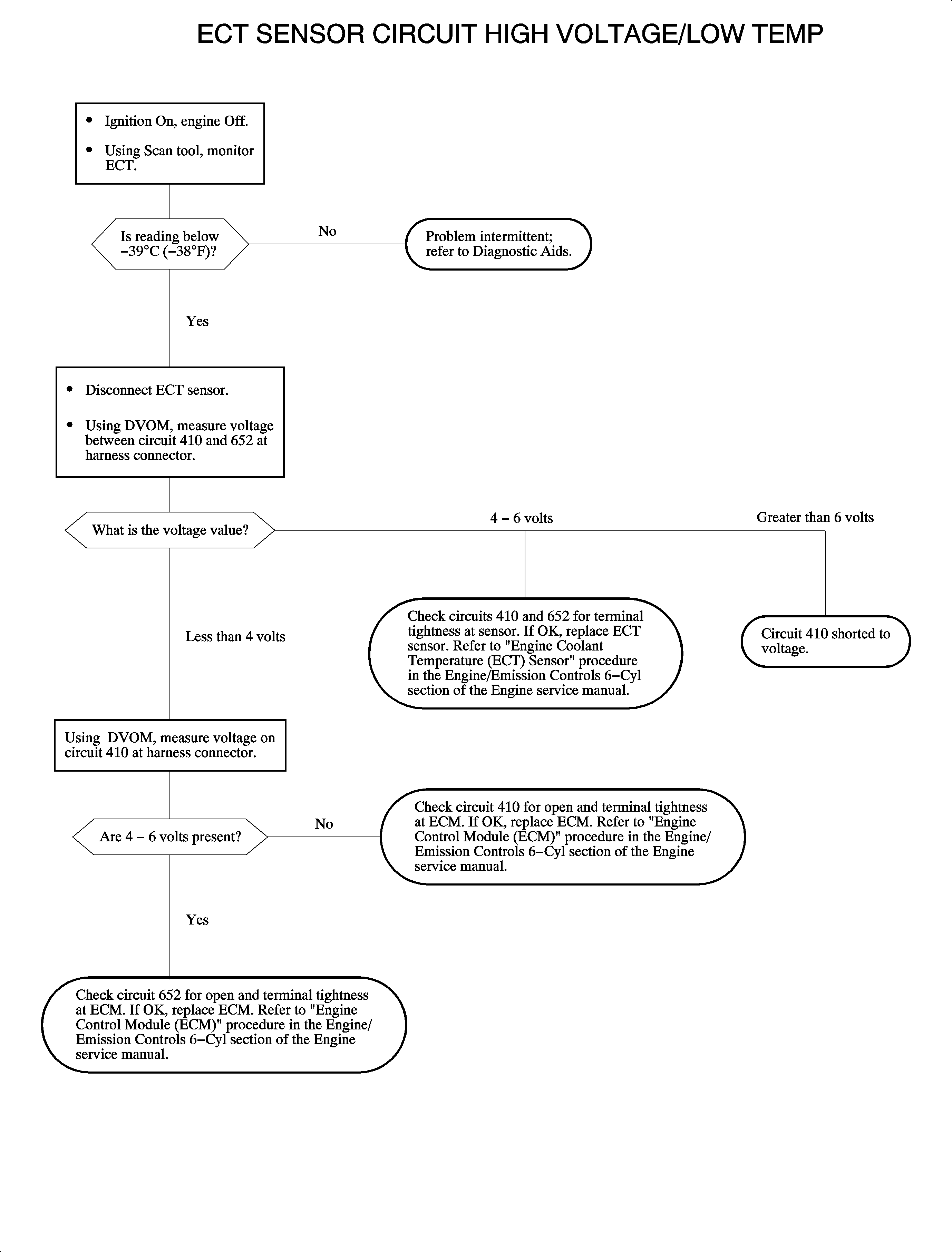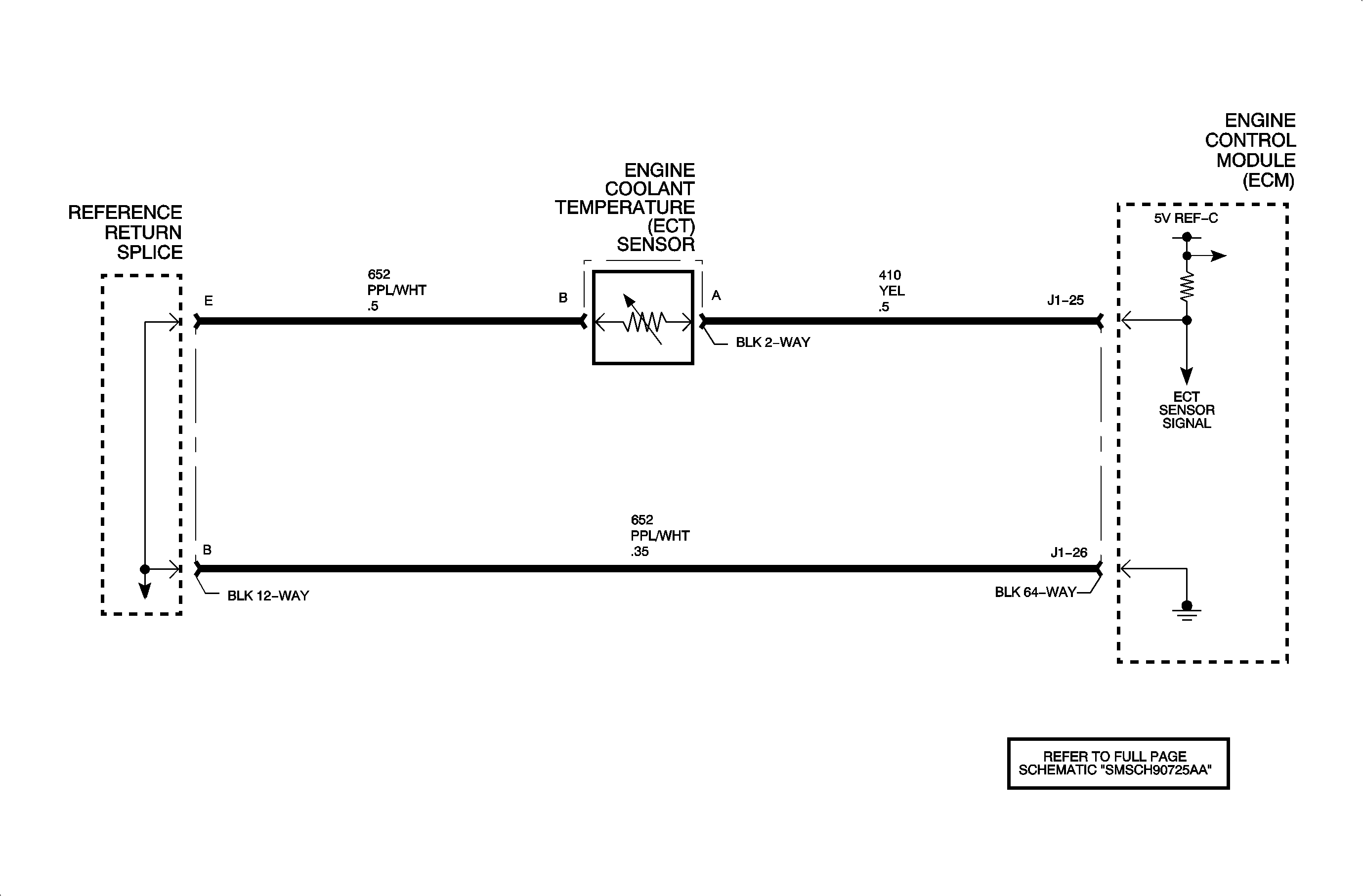
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a thermistor that varies resistance according to changes in engine coolant temperature. The ECM supplies a 5-volt reference through a pull-up resistor to the sensor, which is connected to a ground. When the sensor is cold it has high resistance (high signal voltage at ECM). As the sensor temperature increases, its resistance decreases (lower signal voltage at ECM). The ECM uses the signal voltage to determine engine coolant temperature. DTC P0118 sets when the ECT sensor signal voltage at the ECM is below the calibrated voltage value (over the calibrated temperature value).
DTC Parameters
DTC P0118 will set if the ECT sensor temperature is below -39°C (-38°F) when:
| • | The condition exists for longer than 0.5 seconds. |
| • | The engine speed is greater than 20 RPM. |
DTC P0118 diagnostic runs continuously with the engine cranking/running.
P0118 is a type B DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
To locate an intermittent problem, use the scan tool to monitor the ECT sensor temperature with the ignition On, and the engine Off. Wiggling the wires while watching for a change in the ECT sensor temperature may locate the area where a short to ground may exist.
An intermittent open in the ECT sensor can set this DTC. Run the engine after it has cooled down and monitor the ECT on the scan tool. The temperature should rise smoothly to 88°C (190°F) as the thermostat opens and stabilizes the temperature of the engine coolant.
The coolant temperature gage will display COLD if DTC P0118 is active.
The ECM will command the cooling fans On if DTC P0118 is active.
The CMP/ECT/IAT/EGR/MAF/MAP/TPI/TP2 sensors share the same sensor return circuit 652.
Refer to ECT General Description for the Temperature vs. Resistance chart.
Important: A direct short to voltage on circuit 652 may cause internal damage to the ECM ground trace, or open the sensor element in the ECT, IAT and/or MAP sensors.