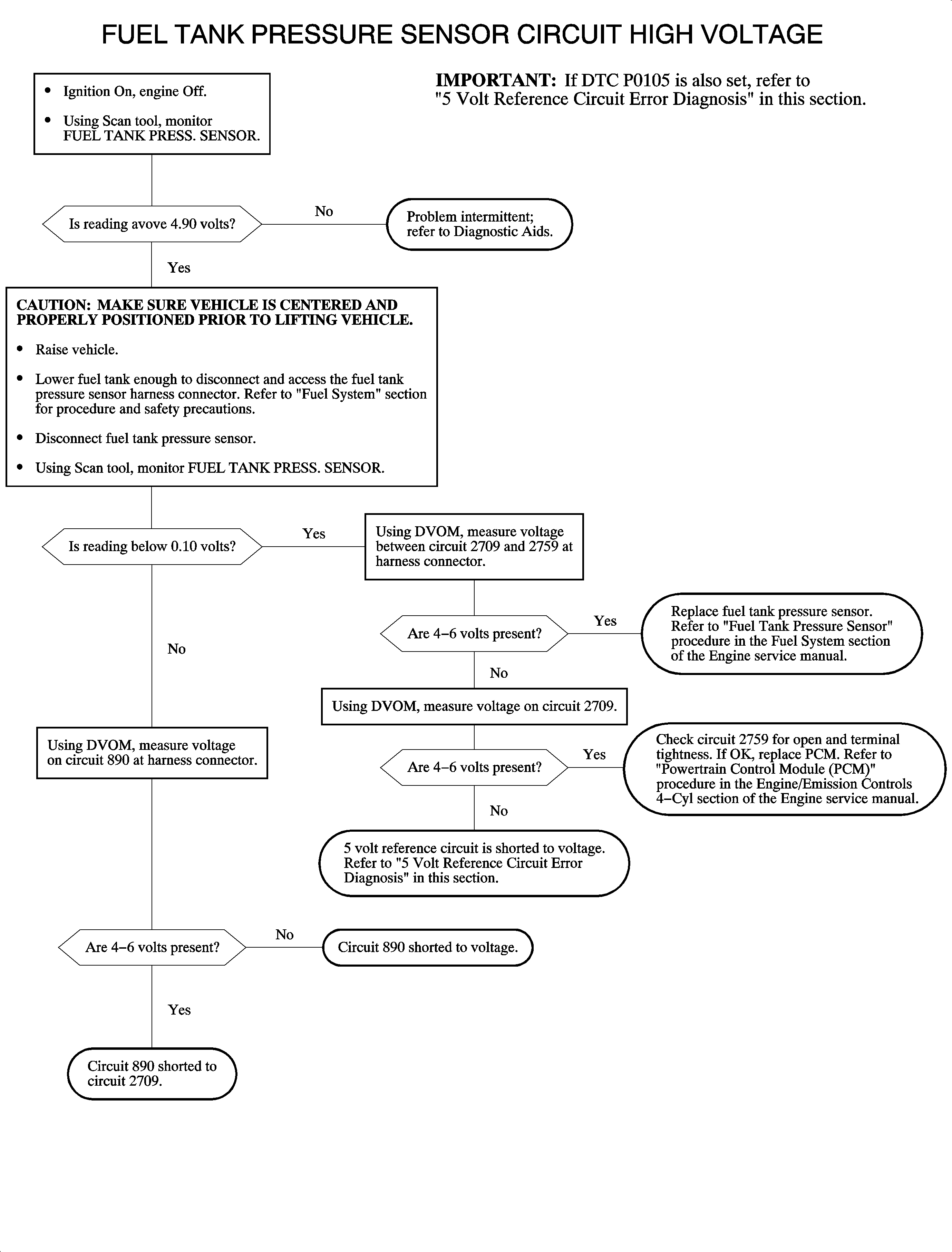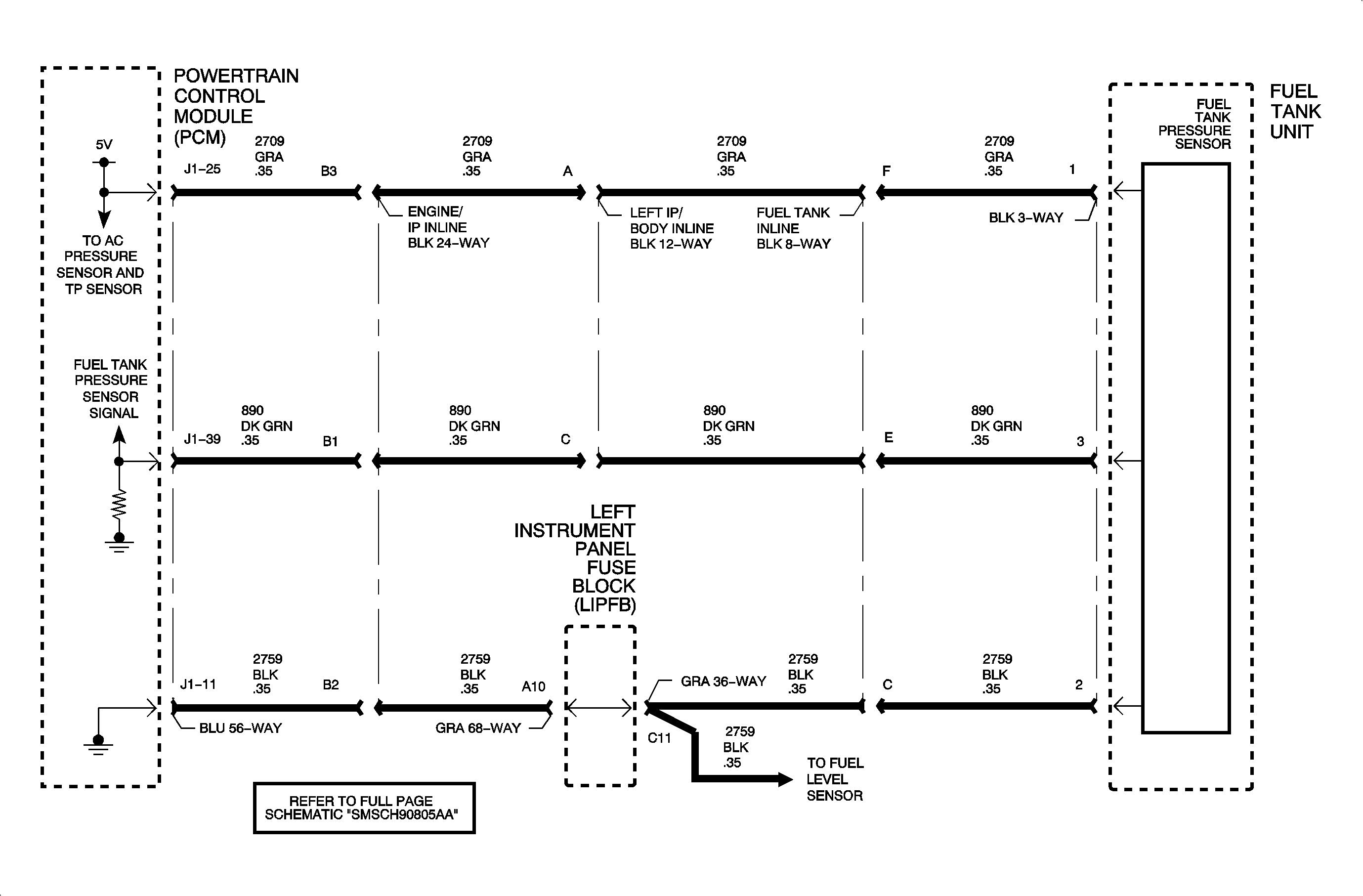
The evaporative emission (EVAP) system is used to store fuel vapors as to reduce the amount of unburned fuel from escaping into the atmosphere. The function of the fuel tank pressure sensor is solely for EVAP leak diagnostics. The fuel tank pressure sensor is a transducer that varies resistance according to changes in fuel tank pressure, which is the difference between fuel tank vapor and outside air pressure. The PCM measures the signal voltage from the fuel tank pressure sensor, which is a reduced value of the PCM 5 volt reference. The signal voltage will read low when the pressure in the fuel tank is low (vacuum) and will increase as the pressure in the tank increases. DTC P0453 sets when the signal voltage at the PCM is above the calibrated voltage value.
DTC Parameters
DTC P0453 will set if fuel tank pressure sensor voltage is greater than 4.9 volts when:
| • | The condition exists for longer than 25 seconds. |
| • | The engine is running. |
DTC P0453 diagnostic runs continuously with the engine running.
DTC P0453 is a type B DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
If DTC P0105 is also set, a short to voltage on the 5 volt reference circuit may exist. Refer to 5 Volt Reference Circuit Error Diagnosis.
To locate an intermittent problem, use the scan tool to monitor the FUEL TANK PRESS. SENSOR voltage with the ignition ON and the engine OFF. Wiggling the wires while watching for a change in the FUEL TANK PRESS. SENSOR voltage may locate the area where an open or short to voltage in the wiring could lie.
Important: The A/C pressure sensor, fuel tank pressure sensor, and TP sensor are all tied to the same 5 volt reference source.
Important: Inaccurate readings will occur if resistance measurements are taken on a fuel tank pressure sensor. The fuel tank pressure sensor contains an internal amplifier circuit that requires applied voltage to function properly.
The signal voltage with the fuel cap OFF should read between 2.35-2.85 volts, which represents atmospheric pressure or 0 inches of vacuum.