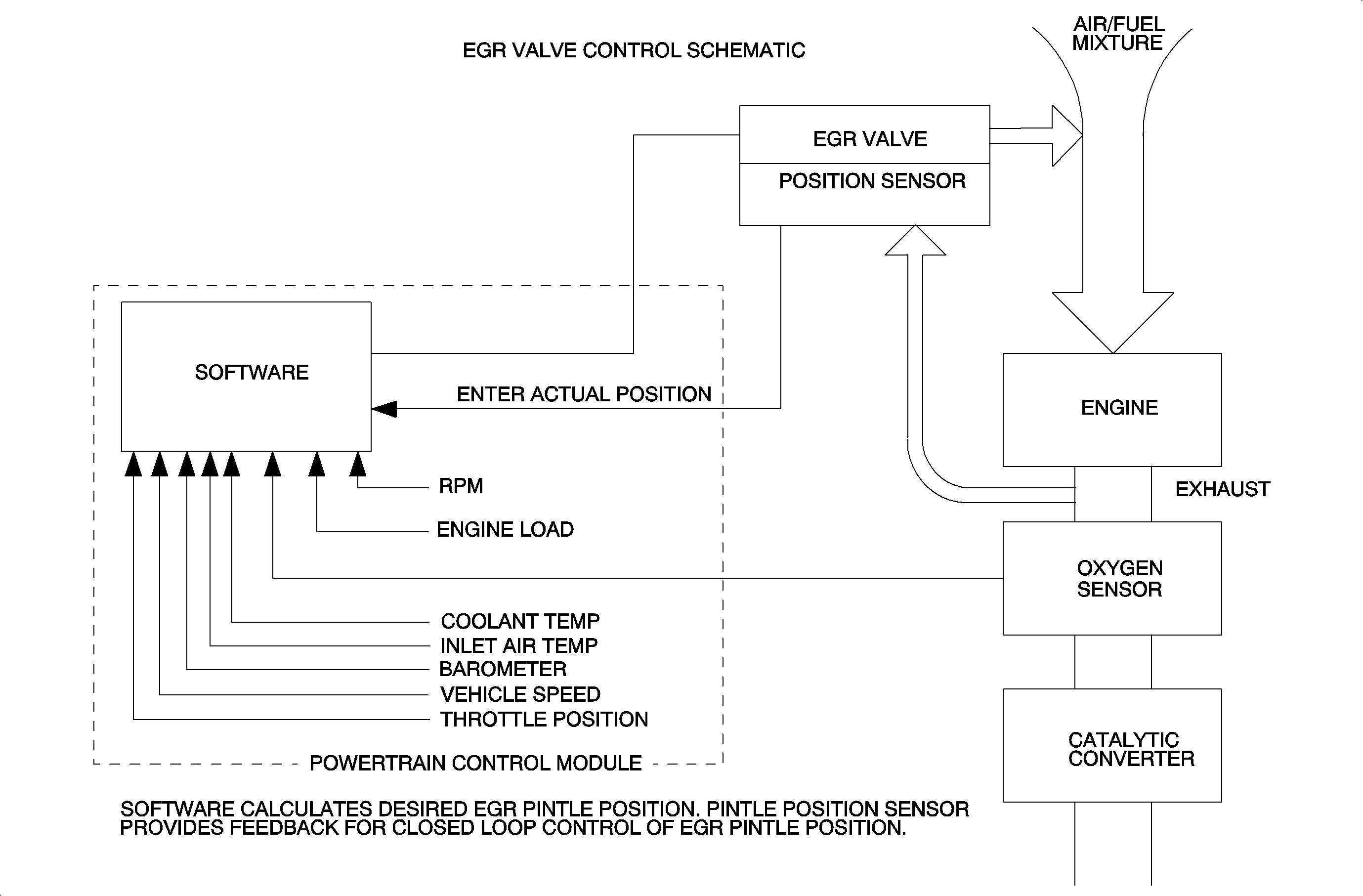
EGR System Operation
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system is used to decrease the emission
levels of oxides of nitrogen (NOX). NOX is a group of chemical compounds containing
nitrogen and varying amounts of oxygen, which in large quantities, can have harmful
environmental effects.
NOX forms during the combustion process in amounts that are dependent on the
concentration of oxygen in the combustion chamber and the duration that the combustion
process exceeds 822°C (1512°F). Decreased NOX levels are accomplished by
reducing the peak combustion temperature through the dilution of the incoming air/fuel
mixture with exhaust gas. Exhaust gas, largely non-reactive carbon dioxide and water
vapor, reduces combustion temperatures because of lower oxygen content.
Correct amount of EGR depends upon the geometry of the combustion chamber and
the operating condition of the engine. Too little EGR can yield:
While too much EGR can yield:
| • | Engine stalling at idle |
The powertrain control module (PCM) regulates the amount of EGR needed under
all engine operating conditions. The EGR system consists of the EGR valve and the
PCM. The PCM bases EGR solenoid control off the following inputs:
| • | Engine coolant temperature |
| • | Manifold absolute pressure |
The EGR valve consists of a pintle valve that moves by the use of an internal
solenoid and an internal pintle position sensor (potentiometer) used to determine
pintle valve position. The PCM controls the solenoid by pulse width modulating ignition
voltage whenever the EGR valve is commanded ON.
The internal position sensor is supplied a 5-volt reference and a ground from
the PCM. The sensor varies resistance which changes signal line voltage used to determine
actual pintle valve position.
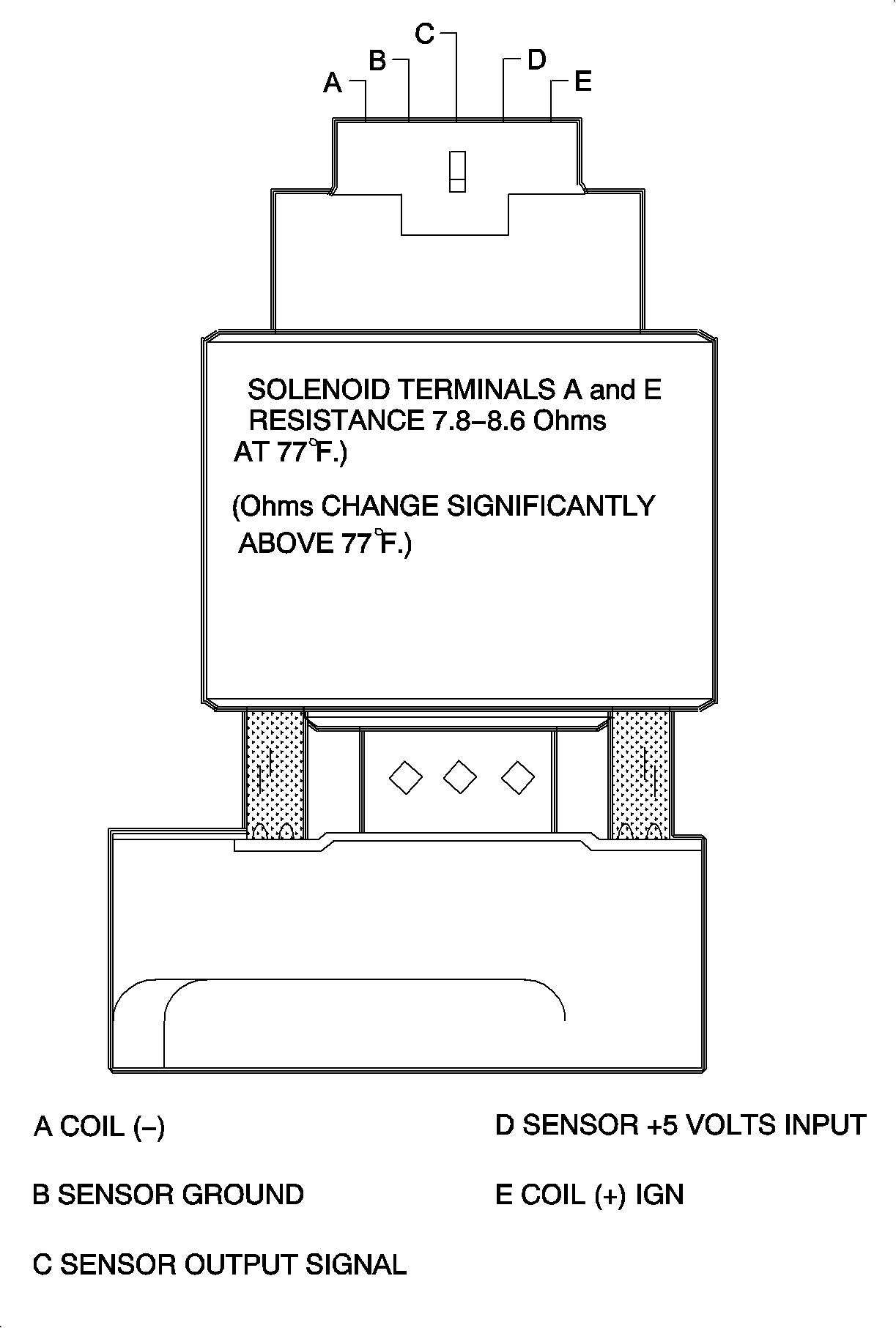
Positioned at the top of the EGR valve are five terminals:
| • | B, C, D are terminals from the PCM for the internal position sensor. |
| - | D is sensor 5 volt supply. |
| • | E is solenoid pulse width modulated ignition voltage. |
EGR System Diagnostics
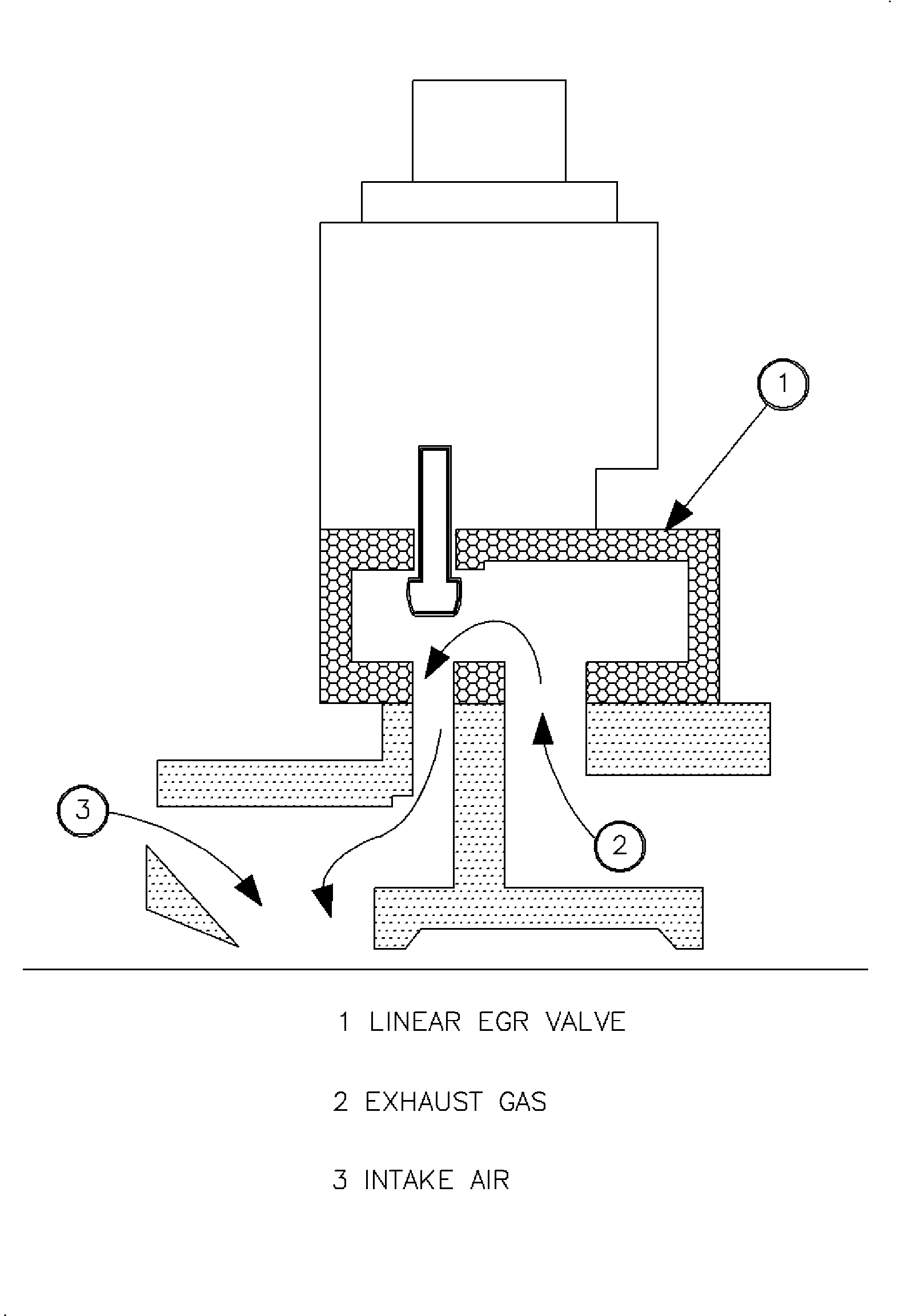
The PCM monitors the internal EGR valve solenoid (DTC P0403 and P1403)
and position sensor (DTC P0405 and P01404) for low and high voltage faults.
The PCM also monitors the EGR valve for a closed position error (P1404) and for a
rational check of the valve position (P0404). A rational check of the valve position
ensures the commanded duty cycle percent the PCM is commanding correlates to a correct
position the sensor is indicating.



