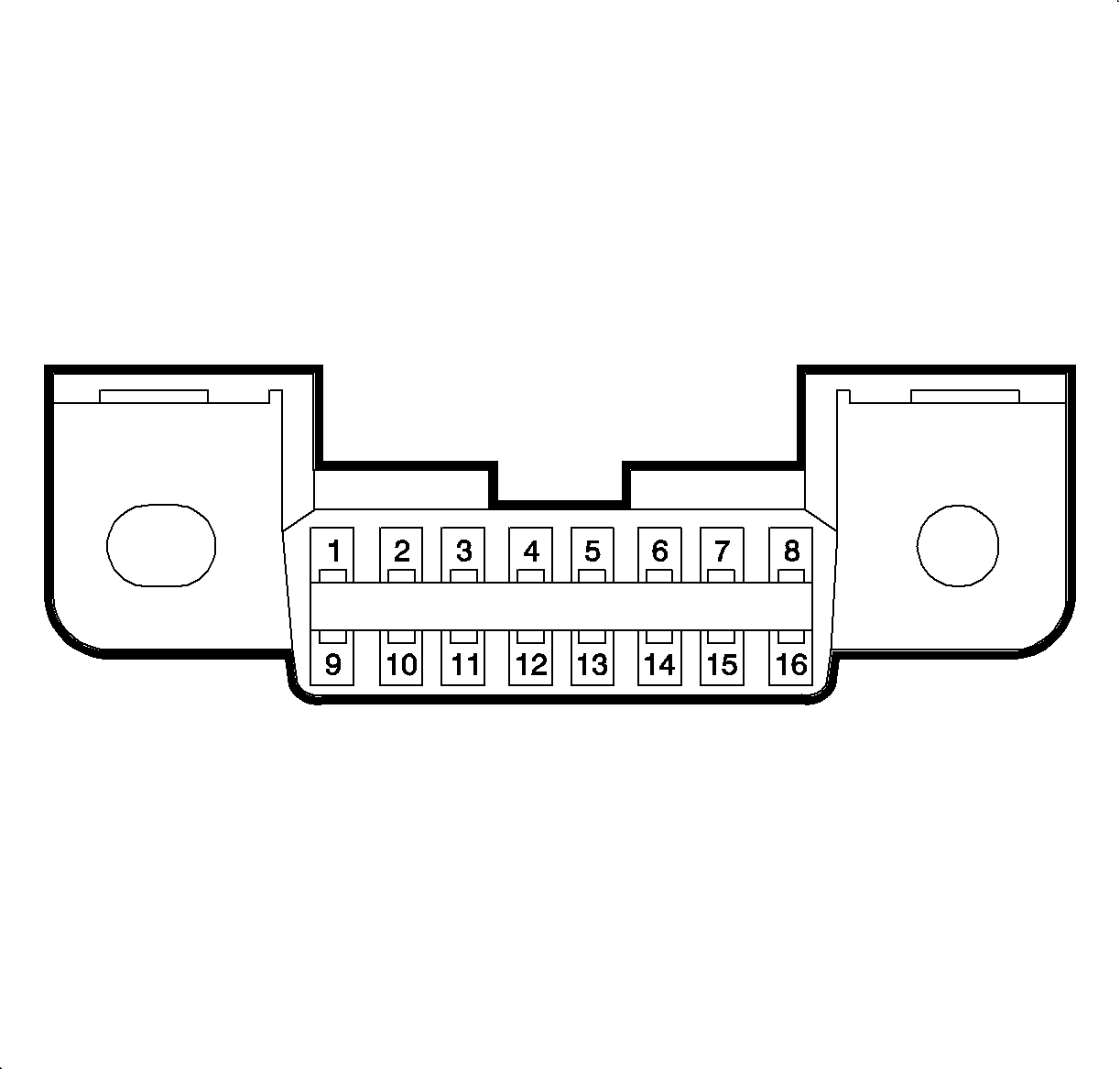
Pin | Wire Color | Circuit # | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
2 | PPL | 1807 | Class II Data Link |
4 | BLK | 550 | Ground |
5 | BLK/WHT | 451 | Ground |
7 | BRN | 2960 | ECM/TCM KW 2000 |
12 | BRN | 2960 | EBTCM KW 2000 |
16 | ORN | 2140 | Battery |
The Saturn L-series may consist of up to 3 types of serial data communication links. The type of links used for a given vehicle will depend on the engine type and whether it is equipped with an electronic brake traction control module (EBTCM).
The 3 serial data communication links are:
Class II
The Class II serial data link is used by the body control module (BCM), instrument panel (I/P) cluster, sensing and diagnostic module (SDM), and the powertrain control module (PCM) 4 cylinder only. The Class II link is used for normal vehicle communication between the control modules and for the scan tool diagnostic communication.
Class II is a 10.4 k/baud (k/bits per second) digital data communication protocol that operates only on logic 1's and logic 0's. Logic 0 is defined as 0 volts and logic 1 is defined as 7 volts. The Class II serial data structure incorporates a variable pulse width, so a logic 1 for instance would not be at 7 volts for the same amount of time for all messages. This is used to allow faster messaging to specific controllers.
The Class II link allows the reduction of separate wires that would otherwise be used to turn ON or turn OFF a device. For example, if the PCM needed the SERVICE ENGINE SOON telltale ON because it detected an emission related fault. It would send a message to the I/P cluster to turn ON the telltale instead of discretely sending a signal over a specified wire. Also, each controller could pass any type of information to other controllers at all times improving on-board convenience features. All messages that each controller uses are sent continuously whether the controller needs them or not. If the SES light is not being commanded ON, the PCM to I/P cluster message will indicate to keep the light OFF. Most likely, logic 0 would be sent to keep the SES telltale OFF. When the PCM needed the SES telltale to be turned ON, it would change the bit to logic 1. This method of continuous messaging allows each controller to know when another controller is not communicating on the Class II link.
Each Class II module does not know which controller sent a message until it receives the message. Each message string contains a source identifier, which tells the controller where the message came from. For example, if the PCM lost battery voltage, then the ignition was turned ON, the BCM and SDM would set a DTC U1000. This DTC indicates that an expected message was not received and the source ID was not learned. If, for example, the PCM lost battery voltage after the ignition was turned ON, the BCM and SDM would set a U1064, lost communications with the PCM, since the PCM ID was already learned. This method of "learning" by each control module allows different product lines to use different manufacturer controllers.
Controller Area Network (CAN)
The CAN data link is used by the body control module (BCM), engine control module (ECM), and transaxle control module (TCM). The CAN link is only used for normal vehicle communication between these 3 control modules.
The CAN link scheme is a 500 k/baud digital data communication protocol that operates only on logic 1's and logic 0's. Logic 0 is defined as the CAN high circuit at 3.5 volts and the CAN low at 1.5 volts or a differential of 2 volts across the circuits. Logic 1 is defined as the CAN high and CAN low circuits each at 2.5 volts or a differential of 0 volts across the circuits. One bit is equal to a logic 1 or logic 0. Therefore, CAN speed incorporates a high frequency of 500,000 logic 1's and logic 0's going by on the link every second. This high frequency allows the use of a fixed pulse width. Also, due to the high frequency, electromagnetic noises being produced by the link as well as link noise susceptibly characteristics are the reasons why the CAN high and CAN low wires are twisted together.
Unlike Class II, CAN link controllers have each controller ID stored in memory. If one controller is not communicating on the link, all other controllers know exactly which controller is not communicating no matter when the fault occurred.
Keyword Protocol 2000 (KWP 2000)
The keyword protocol 2000 link is only used for the scan tool communication to the engine control module (ECM), electronic brake and traction control module (EBTCM), and transaxle control module (TCM). This link is NOT used for any normal vehicle control module communication. This communication link transmits at a rate of 10 k/baud. Even though Class II operates at an only slightly higher baud rate, its message lengths and more flexible. The update rate of a Class II message from the BCM transmitted to the scan tool will appear faster than that of a keyword message from the ECM.
On-Board Diagnostics For The Communication Links
Class II
Each Class II module is programmed with a list of serial data messages that are important and should be received by the module. One of those important messages is the state of health (SOH) message. The SOH message is sent out periodically, even if no other information is being transmitted. The SOH message is used to let all the other modules on the serial data circuit know the sending module is working correctly.
Each controller that relies on information from another controller and incorporates a diagnostic associated with that controller. The diagnostic uses the SOH message for performing the diagnostic. Each time the ignition is turned ON all the modules on the Class II serial data circuit first learn the other modules connected to the Class II serial data circuit. If a controller relies on information, but it is not received, the controller will not know what other device was supposed to send the information. In this case a DTC U1000 will be set indicating a message was not received. Once a controller has learned which controller has sent the information, a DTC indicating which controller stopped communications will be indicated if that message is lost. Each controller will learn which other controller is sending the message it has to receive every ignition cycle.
Refer to specific U code definitions for more details of code setting conditions.
Can Link Diagnostics
Diagnostics on the CAN link are similar to Class II. The main difference is that the source of information a controller relies on is always known, and therefore, a specific code indicating which controller may have stopped communicating is always known.
KWP 2000 Diagnostics
Since this link is only used for diagnostics/reprogramming, and not used for normal vehicle communications, there are no on-board diagnostics associated with this link.
