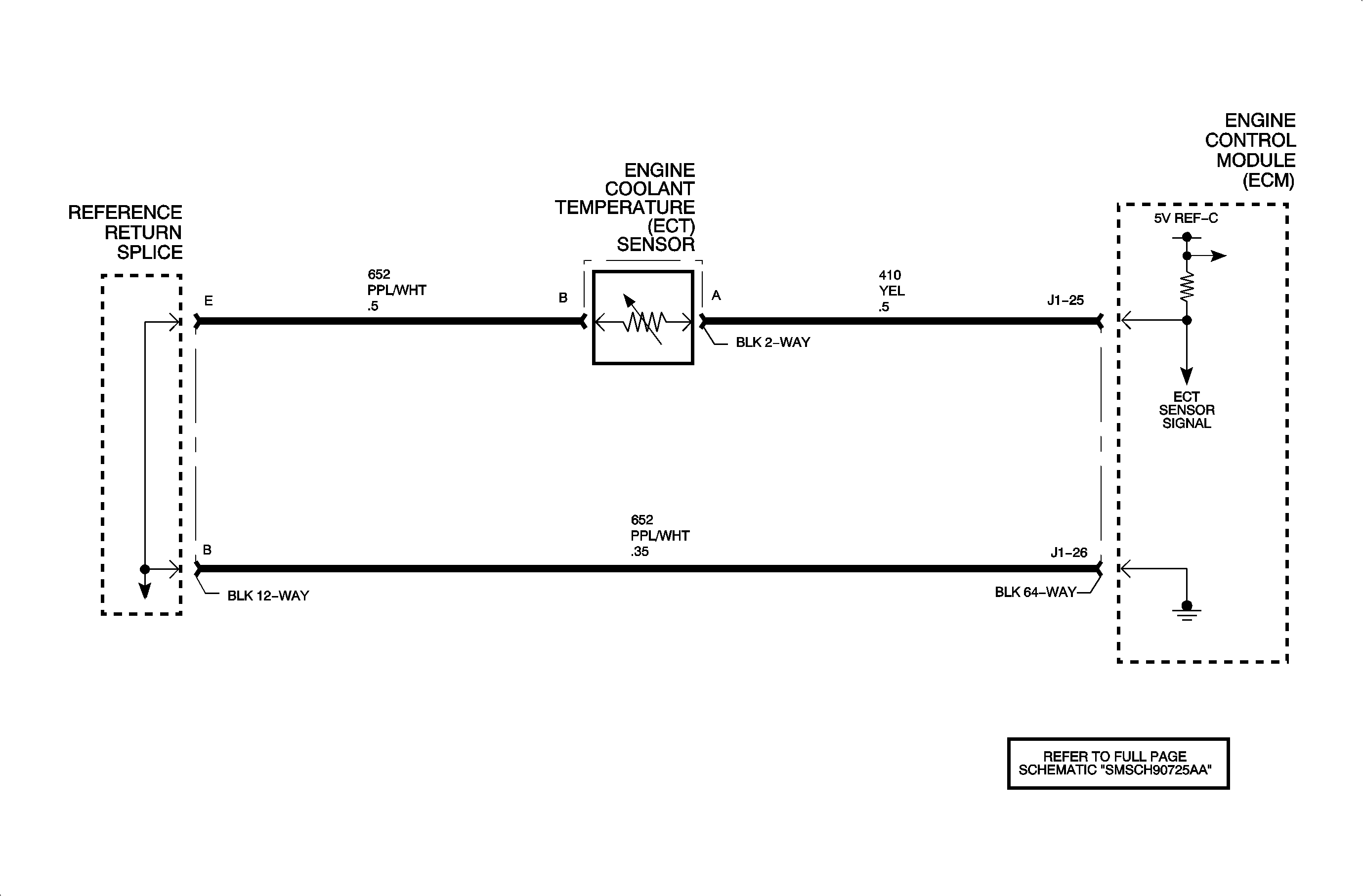
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a thermistor that varies resistance
according to changes in engine coolant temperature. The ECM supplies a 5-volt reference
through a pull-up resistor to the sensor, which is connected to a ground. When the
sensor is cold it has a high resistance (high signal voltage at ECM). As the sensor
temperature increases, its resistance decreases (lower signal voltage at ECM). The
ECM uses the signal voltage to determine the engine coolant temperature. DTC P0128
will set when the engine coolant temperature is consistently a certain temperature
lower than the predicated engine coolant temperature during certain engine accumulated
airflow stages. This DTC indicates that the engine is running cooler than normal.
DTC Parameters
DTC P0128 will set if the ECT is 10.5°C (51°F) lower than normal
based on predicted measurements after a set of calculated accumulated engine airflow
stages have passed when:
| • | Startup ECT is between -7.5 and 50°C (19 and 122°F) |
| • | Startup IAT is between -30 and 45°C (-22 and 113°F) |
| • | ECT is less than 84°C (183°F) |
| • | At least 3 kg of air has passed through the engine |
| • | Vehicle speed is present |
DTC P0128 runs continuously once the above conditions have been met.
DTC P0128 is a type B DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0128 indicates lower than normal engine coolant temperature, which
most likely was NOT caused by a short/open or intermittent short/open in the ECT wiring.
Possible causes of low engine coolant temperature:
| • | The thermostat is stuck open. |
| • | The cooling fan(s) is always On. |
| • | The ambient temperatures are very low. |
| • | There is corrosion in the connector or resistance in the wiring. |
| • | The ECT sensor is skewed. |
Refer to ECT General Description for the Temperature vs. Resistance chart.

