Engine Compression Test Check
Tools Required
SA9127E Gage Bar Set
If there is a lack of power, excessive oil consumption, or poor fuel economy,
etc., measure the compression pressure.
Caution: Compression checks must be performed with the vehicle in park or neutral and
the parking brake applied.
- Start the engine and allow it to reach normal operating temperature.
- Shut the engine OFF and disconnect the ignition module wiring harness
plugs.
- Remove the ignition modules.
Ignition Control Module Replacement
- Remove all 6 spark plugs.
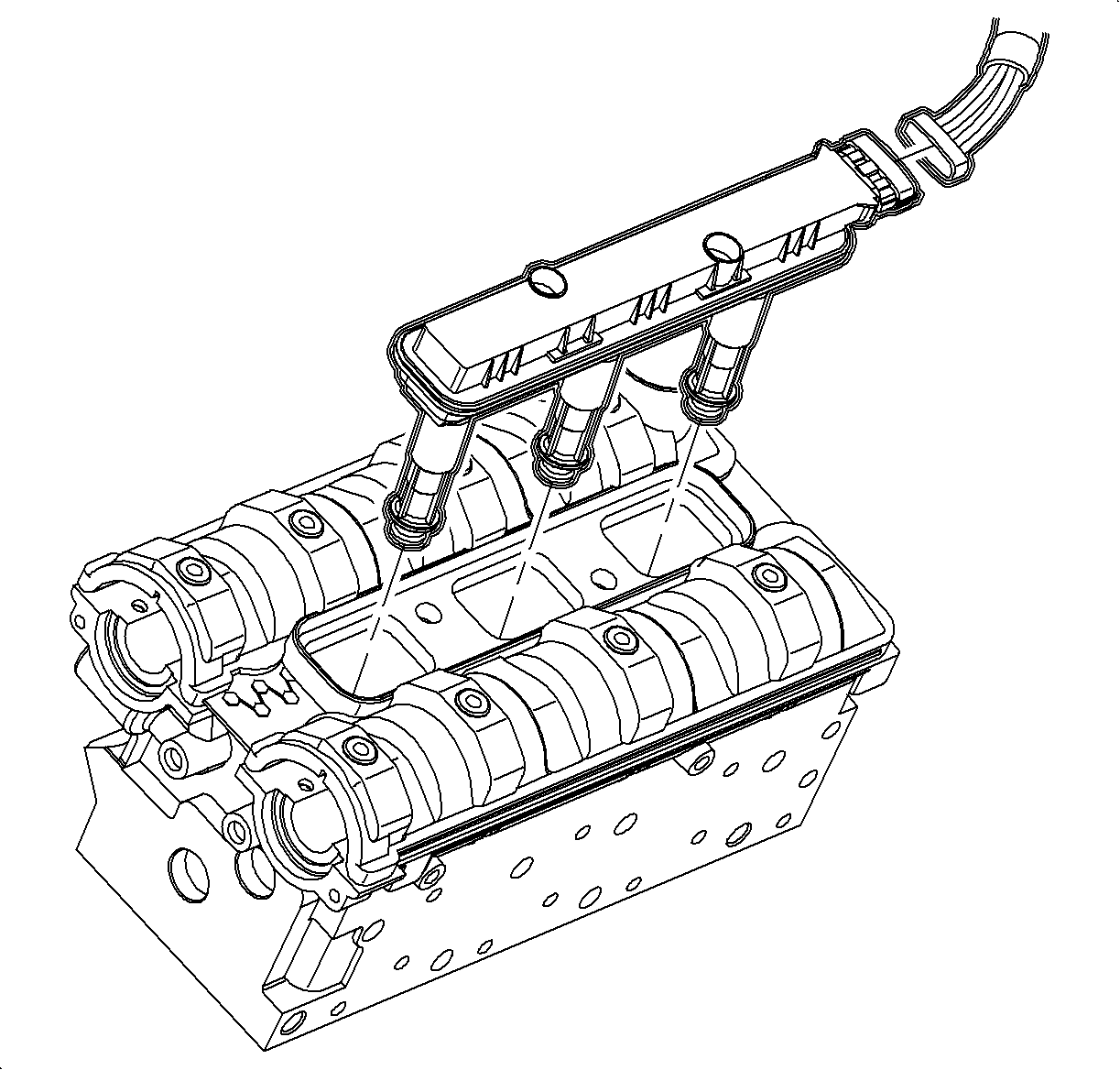
- Insert the SA9127E
into the spark plug hole.
- Fully open the throttle.
Important: Always use a fully charged battery to obtain engine revolutions of a 250 RPM
minimum. Do not crank the engine for more than 15 seconds.
- While cranking the engine, measure the compression. The cylinder should puff
or the compression gage needle should bounce a minimum of 10 times.
Important: All measurements must be completed in as short a time as possible. Check low
cylinders and make sure a minimum of 10 puffs are obtained prior to reading
the gage.
- Repeat the previous steps for each cylinder.
| | Important: No compression in 2 or more cylinders is an indication of damaged timing
chain sprockets, camshafts, and crankshaft key or pins.
|
| | Important: The minimum compression in any one cylinder should not be less than 70 percent
of the highest cylinder. No cylinder should read less than 690 kPa (100 psi).
|
| • | Normal compression: Builds up quickly and evenly to specification in each cylinder. |
| • | Low compression: Damaged piston, rings, valves, or head gasket. |
| • | High compression: Carbon on pistons/combustion chamber. |
Important: A cylinder leakage test can be performed to further determine the location of
the compression leakage if one or more cylinders are extremely low.
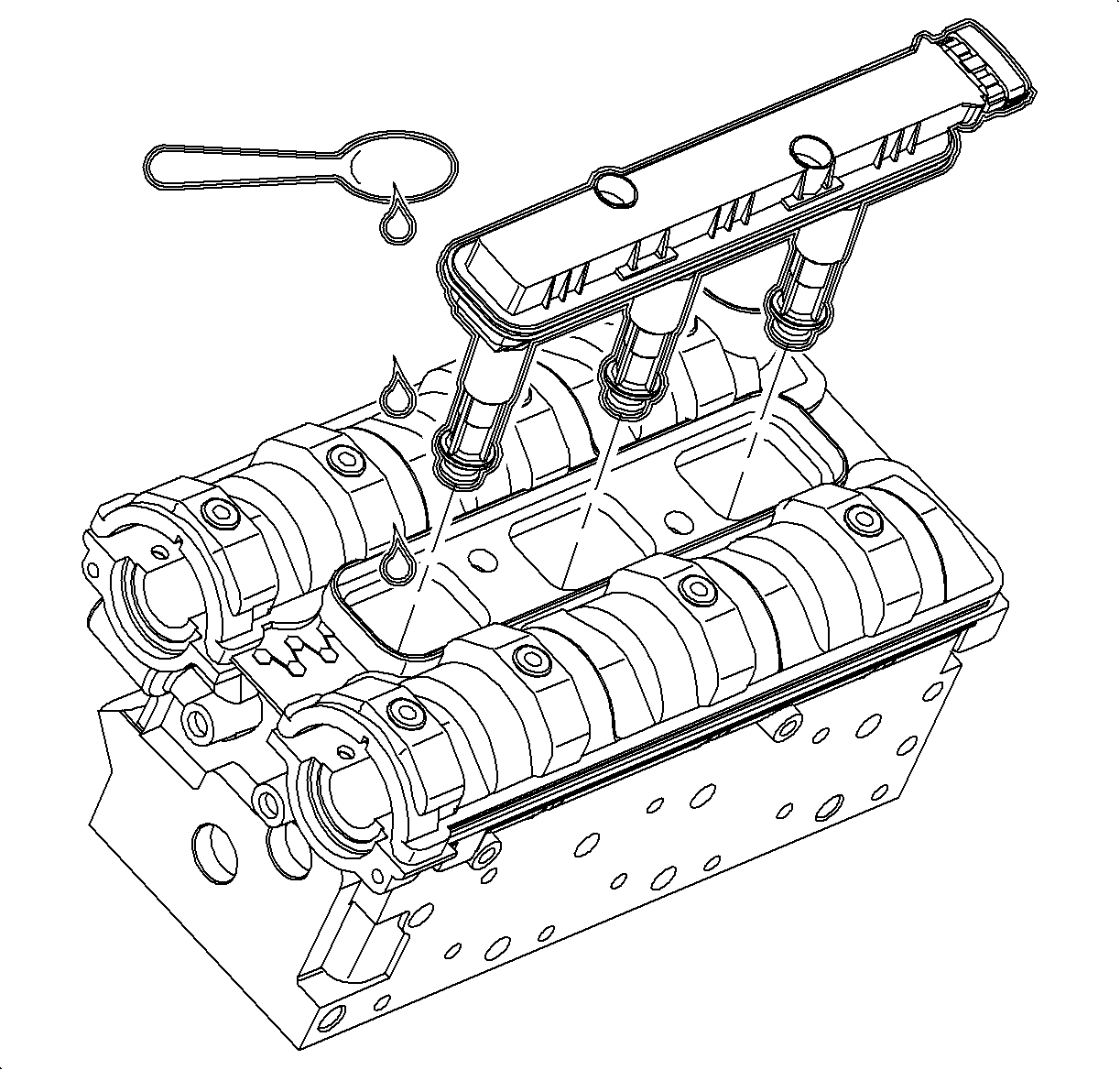
- If the cylinder compression in one or more cylinders is low, pour a small amount
(1 teaspoon) of engine oil into the cylinder through the spark plug hole.
- Place a shop towel
over the plug holes to capture any oil mist/spray.
- Crank the engine over for a few seconds without the compression gage or
spark plugs installed.
- Repeat previous steps 4-7 and measure the compression.
- If adding oil increases the compression readings the piston rings are leaking.
Compression is low on the first stroke (first gage puff) and tends to build
up on following strokes, but does not reach normal compression pressure. The compression
Improves considerably with oil. Inspect for worn or broken rings and piston ring land
wear (pound out).
- If adding oil does not increase the compression:
| • | Valves or head gasket leaking: Compression is low on the first stroke.
Compression does not tend to build up on the following strokes. Compression does not
improve with adding oil to the cylinder. |
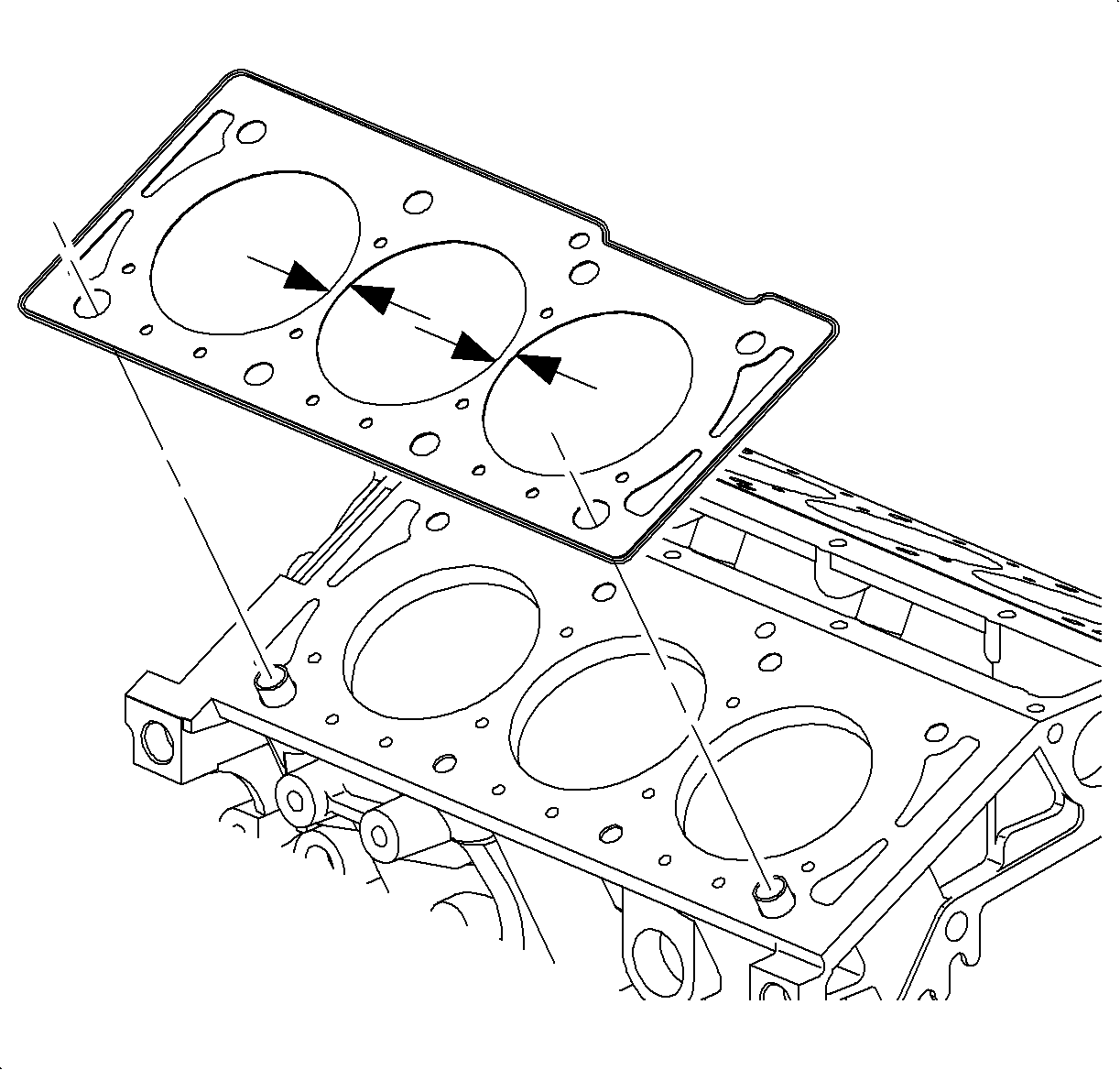
| • | Head gasket: Two
adjacent cylinders have lower than normal compression and adding oil to the cylinder
does not improve compression. |

- Remove the compression
tester and install the spark plugs.
Tighten
Tighten the spark plugs to 25 N·m (18 lb ft).
- Install the ignition module.
Tighten
Tighten the ignition module bolt to 8 N·m (71 lb in).
- Connect the ignition module electrical connection.
Engine Compression Test Test
- Perform the following steps in order to conduct a compression test for
the L81:
| 1.1. | Engine should be at room temperature. |
| 1.2. | Disconnect wiring from the ignition module. |
| 1.3. | Remove the spark plugs. |
| 1.4. | Throttle body valve should be wide open. |
| 1.5. | Battery should be at or near full charge. |
- For each cylinder, crank engine through four compression strokes.
- The lowest reading cylinder should not be less than 70 percent of the
highest.
- No cylinder reading should be less than 689 kPa (100 psi).
Important: The results of a compression test will fall
into the following categories:
| • | Normal - Compression builds up quickly and evenly to specified compression
on each cylinder. |
| • | Piston Rings - Compression low on first stroke. Tends to build up on following
strokes but does not reach normal. Improves considerably with addition of oil. |
| • | Valves - Compression low on first stroke. Does not tend to build up on
the following strokes. Does not improve much with the addition of oil. Use approximately
three squirts from a plunger-type oiler. |








