Circuit Description
The ECM can control the idle speed by electrically controlling the throttle
plate, advancing/retarding the spark timing, or increasing/decreasing the air/fuel
ratio. The ability for the ECM to control the throttle plate is performed by the use
of the throttle actuator control (TAC) module. This assembly, internal to the throttle
body assembly, houses a DC motor along with 2 independent throttle positions
sensors, which relay the position of the throttle plate. The throttle plate is held
open 7 percent to a mechanical stop by the use of spring pressure for minimum
idle air and in the event of a motor circuit malfunction. The ECM monitors the throttle
actuator control system for faults in the TP sensors, TAC motor circuit, and for a
correlation speed to ensure the idle control is in check. DTC P0507 will set
if the actual idle speed is greater than a calibrated amount from the ECM commanded
idle speed after a certain period of time.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0507 will set if the actual idle speed is greater than 200 RPM
from the ECM commanded idle speed when:
| • | The condition exists for longer than 2 seconds after the ECM has
attempted to correct the condition within a limited range. |
| • | The ECT is greater than 80°C (176°F). |
| • | The IAT is greater than 34°C (93°F). |
| • | Vehicle speed is 0 mph. |
| • | EVAP leak diagnostics are not running. |
| • | No ECT, EVAP leak, EVAP purge solenoid, IAT, TP, or vehicle speed DTCs
have been set. |
DTC P0507 diagnostic runs continuously once the above conditions have
been met.
P0507 is a type B DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
Important: If an EGR, fuel trim, HO2S MAF, misfire, system voltage, or throttle actuator
DTC is also set, diagnose that DTC first.
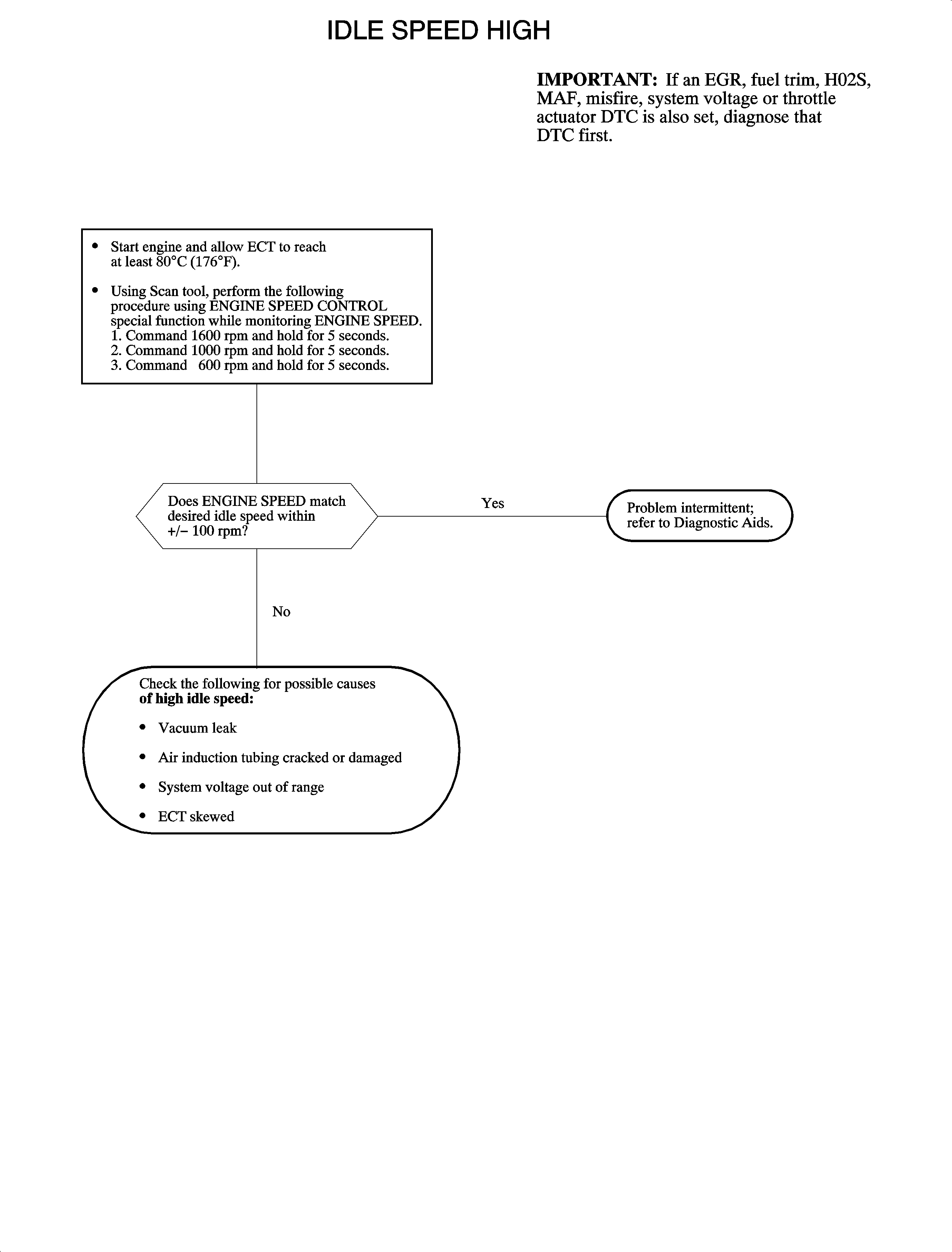
Verify the ECM ability to control engine speed by using the scan tool to perform
the ENGINE SPEED CONTROL special function. The test will allow the RPM to be raised
or lowered in increments of 25, 100, and 500 RPM. Compare the actual ENGINE
SPEED to the DESIRED IDLE SPEED. Both should be within 100 RPM of each other.
Make an underhood visual inspection first. Possible causes of high idle speed:
| • | Air induction tubing cracked or damaged |
| • | System voltage out of range |