Circuit Description
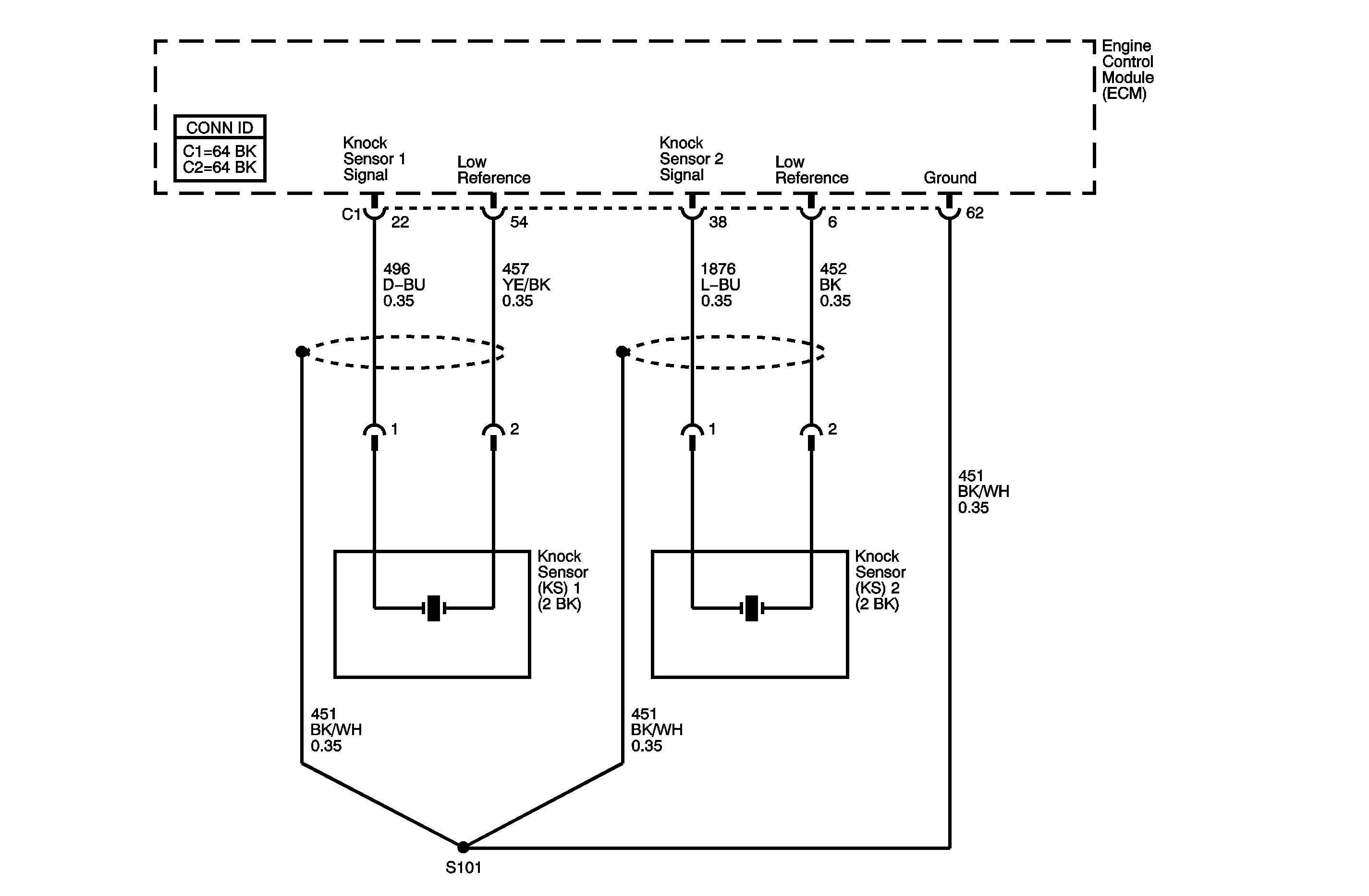
The knock sensor (KS) system enables the engine control module (ECM) to control the ignition timing for the best possible performance while protecting the engine from potentially damaging levels of detonation. The KS system uses two sensors. KS 1 is located on the right side of the engine, or the rear of the engine compartment. KS 2 is located on the left side of the engine, or the front of the engine compartment. The KS produces an AC voltage signal that varies depending on the vibration level during engine operation. The ECM adjusts the spark timing based on the amplitude and the frequency of the KS signal. The ECM receives the KS signal through a signal circuit. The KS ground is supplied by the ECM through a low reference circuit. The ECM learns the minimum and maximum amplitude of the noise the engine produces. The ECM should monitor a normal KS signal within the voltage range. If the ECM detects the KS signal exceeding the voltage range a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) sets. DTC P0328 refers to KS 1 and DTC P0333 refers to KS 2.
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
| • | DTC P0328 Knock Sensor (KS) Circuit High Voltage Bank 1 |
| • | DTC P0333 Knock Sensor (KS) Circuit High Voltage Bank 2 |
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is more than 40°C (104°F). |
| • | The engine speed more than 2,000 RPM. |
| • | The engine load is more than 40 percent. |
| • | DTC P0328 and P0333 run continuously once the above conditions are met. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The KS signal is above the normal operating range for more than 300 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module stores the DTC information into memory when the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will not illuminate. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The control module stores this information in the Failure Records. |
| • | The driver information center, if equipped, may display a message. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A current DTC Last Test Failed clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the DTC with a scan tool. |
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Control Module Connector End Views or Engine Controls Connector End Views | ||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle in Vehicle DTC Information |
2 |
Does the DMM display a voltage above the specified value? | 1 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 3 |
3 |
Does the DMM display a voltage above the specified value? | 1 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 4 |
4 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 5 |
5 |
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Detonation/Spark Knock |
6 | Test the KS signal circuit for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 8 |
7 | Test the KS low reference circuit for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 8 |
8 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the ECM. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Replace the ECM. Refer to Control Module References in Computer/Integrating Systems for replacement, setup, and programming. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 10 | -- |
10 |
Does the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle in Vehicle DTC Information | System OK |
