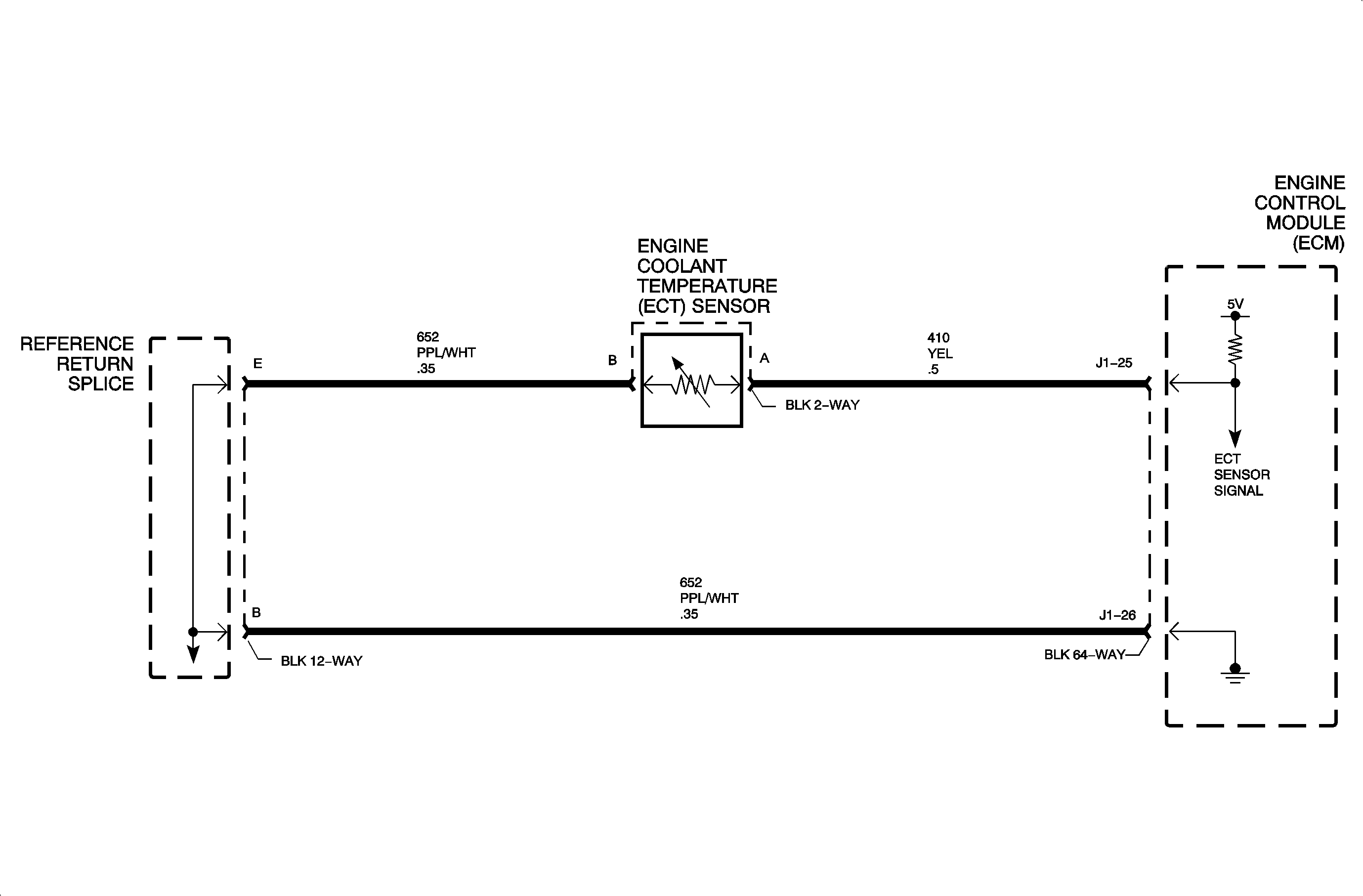
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a thermistor that varies resistance according to changes in engine coolant temperature. The ECM supplies a 5 volt reference through a pull-up resistor(s) to the sensor, which is connected to ground. When the sensor is cold it has a high resistance (high signal voltage at ECM). As the sensor temperature increases, its resistance decreases (low signal voltage at ECM). The ECM uses the signal voltage to determine engine coolant temperature. The ECM calculates a modeled temperature using start up ECT, MAF, MAP, and engine run time and compares this value to the ECT sensor signal. DTC P0116 sets when the ECT sensor signal deviates more than 12°C or 22°F from the ECM modeled temperature.
DTC PARAMETERS
DTC P0116 sets when the ECT sensor signal deviates more than 12°C or 22°F from the ECM modeled temperature when:
Engine is cranking/running.
DTC P0116 runs continuously once the above conditions have been met.
P0116 is a (type B) DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0116 indicates that the ECT sensor readings are valid but deviate more than 12°C or 22°F from the ECM modeled temperature.
Possible causes of low engine coolant temperature:
| • | Skewed sensor. |
| • | Very low ambient temperatures. |
| • | Corrosion in connector or resistance in wiring. |
| • | Poor connections in ECT circuit. |
| • | Thermostat malfunction. |
| • | Cooling fan(s) malfunction. |
| • | Extreme ambient temperature. |
ECT sensor reading may be compared to IAT sensor reading on Scan tool after the vehicle has been sitting longer than 6 hours with the ignition Off. Both readings should be within 6°C or 10°F of each other.
Refer to ECT General Description for a Temperature vs. Resistance chart.
