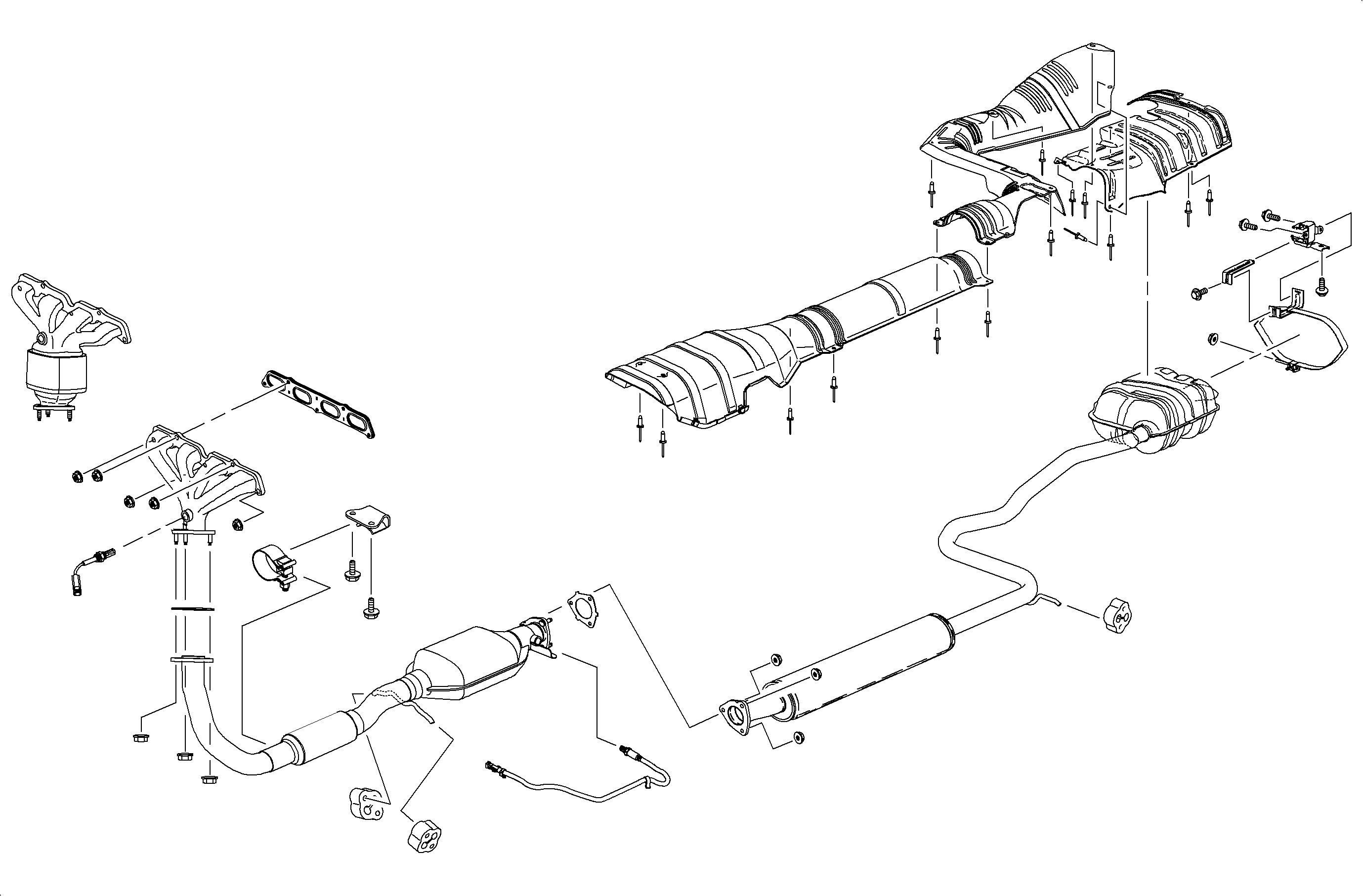
When inspecting or replacing exhaust system components, ensure there is adequate clearance from all points on the underbody to avoid possible overheating of the floor pan and possible damage to the passenger compartment insulation and trim materials.
Check complete exhaust system and nearby body areas for broken, damaged, missing or mis-positioned parts, open seams, holes, loose connections, or other deterioration which could permit exhaust fumes to seep into the passenger compartment. Dust or water in the passenger compartment may be an indication of a problem in one of these areas. Any damage should be corrected immediately.
Annoying rattles and noise vibrations in the exhaust system are usually caused by misalignment of parts. When aligning the system, leave all bolts or nuts loose until all parts are properly aligned, then tighten, working from the rear.
Periodic maintenance of the exhaust system is not required. When the vehicle is raised for service, check the general condition of the three way catalytic converter, pipes, mufflers, and heat shields. The steel for the exhaust system is resistant to corrosion by exhaust gases, but rapidly shows surface corrosion on the outside. This surface corrosion is not a cause for replacement.
The installation of exhaust system supports is very important, since improperly installed supports can cause annoying vibrations which are difficult to diagnose.
Exhaust system performance complaints, such as excessive back pressure, are noticeable by their effect on engine performance. Other faulty vehicle components, such as emission control devices, have similar effects on engine performance and may be characterized by the same symptoms or complaints.
Three Way Catalytic Converter
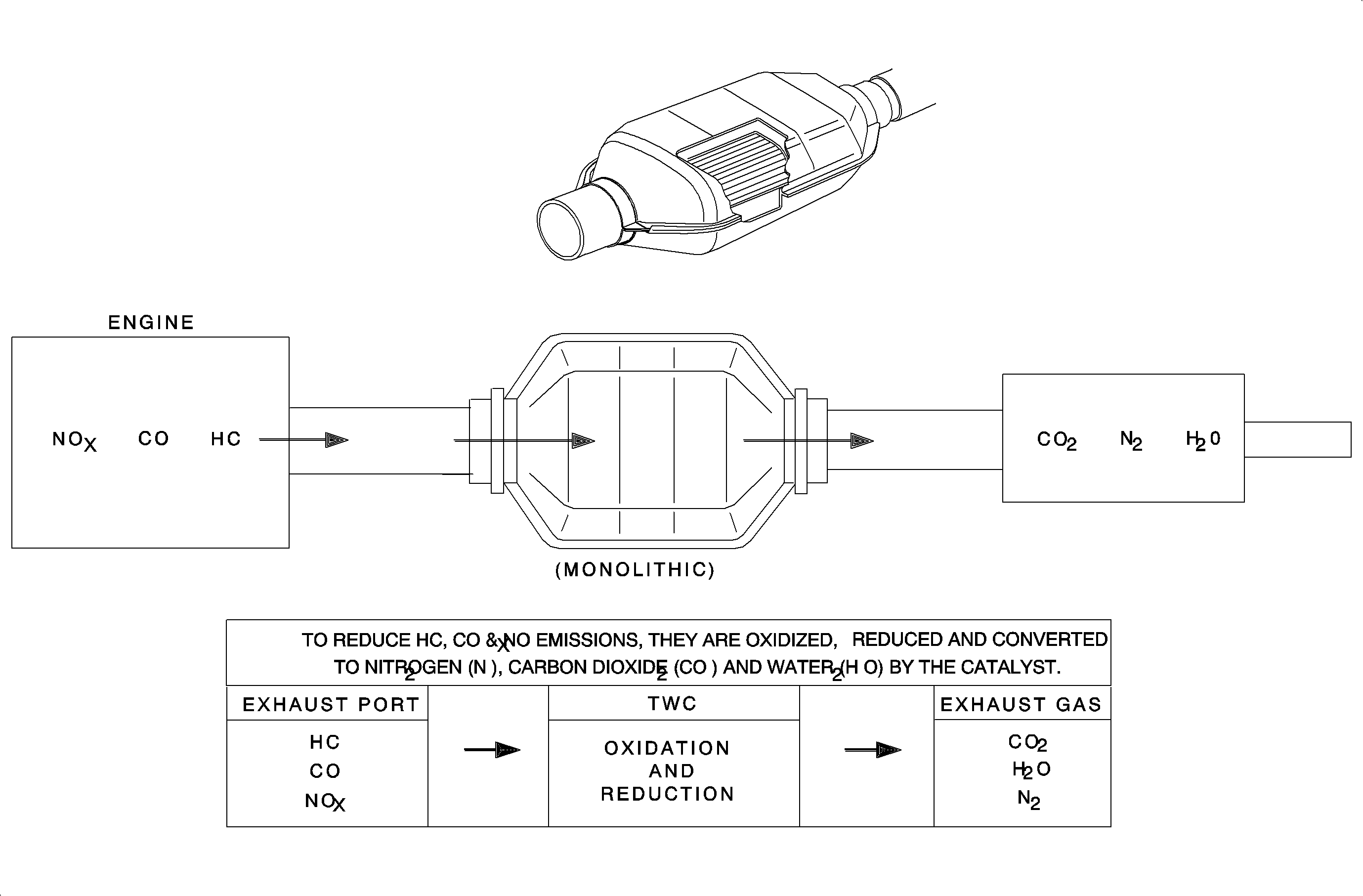
The three way catalytic converter is an emission control device added to the exhaust system to reduce pollutants from the exhaust gas stream and requires the use of unleaded fuel only.
The 3-way catalytic converter coating on the 3-way (reduction) 3-way catalytic converter contains platinum and rhodium which lowers the levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOx) as well as hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO).
Periodic maintenance of the exhaust system is not required. If the vehicle is raised for other service, it is advisable to check the condition of the complete exhaust system.
Exhaust Manifold/Oxygen (O2) Sensor
The exhaust manifolds used on the SOHC (L24) and DOHC (LL0) engines are cast iron. The oxygen sensor is located in the exhaust manifold of all engines.
Front Oxygen Sensor (O2S)
The front oxygen (O2S) sensor is mounted in the exhaust system where it can monitor the oxygen content of the exhaust gas stream. An oxygen sensor acts as an electrochemical cell, or battery, to produce a voltage in response to the oxygen content in the exhaust stream compared to the oxygen content of the atmosphere. A lean mixture, high oxygen content in the exhaust, will produce a low voltage and a rich mixture, low oxygen content in the exhaust, will produce a high voltage. The oxygen content in the exhaust reacts with the oxygen to produce a voltage output. This voltage ranges from approximately 100 millivolts (0.1 volts), high-oxygen lean mixture, to 900 millivolts (0.9 volts), low oxygen-rich mixture.
Important: DTC 44 or 45 usually indicates a rich or lean engine operation, rather than a defective oxygen sensor or circuit. Therefore, it is important that the Fuel System Check be used to diagnose these codes.
By monitoring the voltage output of the oxygen sensor, the PCM/ECM will know what fuel mixture command to give to the injector, lean mixture - low voltage - rich command; rich mixture - high voltage - lean command.
Front Exhaust Pipe
The front exhaust pipe incorporates a stainless steel braided sleeve over a flexible bellows section along with the catalytic converter. The entire pipe assembly is welded joint construction and is only serviced as an assembly.
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S-2)
The heated rear oxygen sensor, mounted behind the catalytic converter, monitors oxygen content in the exhaust to determine the efficiency of the catalytic converter. The HO2S-2 is a 4 wire sensor, 2 which heat the sensor, B+ and ground, the other 2 which are the signal reference and ground. The sensor acts as an electro chemical cell, or battery to produce a voltage in response to the oxygen content in the exhaust. A bias voltage (voltage sent from the PCM) is between 350-550 mv which is the voltage the PCM will see when the sensor is inactive or cold. As the heater and the converter temperature heat the sensor up to around 275°C (527°F), the sensor will produce its own voltage to counteract the bias voltage. Low voltage from the sensor indicates high oxygen content, lean mixture, whereas high voltage indicates low oxygen content, rich mixture. The wires to the sensor carry air reference which is used to compare differences in oxygen from the atmosphere to the exhaust stream.
The rear HO2S-2 will react slower than the front OS2 due to the oxygen storage in the catalytic converter. The rear oxygen sensor is used only for converter efficiency, not for A/F ratio control.
The rear oxygen sensor operates between 275°C (527°F) to 850°C (1562°F).
Intermediate/Resonator Pipe
The intermediate pipe is part of a welded exhaust system and is serviced without the muffler.
Muffler
The muffler is part of a welded exhaust system and is serviced.
Hangers and Isolators
The exhaust system is supported by free hanging rubber mountings which permit some movement of the exhaust system but do not permit transfer of noise and vibration into the passenger compartment.
The installation of exhaust system supports/isolators is very important as improperly installed supports/isolators can cause annoying vibrations which can be difficult to diagnose.

There are 3 rubber isolator blocks that support the exhaust system ahead of the muffler. These isolator blocks are installed on wire rods that are welded to the underbody and the exhaust system.
Clamps
Two types of clamps are used for connecting exhaust system slip joints:
| • | Saddle/U-bolt |
| • | Guillotine |
Shields and Rivets
The heat shields are aluminum; they prevent exhaust system heat from penetrating the floor of the vehicle or the fuel tank. Inspect the shields for cracks, tears, and missing rivets. Shields must always be re-installed if they are removed for exhaust system or body repairs. The rivet is unique and must always be replaced with the same type of fasteners to prevent vehicle damage.
