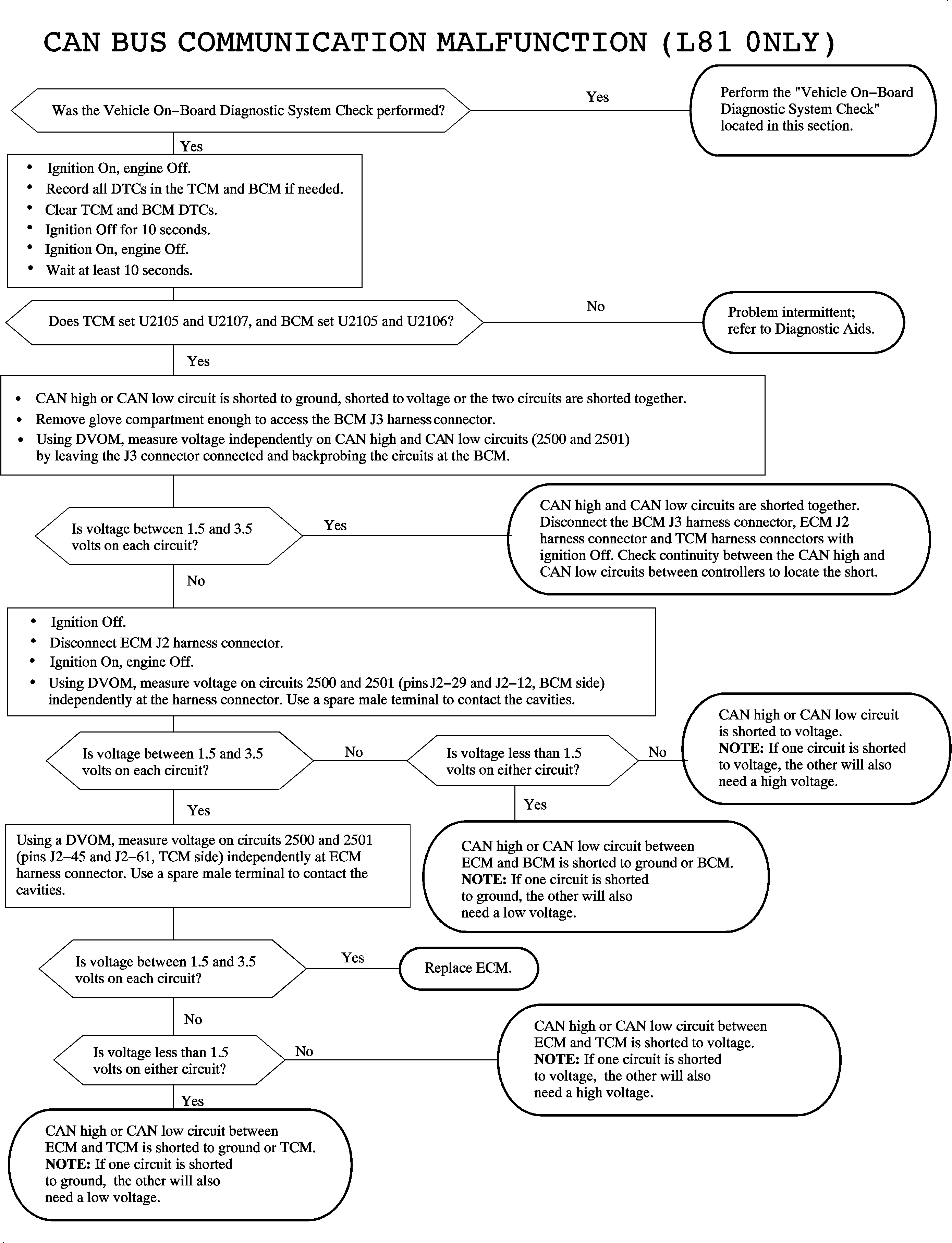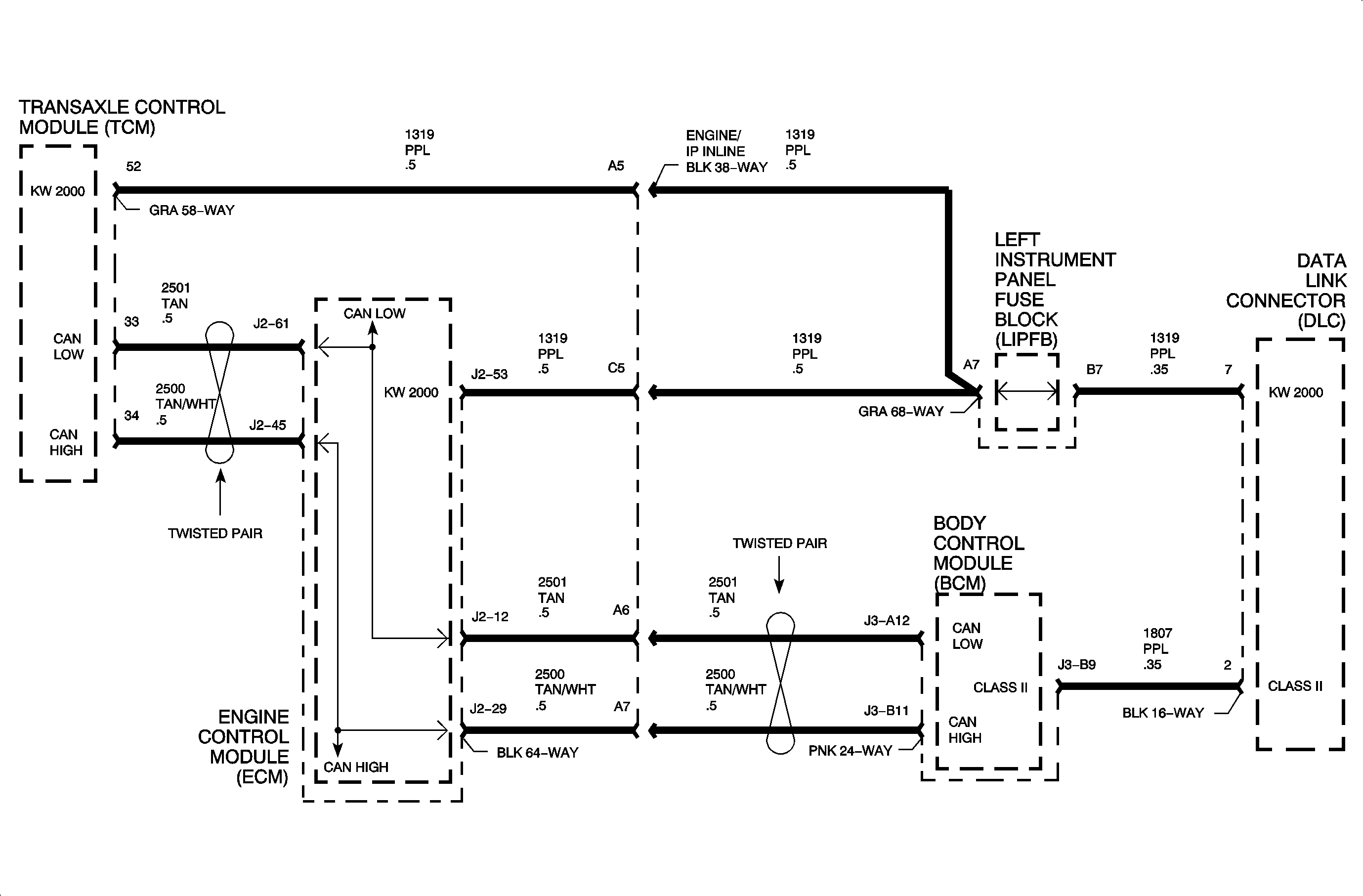
The engine control module (ECM), transaxle control module (TCM), and body control module (BCM) communicate normal mode messages over the controller area network (CAN) link circuits 2500 and 2501. Each controller on the CAN link uses a variable pulse width modulated square wave consisting of logic 0's and logic 1's. A logic 0 is denoted as circuit 2501 at 1.5 volts with circuit 2500 at 3.5 volts resulting in a difference of 2 volts across the circuits. A logic 1 is denoted as both circuit 2500 and 2501 at 2.5 volts resulting in a difference of 0 volts across the circuits.
State of health messages are sent from each CAN controller on the link when the ignition is turned ON as well as during normal vehicle operation. These messages allow the BCM, ECM, and TCM to know that each controller on the link is functioning correctly. The ECM monitors the CAN link for low and high voltage faults. All controllers on the CAN link monitor each others messages and can set a DTC if information is not received.
DTC Parameters
DTC U2100 will set if the ECM detected the CAN link circuit in the low state or in the high state for too long when:
| • | The condition exists for longer than 25 seconds. |
| • | The engine is running. |
This indicates that CAN circuit 2500 or 2501 is shorted to ground, shorted to voltage, or that both circuits are shorted together.
DTC U2100 runs continuously with the engine running. The ECM will PASS the diagnostic if no faults exist for 2 seconds.
DTC U2100 is a type A DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect the CAN link wiring for signs of chafing or broken insulation.
With the ignition ON, each CAN high or CAN low circuit should have between 1.5-3.5 volts measuring into a control module no matter how many modules are left connected.
The TCM sends the ECM vehicle speed over the CAN link. The ECM sends the BCM fuel level over the link as well. If the CAN link contains a circuit fault, vehicle speed in the scan tool ECM DATA TABLE will read 0 mph, with the vehicle moving, and the fuel gage on the I/P cluster will slowly go to EMPTY. This may be used for intermittent diagnosis.