Circuit Description
The catalyst is a device used to control emission content. Although the catalyst
is active as soon as exhaust gas is passed through it, this diagnostic will not run
until the front and rear oxygen sensors are both in closed loop. The oxygen storing
capability of the catalyst is monitored by viewing the rear oxygen sensor's response
to an oscillating air-fuel ratio. The ECM computes how a near-failure catalyst would
cause a rear oxygen sensor to react to an oscillating air-fuel ratio. These values
are compared with the actual rear oxygen sensor response. If the actual response deviates
a calibrated amount from the computed values, this code will set.
DTC Parameters
DTC P0431 and P0432 will set when:
| • | Engine speed is between 1400 and 2000 RPM. |
| • | Engine load is between 20% and 45%. |
| • | Catalyst temperature greater than 350°C (662°F). |
| • | No front or rear oxygen sensor, misfire, MAF, TP, purge solenoids codes
set. |
P0431 and P0432 are (type B) DTCs.
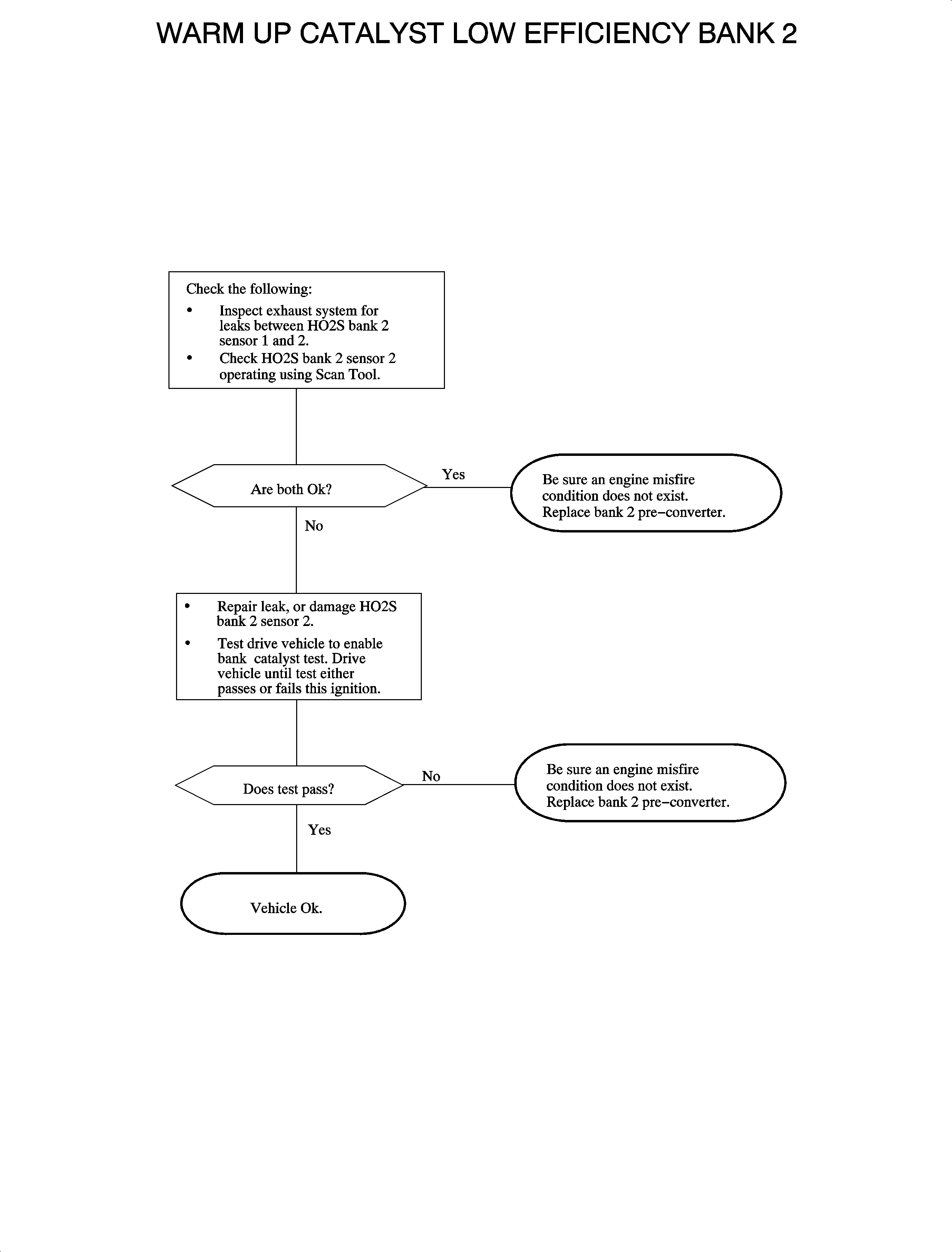
Diagnostic Aids
Once set, this code should remain active. Under certain driving conditions the
catalyst monitor test may pass. This condition may occur if driving the vehicle at
highway speeds (high air flow) but if this code is set, and there are no exhaust leaks,
the converter should be replaced. If a misfire code is detected, the catalyst monitor
test will not run. Be sure to correct a misfire condition before replacing the converter.
Possible causes:
| • | Exhaust system leaks between front and rear sensors, or rear sensor leaking. |
| • | Catalyst deteriorated due to excessive time operating vehicle with a catalyst
damaging misfire. |
| • | Contamination of converter due to incorrect sealant, fuel, or fuel additive. |