The following definitions are being provided to establish a common language and assist the user in describing transaxle related conditions. Some of these terms or conditions are used in this service manual.
Shift Control Related
Binding: A shift condition where a driver feels resistance/light friction when shifting into gear.Cable drag: A kink or bend in the cable that results in rough or binding shift feel.
Cold gear clash: A grinding/growling sound that is made when attempting to shift into gear during cold conditions.
Double bump: A shift condition where a driver experiences two separate peak loads when shifting into gear.
Gear clash/grinding: A grinding/growling sound that is made when attempting to shift into gear. Usually caused by a worn blocker ring or blocker ring spring.
Gear rattle: A rattle that usually occurs at the engine lugging conditions or low idle speeds with he transaxle in neutral and the clutch engaged.
Hard shift (dynamic/engine running): Difficulty in shifting when the vehicle is in motion.
Hard shift (static/engine OFF): Difficulty in shifting when the vehicle is not moving.
Hop-out: A condition where the transaxle will consistently disengage from the gear without operator assistance.
Intermittent hop-out: A condition where the transaxle will periodically disengage from the gear without operator assistance.
Spline lock: A "scallop" feature machined alternately in the internal spline of the synchronizer sleeve designed to engage with the gear, clutch teeth, to prevent hop-out.
Clutch/Clutch Hydraulics Related
Clutch shudder: A repeated jerking sensation caused by the slipping and grabbing of the clutch disc when releasing the clutch/launching the vehicle.High pedal effort: When an unusual amount of force is required to depress the clutch pedal.
Pedal vibration: A vibration that is transmitted through the clutch pedal.
Spongy clutch: A spongy feel when depressing the clutch and usually an indication of the air in the hydraulic system.
Squeaky clutch: When a squeak is generated while depressing or releasing the clutch pedal.
Inoperative clutch: A non-functional clutch.
High engage point: A long clutch pedal travel during pedal release before the clutch disc engages.
Noise Conditions
Final drive noise: A howl/whine related to the vehicle speed and is noticeable in all gears.Gear noise: A whine that is due to the gear contact that is related to a certain gear and vehicle speed. The noise disappears after an upshift. The nose is usually "gear profile" related.
Gear clicking noise: Ticking noise observed on every rotation of a gear pair that is usually caused by a "nick" or "ding" on a gear tooth.
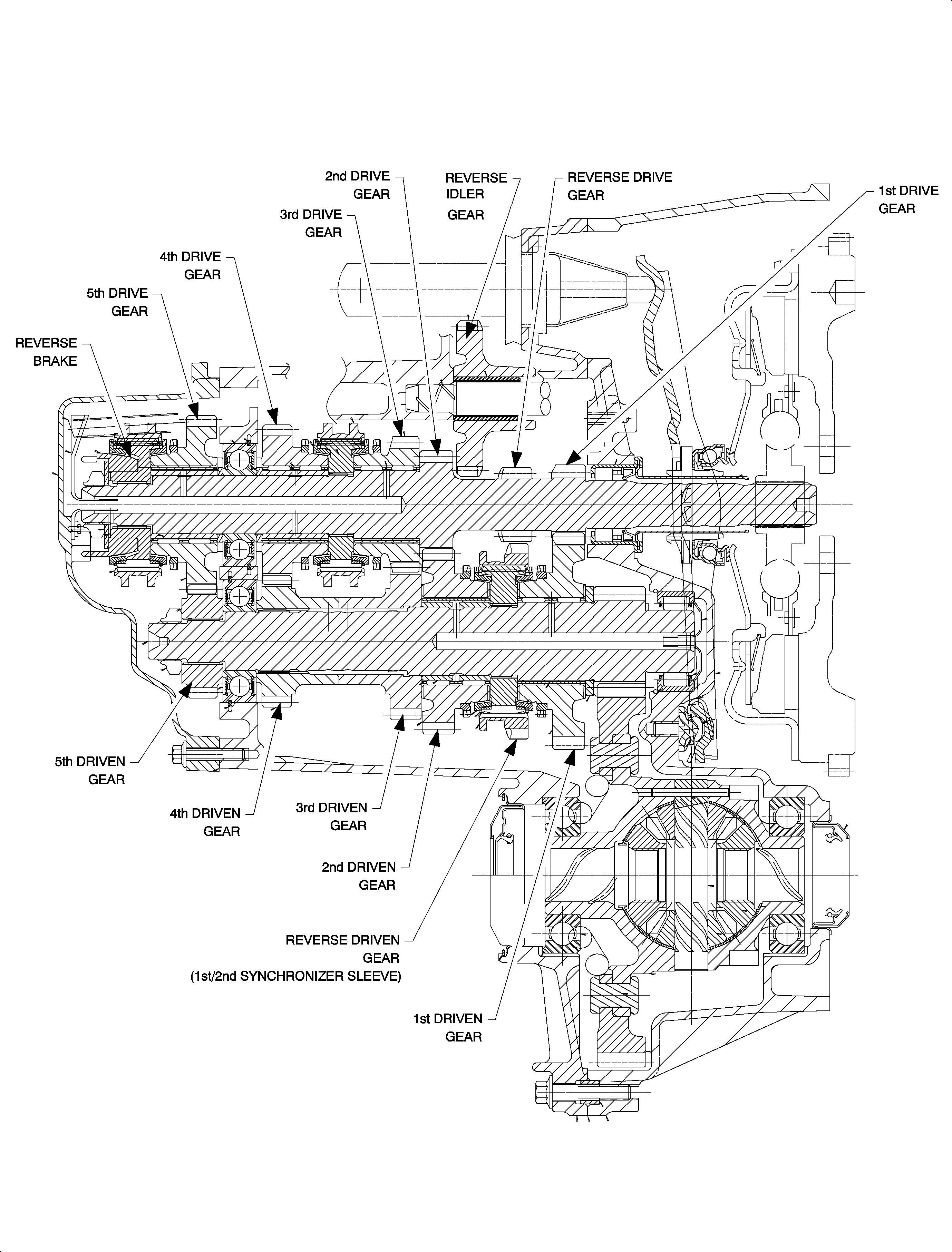
The five-speed manual transaxle assembly consists of a differential unit and a constant-mesh design transaxle in a single case. All forward gears are in constant mesh. Synchronizers with blocker rings, controlled by shift forks, are used for ease of shifting and selection of the desired gear range. A sliding idler gear arrangement is used for reverse.
All of the fundamental components, including aluminum transaxle case, aluminum clutch housing, input shaft, output shaft, and the differential assembly, are supported by ball and roller bearings. No pre-load of the bearings is required.
Lubrication Flow
A common sump supplies oil for the manual transaxle. When the manual transaxle is operating normally, the differential assembly splashes the oil form the sump to provide lubrication. The splashed oil is collected in an oil trough. The oil travels down the trough and into the cover assembly. The cover assembly feeds the oil into the input shaft and the oil is supplied to the 3rd, 4th, and 5th drive gear bearings through internal passages in the input shaft. The designated oil is Saturn Transaxle Fluid.
Power Flow
Neutral: In neutral, with the engine running and the clutch engaged, the input shaft will turn. With the 1st/2nd, 3rd/4th, and 5th synchronizers in a neutral position, power will not flow to the output shaft.1st Gear: In 1st gear range, the 3rd/4th and 5th synchronizers are in neutral and the 1st/2nd synchronizer sleeve is moved to the right to engage the 1st speed blocker ring and the 1st gear. Because the 1st/2nd synchronizer hub is splined to the output shaft, torque is transmitted from the input gear through 1st speed gear, the synchronizer sleeve and hub, the output shaft, and into the differential, final drive, assembly.
2nd Gear: In 2nd gear range, the 3rd/4th and 5th synchronizers are in neutral and the 1st/2nd synchronizer sleeve is moved to the left to engage the 2nd speed blocker ring and the 2nd speed gear. With the 1st/2nd synchronizer hub splined to the output shaft, torque is transmitted from the input shaft through 2nd speed gear, the synchronizer sleeve and hub, the output shaft, and into the differential, final drive, assembly.
3rd Gear: In the 3rd gear range, the 1st/2nd and 5th synchronizer sleeves are in a neutral position, and the 3rd/4th synchronizer sleeve is moved to the right to engage the 3rd speed blocker ring and the 3rd speed gear. With the 3rd/4th synchronizer hub splined to the input shaft, torque is transmitted form the input shaft through the synchronizer hub and sleeve, the 3rd speed gear, the output shaft, and into the differential, final drive, assembly.
4th Gear: In 4th gear range, the 1st/2nd and 5th synchronizers are in neutral and the 3rd/4th synchronizer sleeve is moved to the left to engage the 4th speed blocker ring and the 4th speed gear. With the 3rd/4th synchronizer hub splined to the input shaft, torque is transmitted from the input shaft through the synchronizer hub and sleeve, the 4th speed gear, the output shaft, and into the differential, final drive, assembly.
5th Gear: In 5th gear, overdrive range, the 1st/2nd and 3rd/4th synchronizers are in a neutral positions and the 5th speed synchronizer hub splined to the input shaft, torque is transmitted from the input shaft through the synchronizer hub and sleeve, the 5th speed gear, the output shaft, and into the differential, final drive, assembly. The unit is now in overdrive.
Reverse: In reverse gear range, all synchronizers are in the neutral position. The reverse idler gear is moved to engage the drive gear on the input shaft and the external teeth on the 1st/2nd synchronizer sleeve. Torque is now transmitted form the input shaft through the reverse idler gear, 1st/2nd synchronizer sleeve and hub, the output shaft, and into the differential, final drive, assembly. To ease reverse engagement, the 5th/Reverse brake synchronizer is instantaneously engaged before the reverse shift is completed to decelerate the rotational speed of the input shaft.
Input Shaft Turning | Output Shaft Turning | Rev Idler Turning | |
|---|---|---|---|
In Neutral Clutch Disengaged | No | No | No |
In Neutral Clutch Engaged | Yes | No | No |
In 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th | Yes | Yes | No |
In Reverse Vehicle Moving | Yes | Yes | Yes |
The following conditions apply when the input shaft only is moving:
| • | 1st drive and 1st driven gears moving |
| • | 2nd drive and 2nd driven gears moving |
| • | Reverse drive gear moving |
| • | All remaining gears including the differential are stationary. |
| • | Input shaft moving over caged bearings and case bearings |
The following conditions apply when the output shaft only is moving:
| • | 2nd drive and 2nd driven gears moving |
| • | 3rd drive and 3rd driven gears moving |
| • | Differential is moving |
| • | 1st drive and 1st driven gears moving |
| • | 5th drive and 5th driven gears moving |