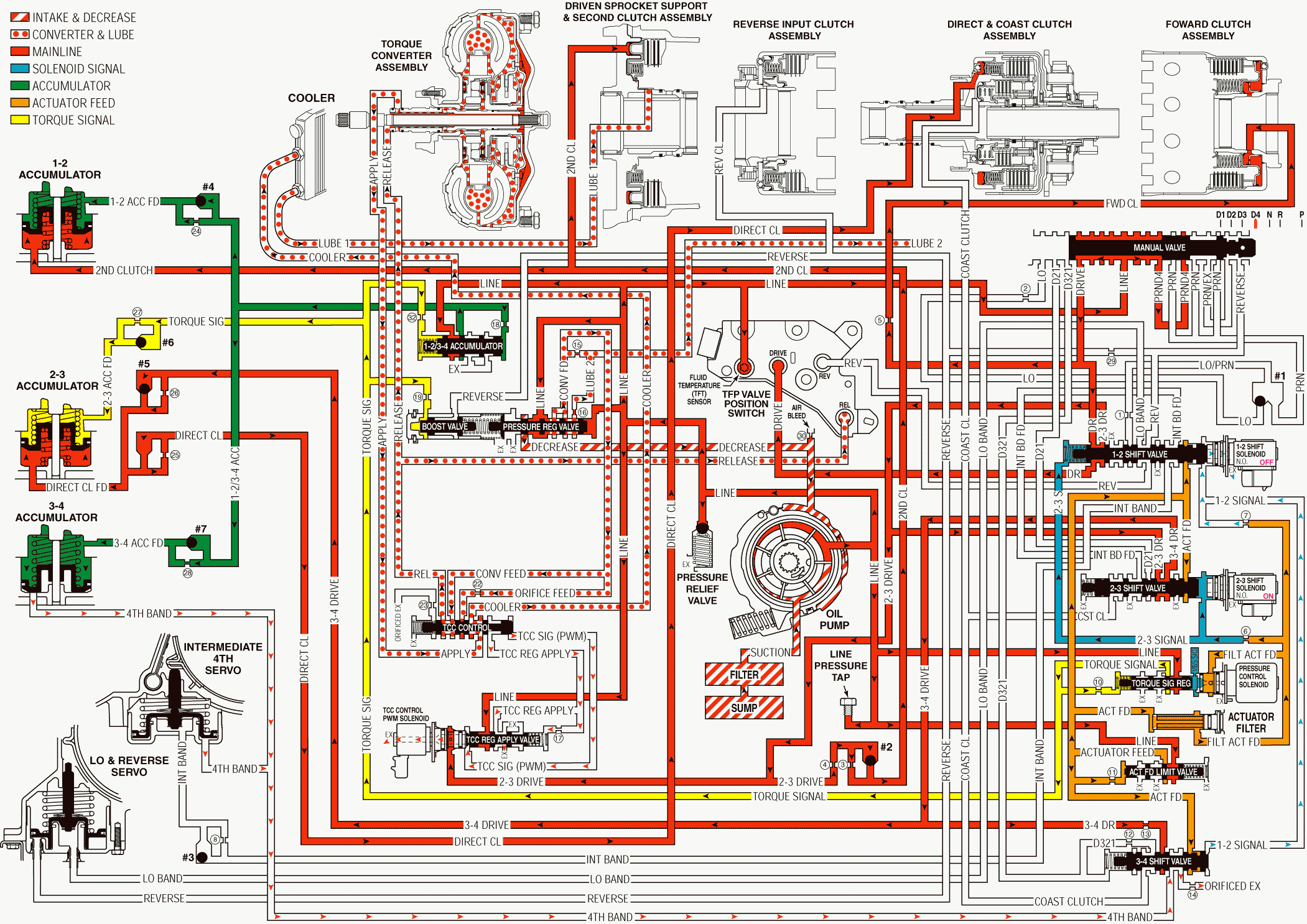
When the transmission is operating in Overdrive Range - Fourth Gear, a forced 4-3 downshift will occur following a significant increase in throttle position. At minimum throttle, vehicle speed will decrease gradually (coastdown) and the PCM will command a 4-3 downshift. The PCM will also initiate a 4-3 downshift if the engine load is increased while the throttle position remains the same (for example, driving up a steep hill).
Line Pressure Increases
Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) Valve
During the downshift, except for a coastdown, the PCM senses the increase in the throttle position or the engine load. When this occurs the PCM increases the PCS duty cycle. The increase in duty cycle increases the output fluid pressure from the PCS, thereby increasing the torque signal fluid pressure at the torque signal regulator valve.
Pressure Regulator Valve
Increased torque signal fluid pressure acting on the boost valve increases line pressure at the pressure regulator valve.
Intermediate and Fourth Band Releases
1-2 Shift Solenoid Valve
The PCM de-energizes the normally open solenoid valve and the 1-2 signal fluid exhausts.
3-4 Shift Valve
The 1-2 signal fluid pressure exhausts from the 3-4 shift valve and a spring force moves the valve into the Third gear position. This opens the Fourth band fluid circuit to an orificed exhaust in order to help control the band release.
Intermediate and Fourth Servo
Fourth band fluid exhausts from the servo and a spring force moves the servo to the release position, thereby releasing the band.
3-4 Accumulator
The fourth band fluid exhausts from the accumulator. A combination of spring force and 3-4 accumulator feed fluid pressure moves the accumulator piston to the Third gear position.
1-2/3-4 Accumulator Valve
The accumulator valve regulates line pressure into the 1-2/3-4 accumulator fluid circuit in order to fill the 3-4 accumulator. Torque signal fluid pressure controls this regulation. Increased torque signal fluid pressure regulates accumulator fluid to a higher pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch
The PCM commands TCC release prior to initiating a 4-3 downshift. When the TCC is in the release position, release fluid pressure is routed to the pressure switch assembly. This fluid pressure signals the PCM that the TCC is in the release position. The TCC is not applied under normal operating conditions in Third gear.
Overdrive Range, 4-3 Downshift - TCC Not Applied
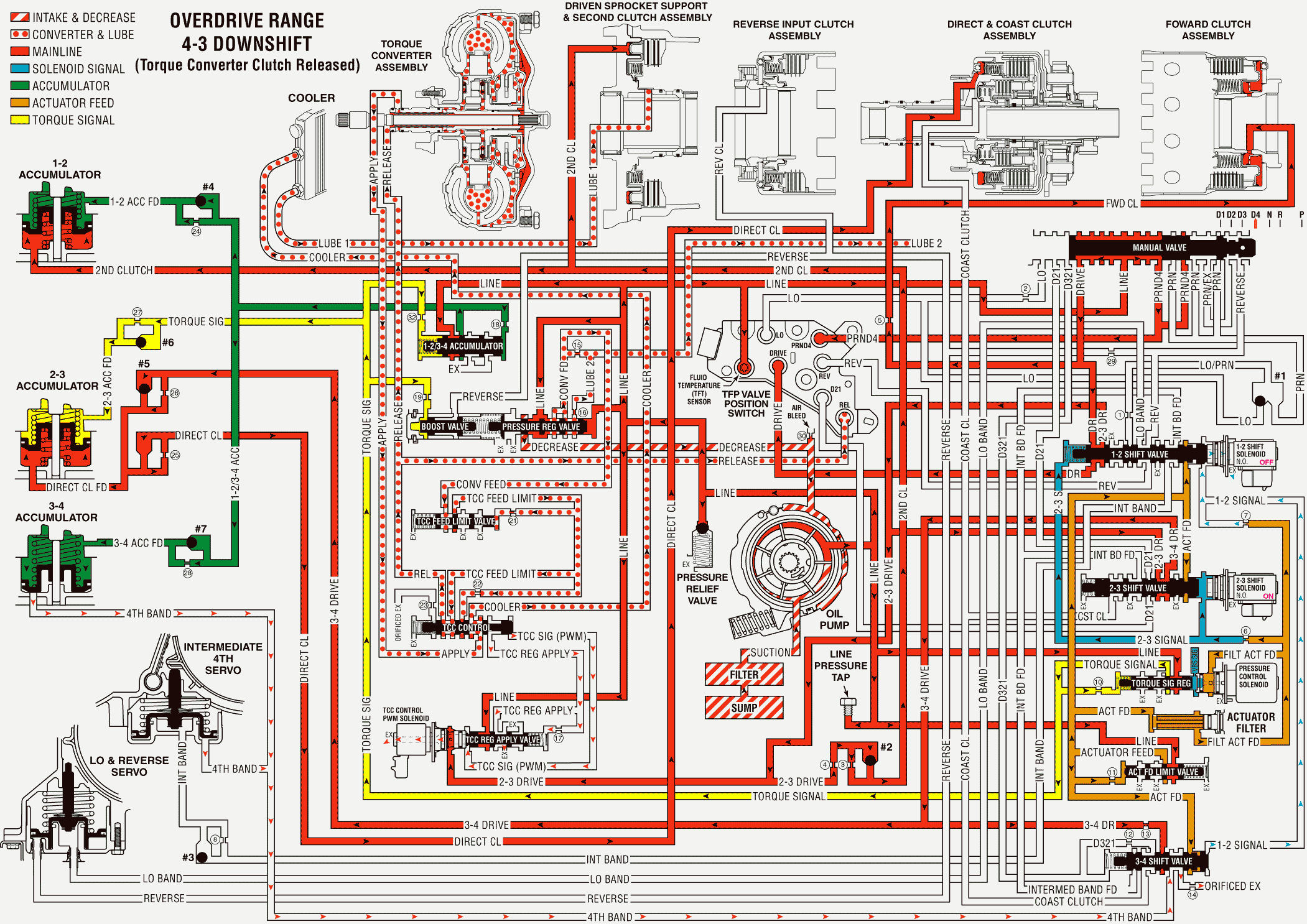
Overdrive Range, 4-3 Downshift - Torque Converter Clutch Not Applied W/O Electronic Range Select Mode
When the transmission is operating in Overdrive Range - Fourth Gear, a forced 4-3 downshift will occur following a significant increase in throttle position. At minimum throttle, vehicle speed will decrease gradually (coastdown) and the PCM will command a 4-3 downshift. The PCM will also initiate a 4-3 downshift if the engine load is increased while the throttle position remains the same (for example, driving up a steep hill).
Line Pressure Increases
Pressure Control Solenoid (PCS) Valve
During the downshift, except for a coastdown, the PCM senses the increase in the throttle position or the engine load. When this occurs the PCM increases the PCS duty cycle. The increase in duty cycle increases the output fluid pressure from the PCS, thereby increasing the torque signal fluid pressure at the torque signal regulator valve.
Pressure Regulator Valve
Increased torque signal fluid pressure acting on the boost valve increases line pressure at the pressure regulator valve.
Intermediate and Fourth Band Releases
1-2 Shift Solenoid Valve
The PCM de-energizes the normally open solenoid valve and the 1-2 signal fluid exhausts.
3-4 Shift Valve
The 1-2 signal fluid pressure exhausts from the 3-4 shift valve and a spring force moves the valve into the Third gear position. This opens the Fourth band fluid circuit to an orificed exhaust in order to help control the band release.
Intermediate and Fourth Servo
Fourth band fluid exhausts from the servo and a spring force moves the servo to the release position, thereby releasing the band.
3-4 Accumulator
The fourth band fluid exhausts from the accumulator. A combination of spring force and 3-4 accumulator feed fluid pressure moves the accumulator piston to the Third gear position.
1-2/3-4 Accumulator Valve
The accumulator valve regulates line pressure into the 1-2/3-4 accumulator fluid circuit in order to fill the 3-4 accumulator. Torque signal fluid pressure controls this regulation. Increased torque signal fluid pressure regulates accumulator fluid to a higher pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch
The PCM commands TCC release prior to initiating a 4-3 downshift. When the TCC is in the release position, release fluid pressure is routed to the pressure switch assembly. This fluid pressure signals the PCM that the TCC is in the release position. The TCC is not applied under normal operating conditions in Third gear.
Overdrive Range, 4-3 Downshift - TCC Not Applied - Without Electronic Range Select Mode