Metric Fasteners
Saturn, along with other North American Industries have adopted portions of standard metric fastener sizes defined by the International Standards Organization (ISO). The ISO standards were adopted to reduce the number of fastener sizes while retaining the best strength qualities in each thread size. For example, the common 1/4 - 20 and 1/4 - 28 screws are replaced by the metric M6 x 1 screw which has nearly the same diameter. The thread pitch is between common coarse and fine thread pitches.
Fastener Head Descriptions And Drive Style
Head Descriptions
The following descriptions and illustrations cover the typical head types and drive styles used on the Saturn vehicle:
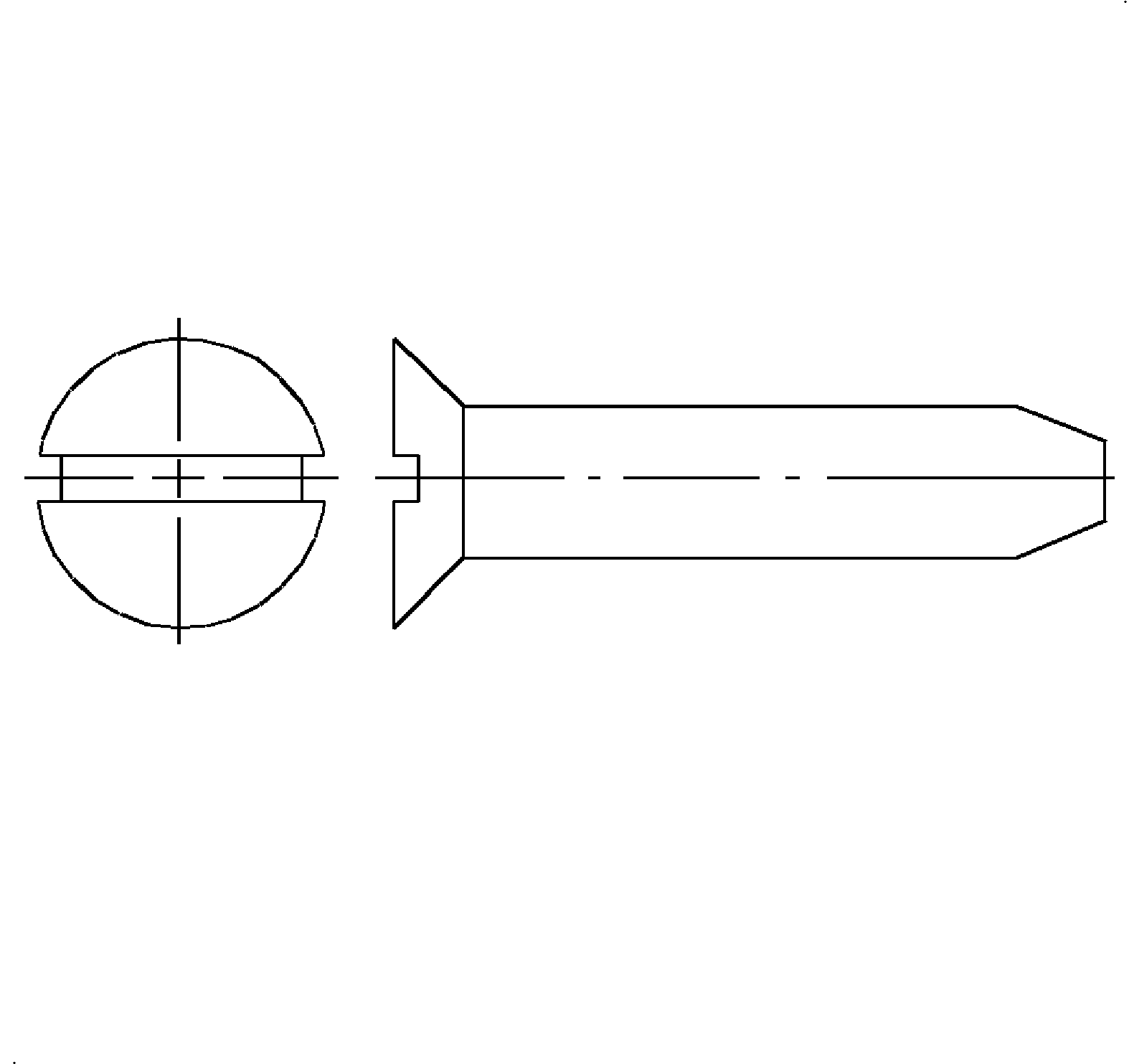
- Flat Head - Flat head screws have a flat surface and a conical (cone shaped) bearing surface. This fastener is used where a flush finish surface is required.
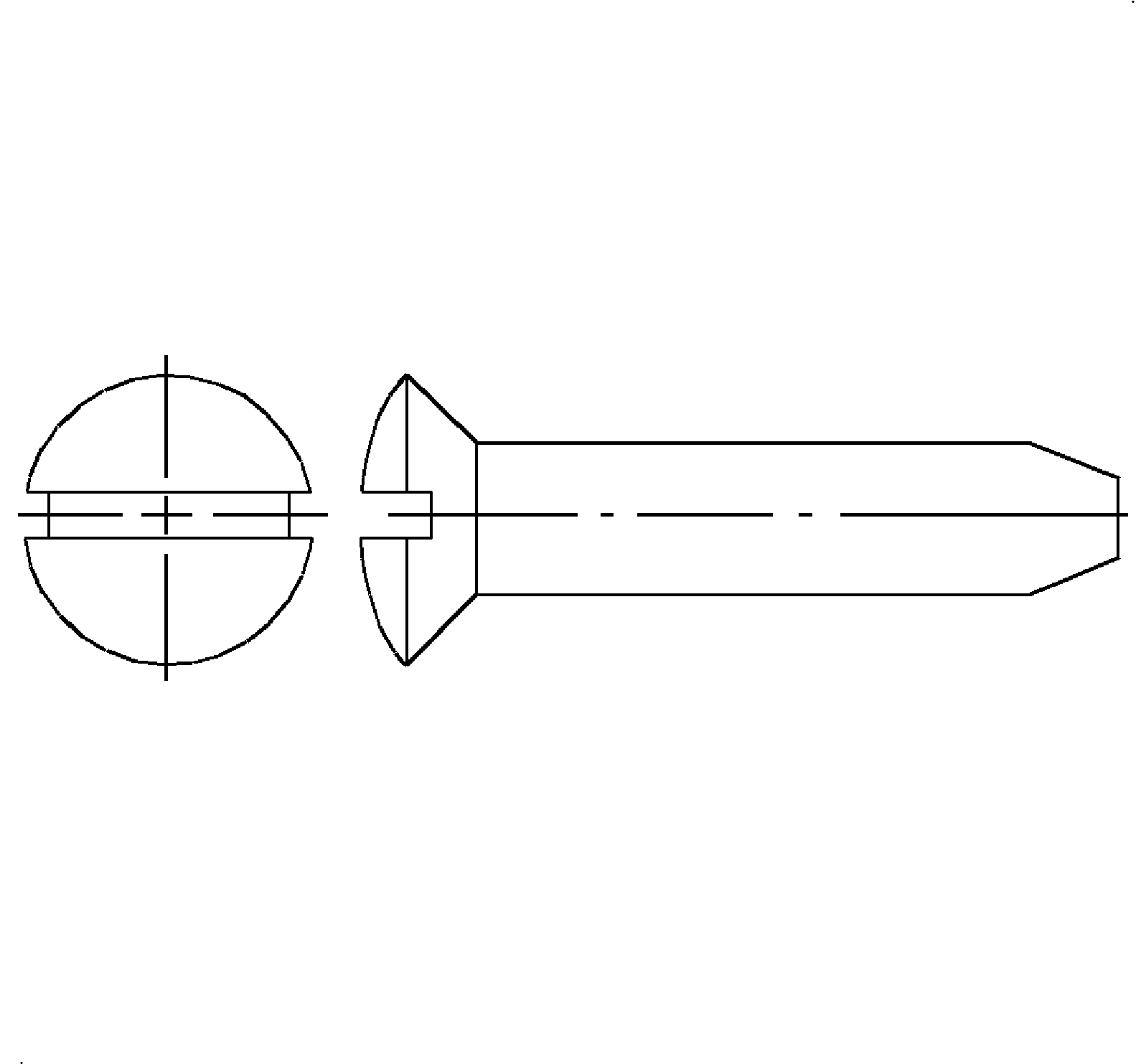
- Oval Head - The surface of this screw is rounded for attractiveness and the bearing surface is conical.
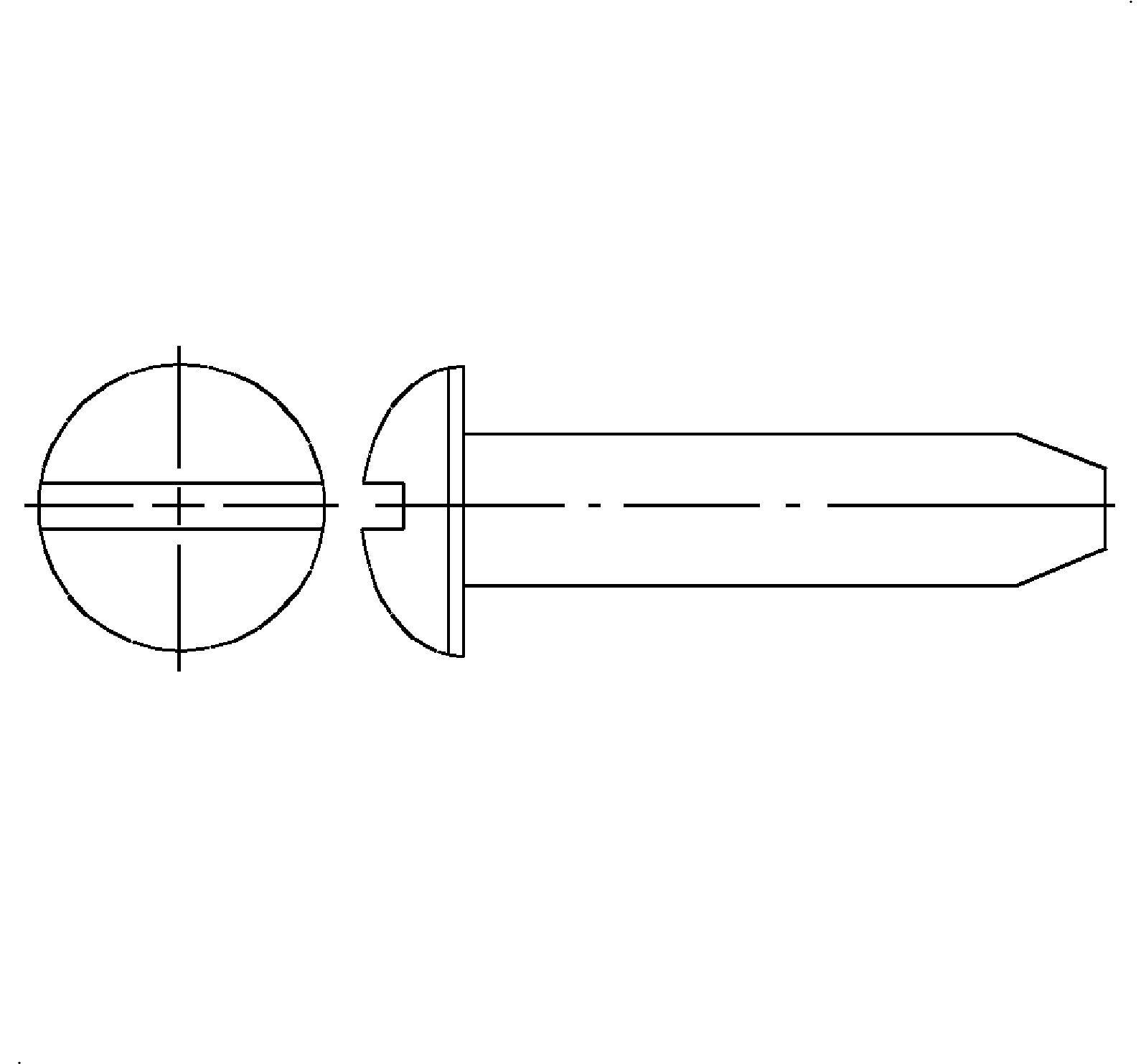
- Pan Head - Slotted pan heads have a flat top surface rounded into cylindrical sides and a flat bearing surface. Recessed pan heads have a rounded top surface blending into cylindrical sides. Both have excellent driving characteristics. It is recommended that pan head screws be used instead of round and truss head screws in all new engineering designs.
- Fillister Head - Fillister head screws have a rounded top surface, cylindrical sides and a flat bearing surface. They are among the more costly screws but are ideal for counterbored holes and minimum clearance applications.
- Truss Head - Truss heads have a neat, low profile rounded top surface, larger than that of a corresponding size round head. This screw is excellent for covering oversize clearance holes. However, they are rather costly because of the difficulty of manufacture. They are also more subject to ruptures at the juncture of the head and shank.
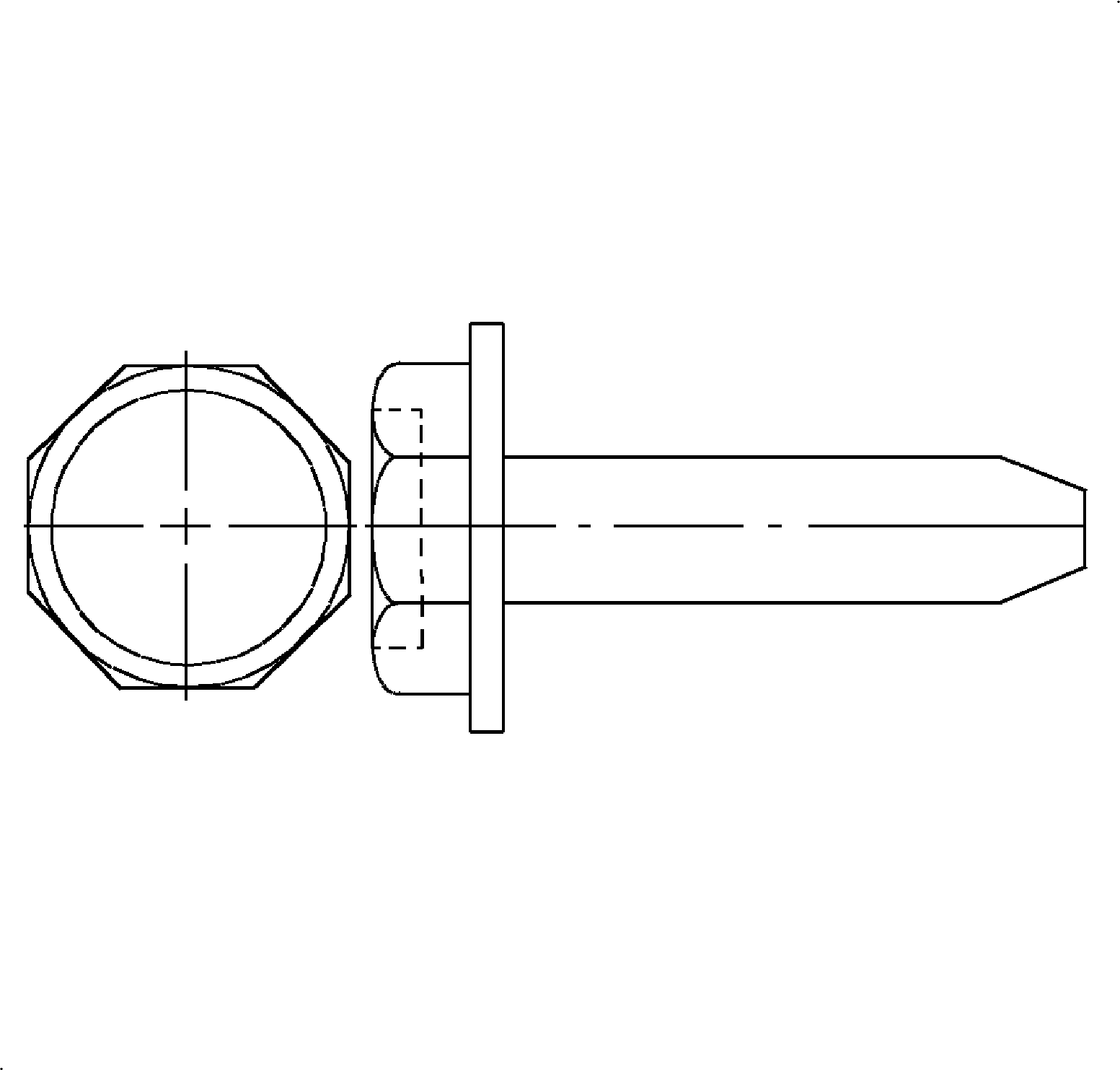
- Hex Head - Hex heads have a flat or intended top surface, six flat sides for wrenching and a flat bearing surface.
- Hex Washer Head - Hex washer heads have an indented top surface with six flats formed integrally with a flat washer to protect a finished surface from wrench marks and provide a larger bearing surface.
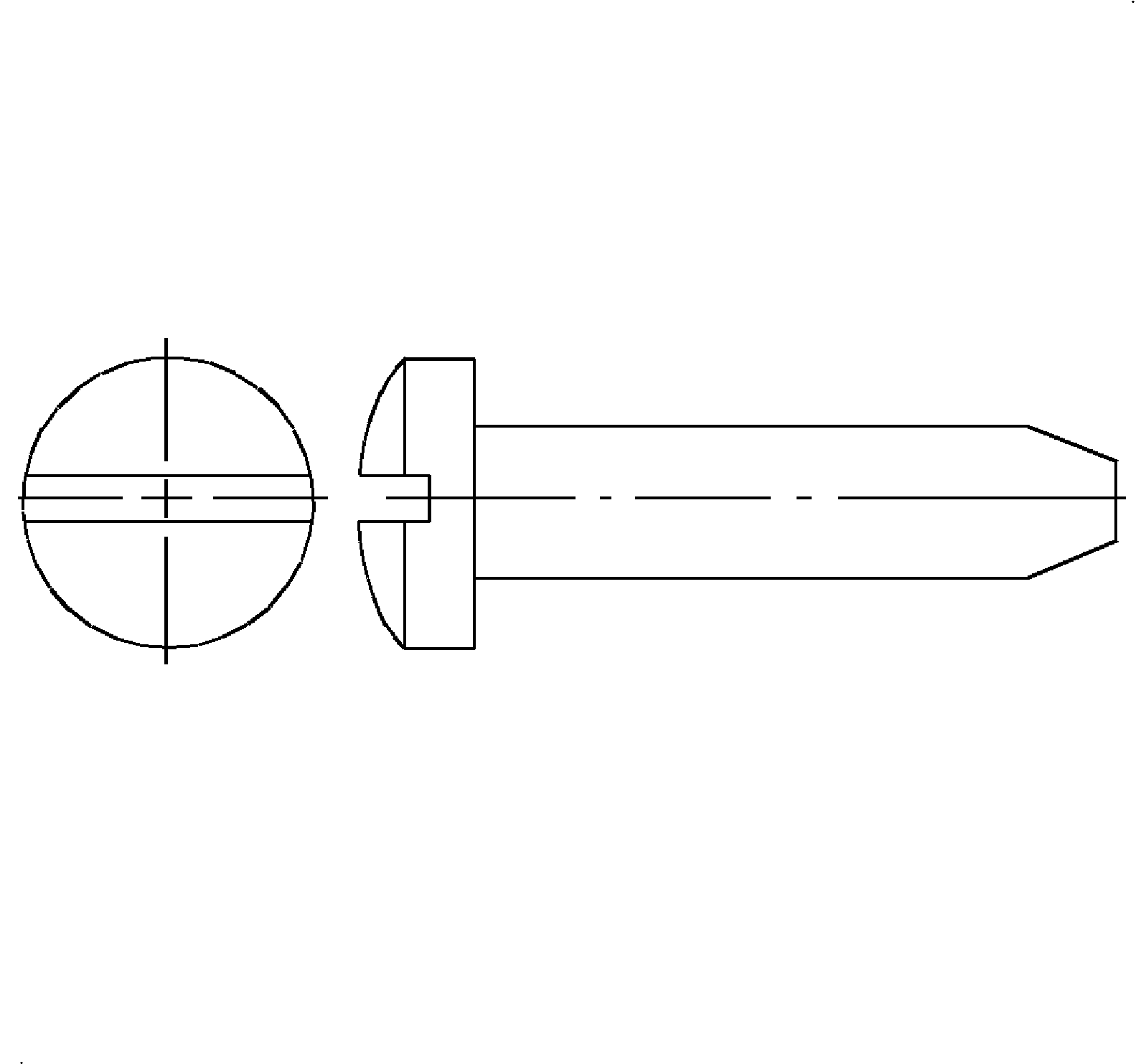
- Round Head - Round heads are general purpose screws with a semi-elliptical top surface and a large, flat underhead bearing surface.
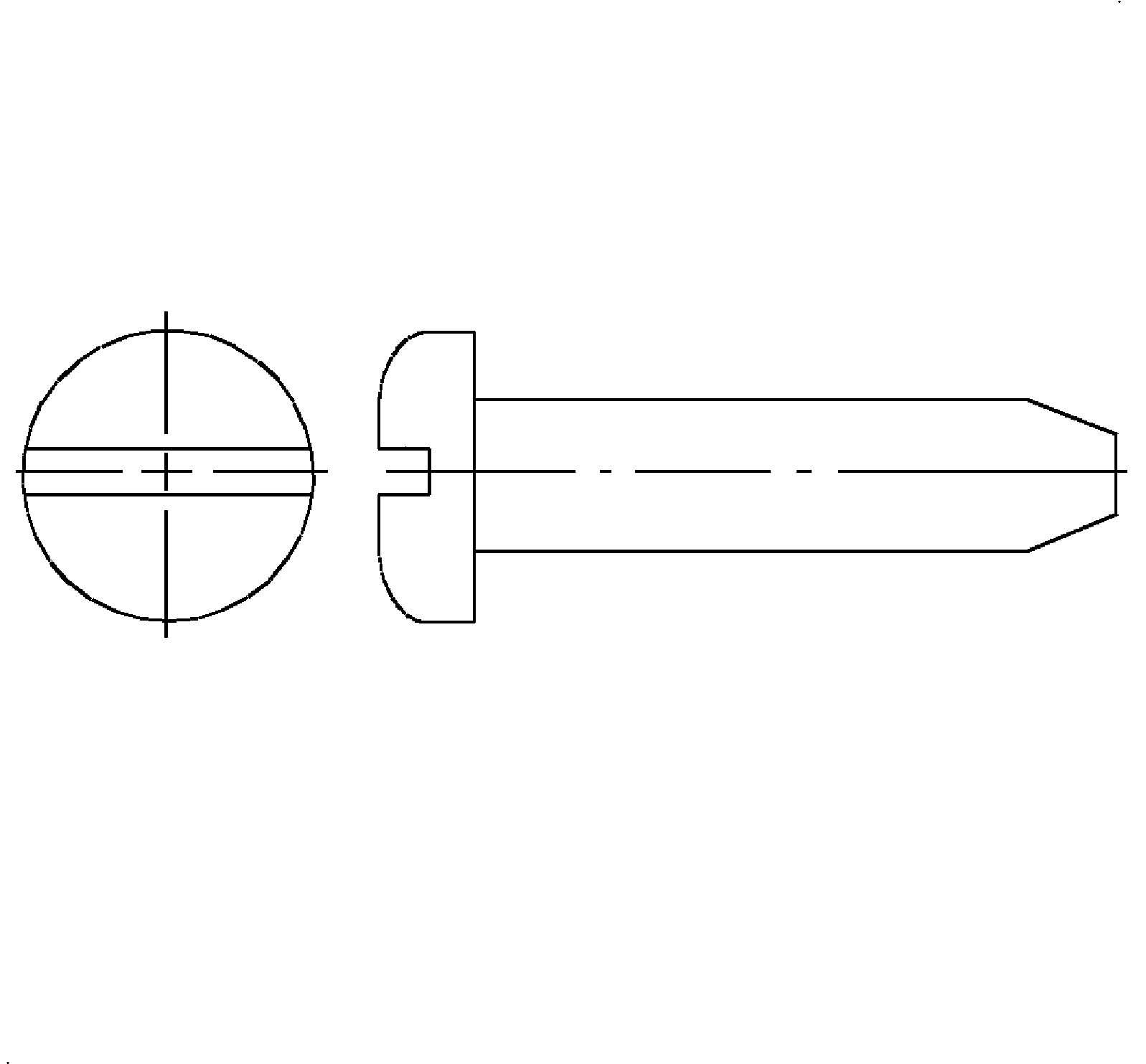
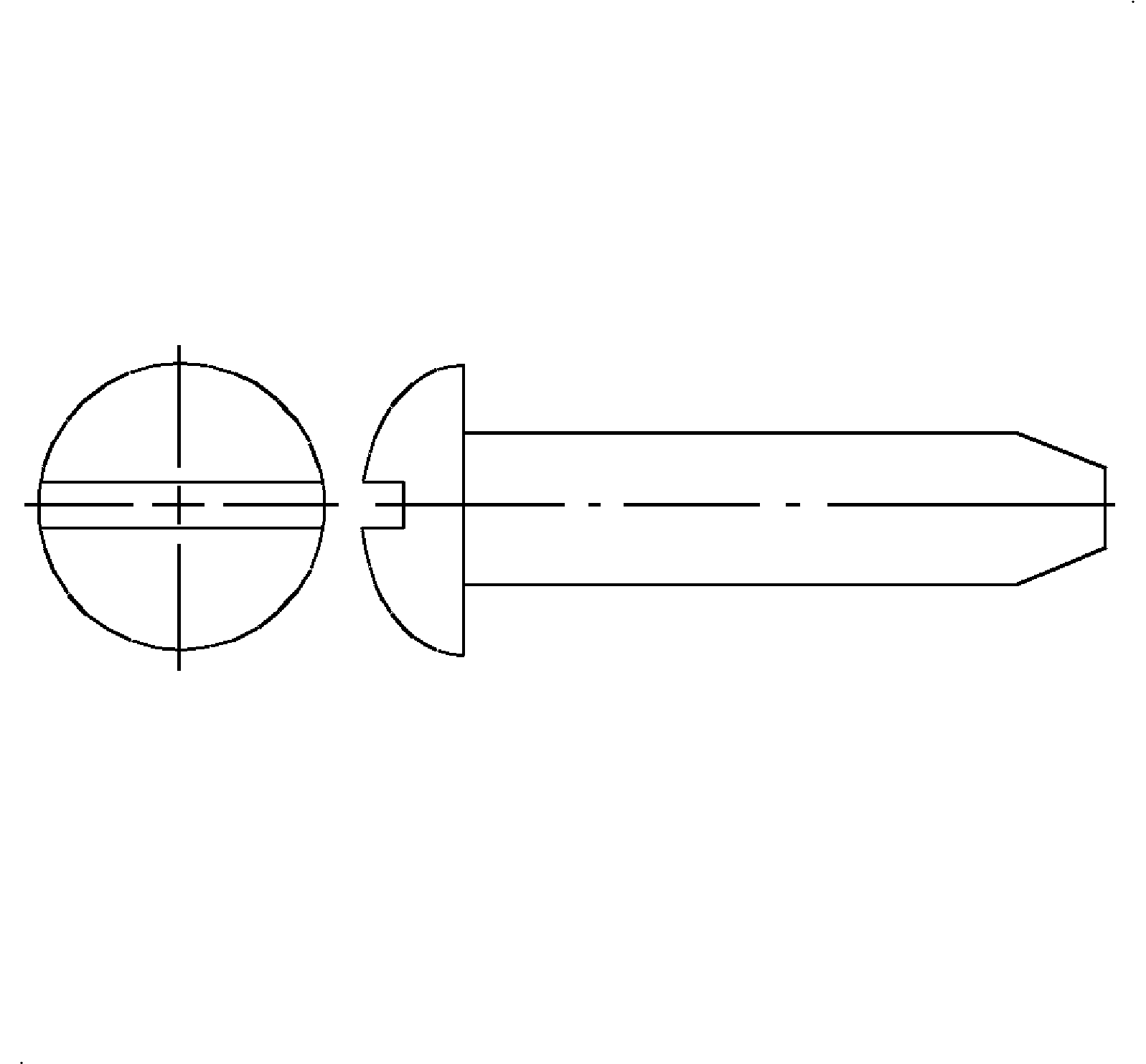

Drive Styles
Drive Styles are standardized by torque, production and tooling requirements, and for appearances, etc.
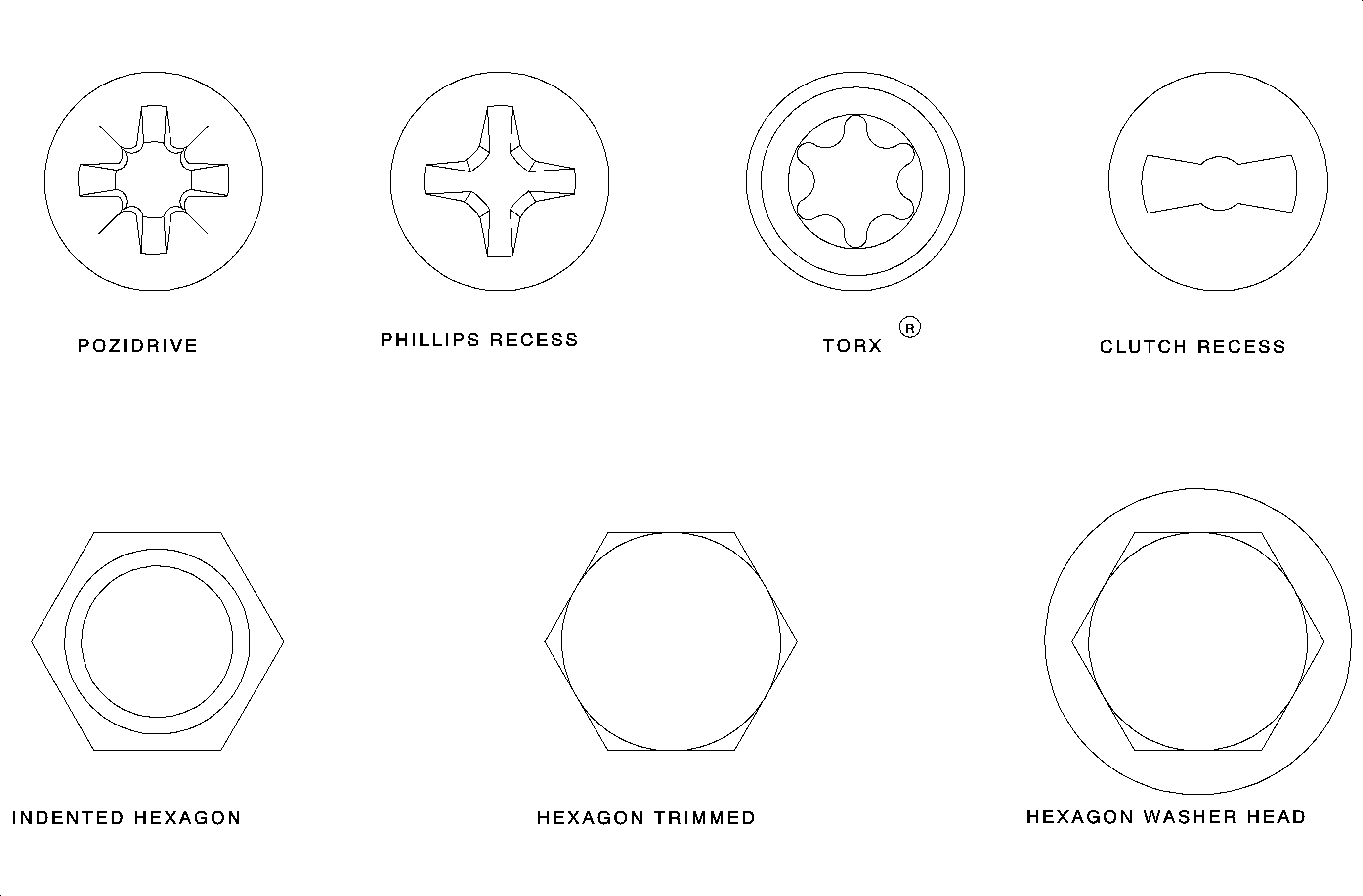
- Pozidrive - The Pozidrive is similar to Phillips, but with grooves in the four inside corners of the recess for a greater area of positive engagement. Pozidrive accepts extremely high torque without cam-out. It should be used with a torque limiting drivers. Pozidrive is an internally driven fastener.
- Phillips Recess - The Phillips is cross recessed with steep sides and cone-shaped bottom. It accepts Phillips screwdrivers. Phillips screws are used in high torque applications to resist cam-out. Phillips is an internally driven fastener.
- Hexagon trimmed - The hexagon trimmed drive is a standard type of wrench-applied hex head. It has clean, sharp corners trimmed to close tolerances. Hexagon trimmed provides high torque wrenching for general commercial applications. It is available with or with out washer surface.
- Hexagon Washer Head - Hexagon washer heads protect surfaces from marring by wrenches, improves straight line driving and spans larger surfaces areas.
- Indented Hexagon - This is an economical wrench head fastener with standard hex head dimensions. They possess an identifying depression in the top surface of the head.
- Torx - Torx is a six - lobed design that offers maximum drive surface to the driver. It eliminates rounding off of corners common with hex shapes. Torx completely eliminates cam-out and end loading. It is available as a recessed or raised head design and also as internally or externally driven design.
- Clutch Recess - Clutch recess is a non-tapered recess which gives skid proof straight driving without cam-out.
Fastener Point Description and Preferred Uses
Machine Screw Point Styles
- Header Point - A standard point on most bolts. The point is partially blunt and has very little thread lead-in (full threads start almost immediately ). Because of the limited lead-in, header pointed fasteners have a high probability of cross threading during manual assembly. Header points are generally used on fixtured automated equipment where bolt-to-nut to tapped hole alignment is strictly maintained without causing a cross threading problem.
- Dog (Pilots) Point - This point is unique in that it offers both joint alignment help and reduction of cross threading. Dog points should be specified for manually assembled joints, joints required awkward assembler positioning for fastener installation and joints that have high repair costs is assembled materials are stripped or damaged.
- Rolled Point (Type AC) - this point is fully threaded to provide positive starting of poorly aligned mating treads.
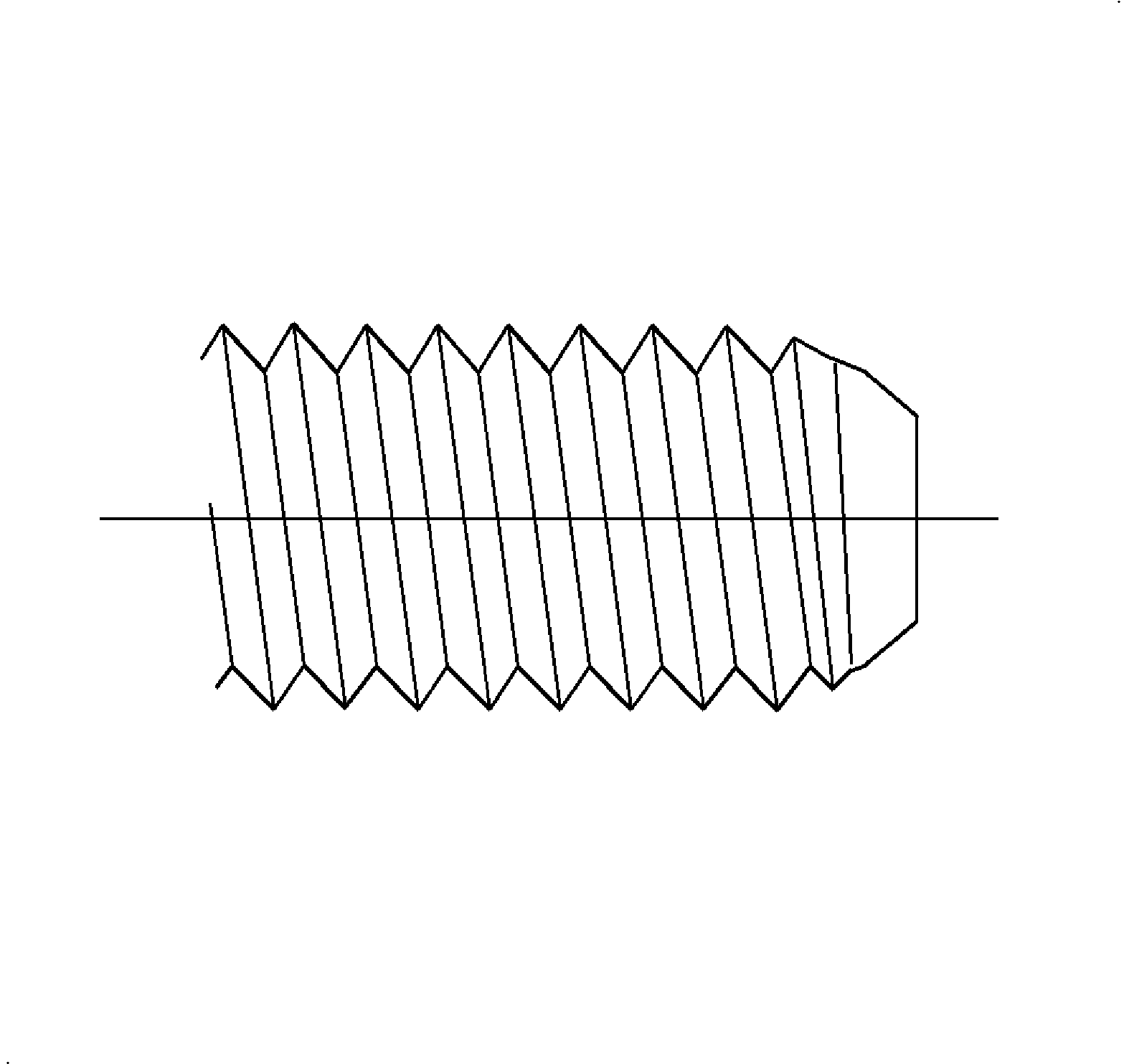
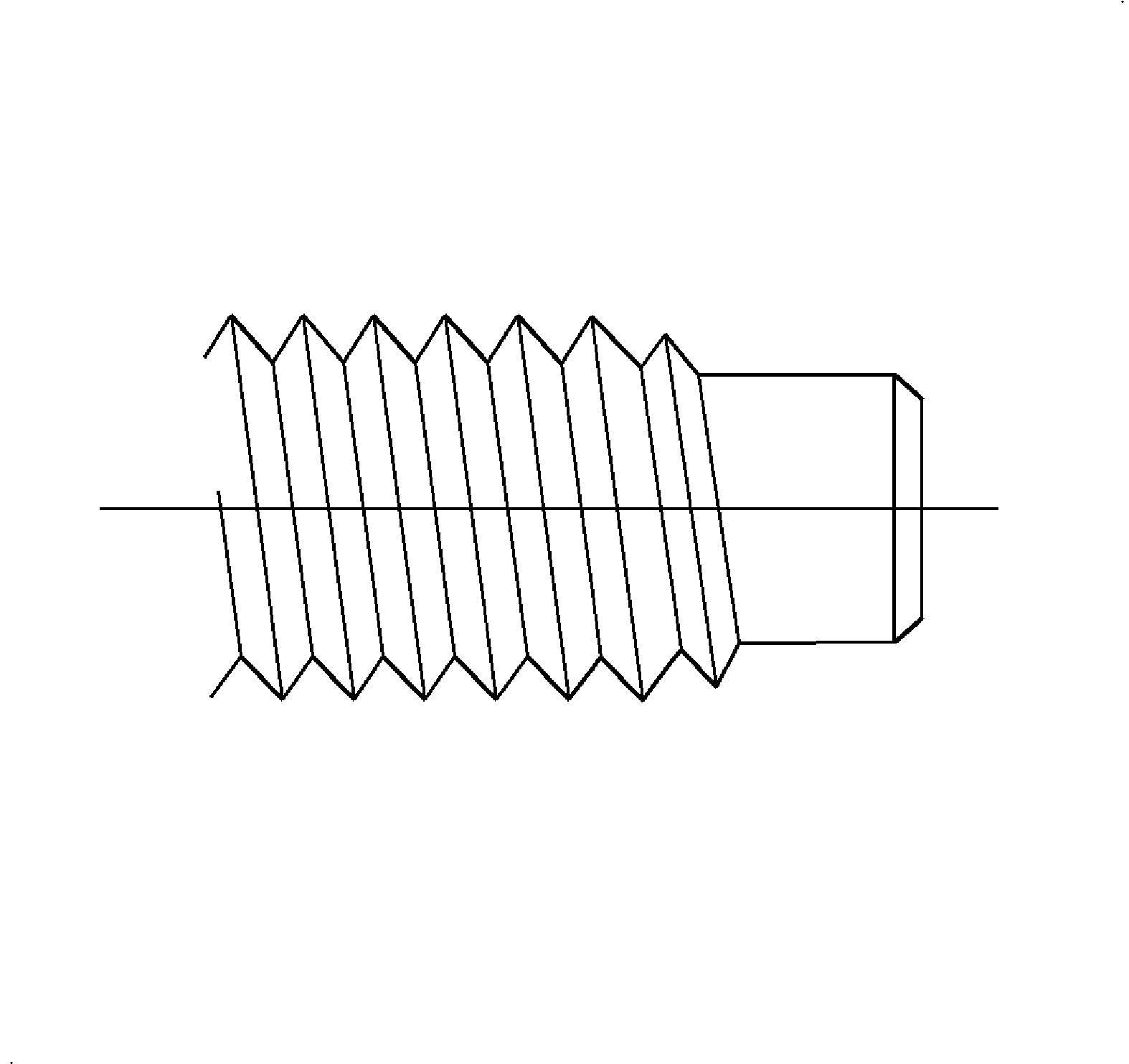
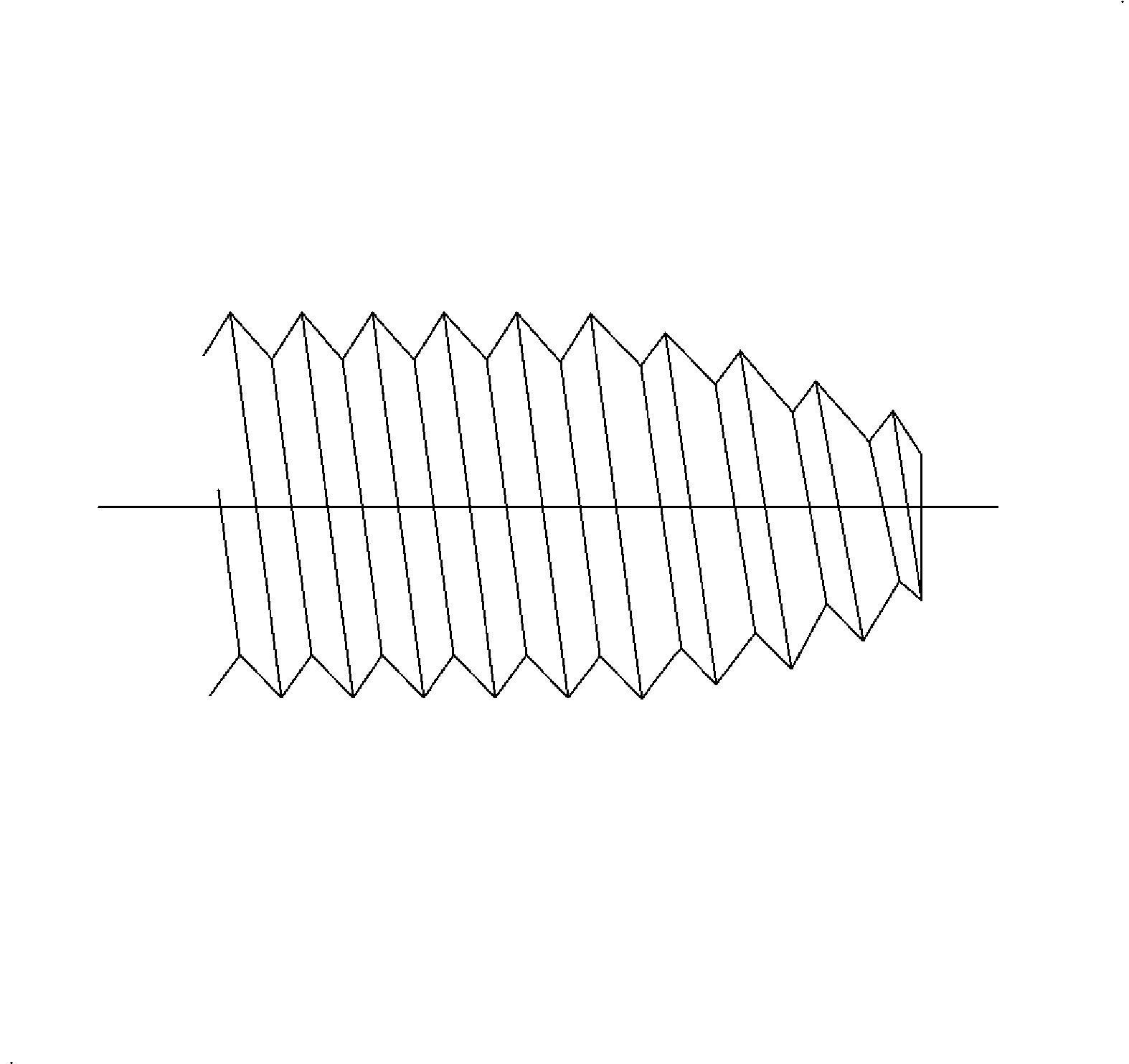
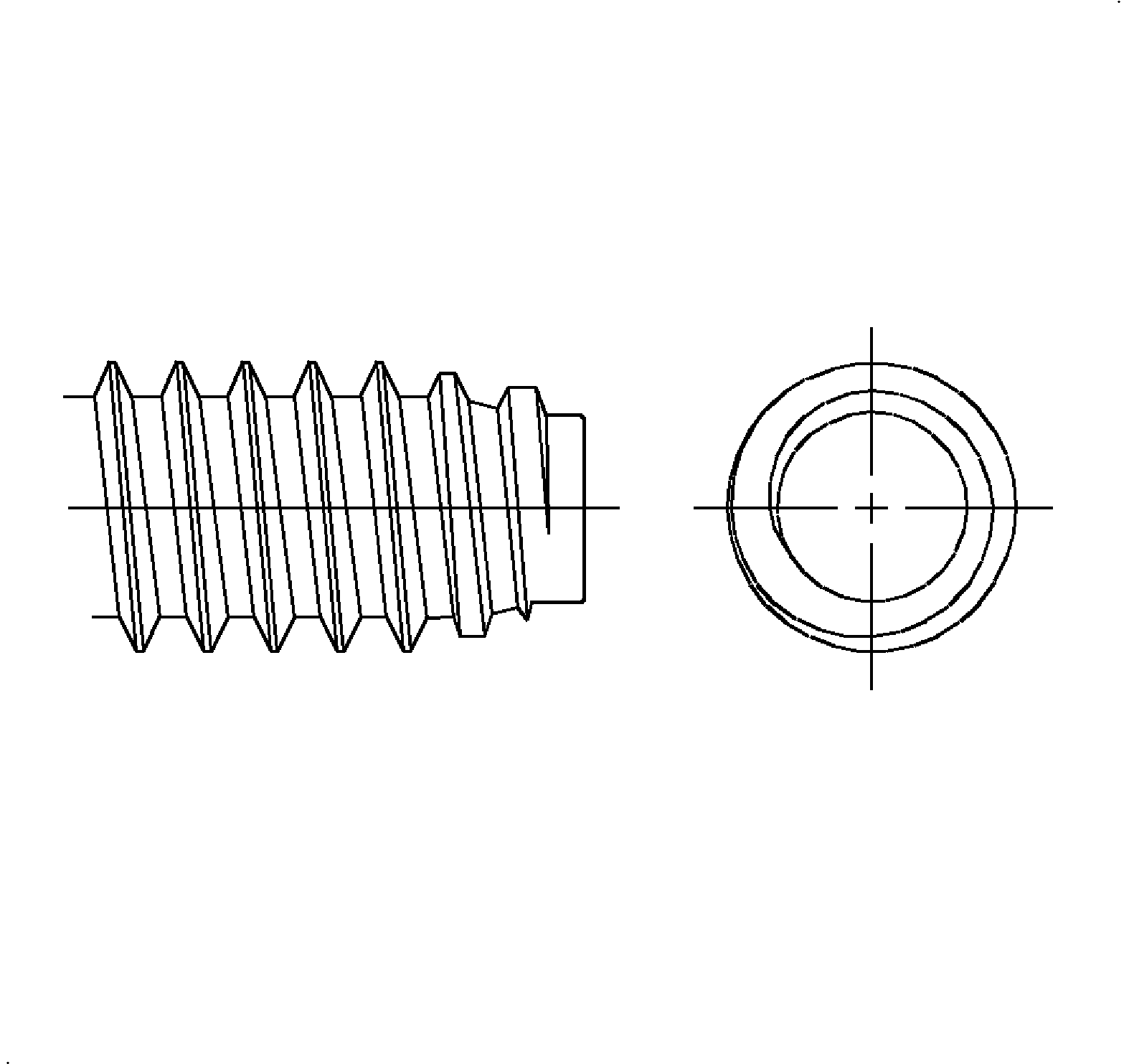
Tapping Screws
- Type AB Points - Type AB has a gimlet point (pointed with threads to the end of the screw). It is thread forming and forms its own threads into pilot holes in sheet metal, plastics and formed embossments in spring nuts.
- Type B Screw - Type B screw has a blunt and tapered point. This design is thread forming and forms threads into pilot holes in sheet metals and into formed embossments in spring nuts where the sharp gimlet point on the Type AB screw is objectionable. It is also used into pilot holes in nonferrous castings and plastics.
- Type BSD Screw - Type BSD screw is a drill screw and has a tapered entering thread. It is thread forming after drilling a pilot hole in sheet metals having a thickness compatible with the length of drill point.
- Type TR Screw - Type TR screw has a blunt, tapered, sharp crested entering thread. TR forms threads into pilot holes in heavy sheet metals, die casting, cast iron and copper alloys.
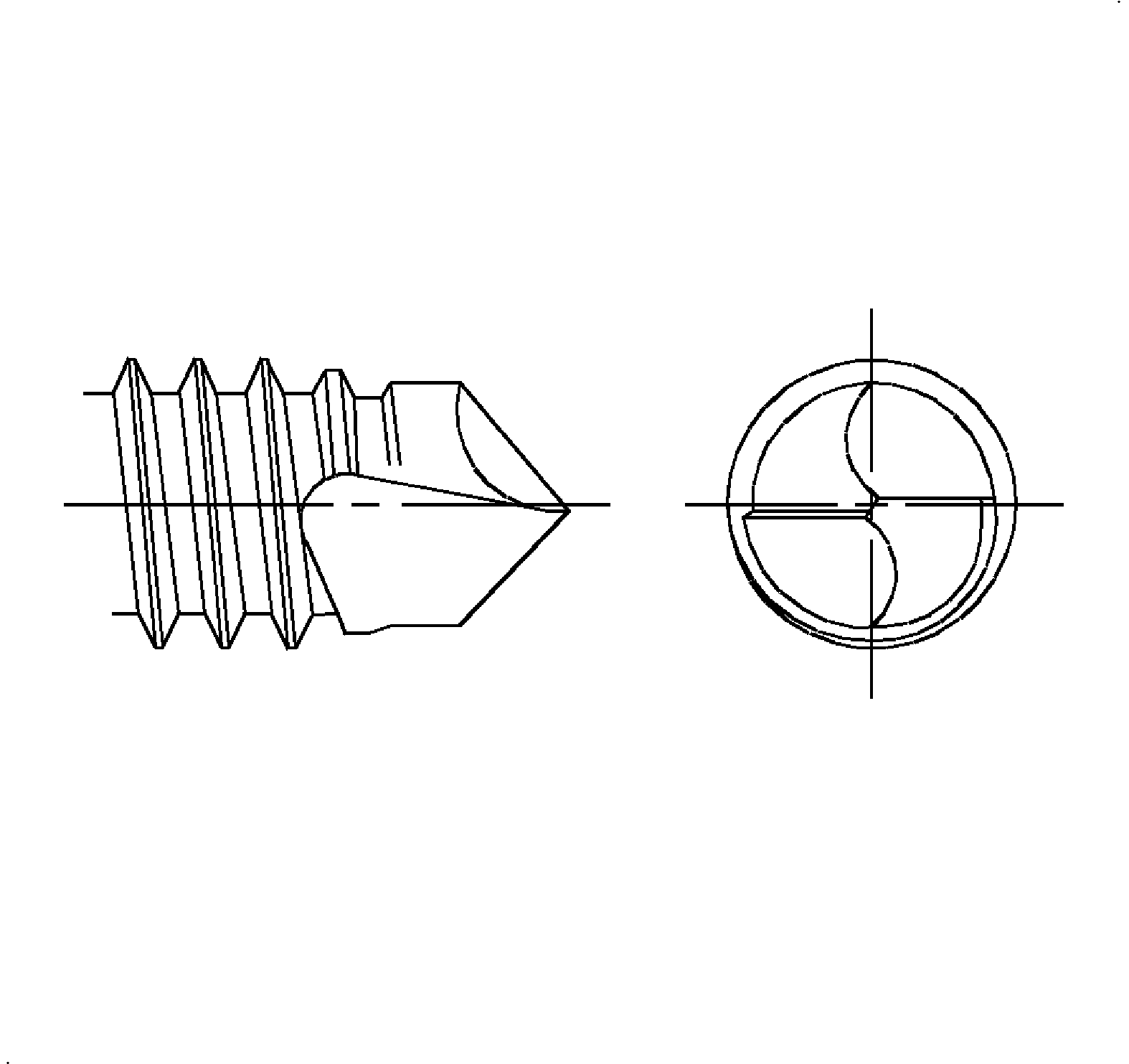
Fastener Strength Information
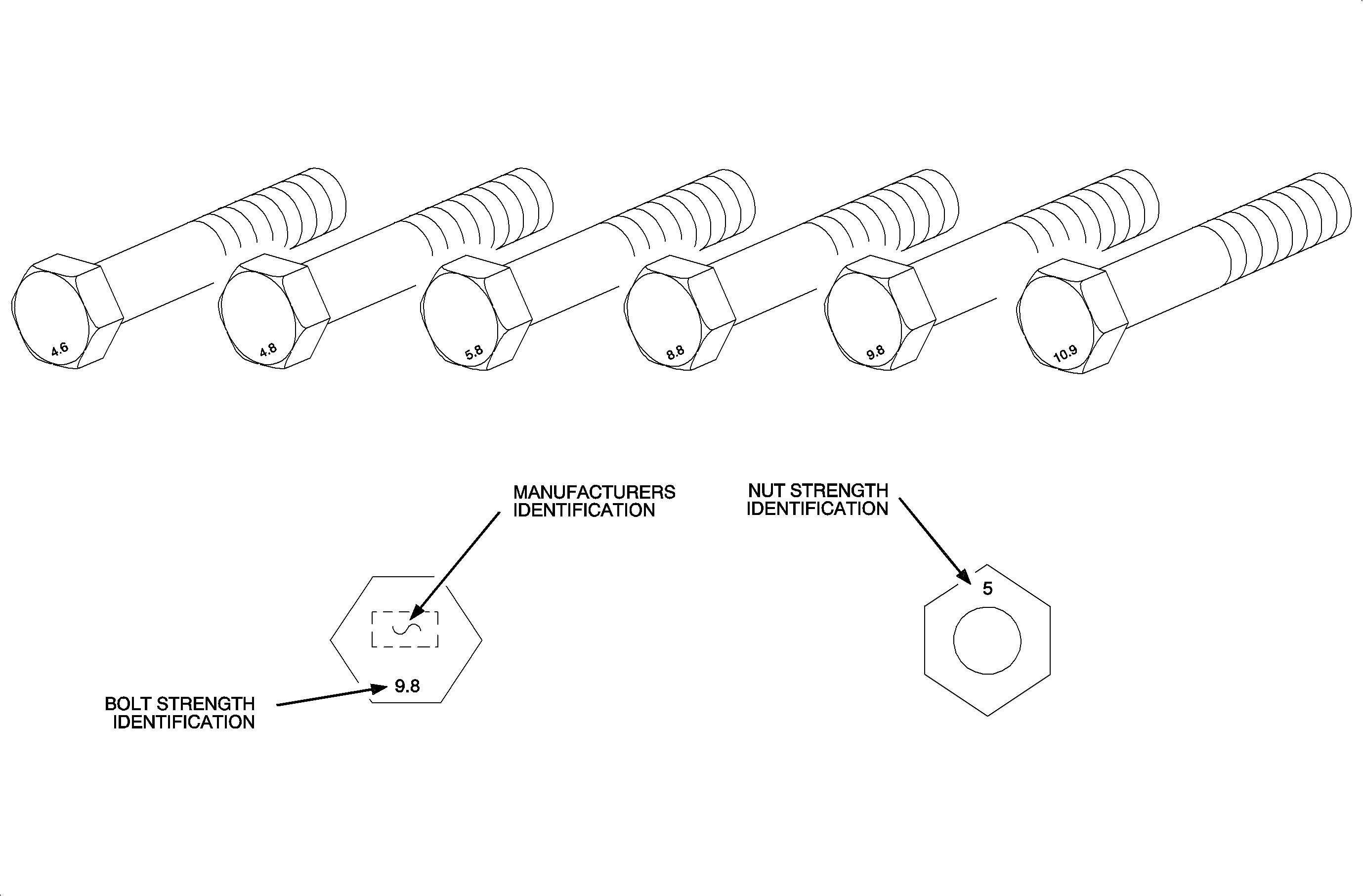
Most commonly used metric strength property classes are 9.8 and 10.9 with the class identification embossed on the head of each bolt. Some metric nuts are marked with strength identification numbers on the nut face. It is extremely important to select replacement fasteners that are designed for the application. Each fastener has been selected to meet performance goals for each joint. The fastener strength, diameter, thread pitch, finish, length, head type and diameter are equally important variables. Any deviation from the specified replacement part could jeopardize integrity.
Saturn Service Parts Organization (SSPO) is a supplier of high quality original equipment replacement fasteners for the Saturn vehicle. If fasteners are purchased from after market suppliers, they must also possess the stringent quality requirement for use on the Saturn vehicle.
Platings - Friction, Grounding And Corrosion Characteristics
Plating
Plating is the application of a metallic deposit on the surface of a fastener by electrolysis, impact or painting. Fastener engineering must consider many plating variables during the fastener design/selection process. These variables include friction, grounding and corrosion characteristics.
Plating friction characteristics include any variable that contributes to torque. Finishes such as zinc are very efficient (slippery) and therefore need lower torque to achieve maximum clamp load. Other finishes such as organic phosphates are very inefficient and therefore need higher torque to achieve similar clamp loads compared to the zinc finishes.
Once a finish has been selected for fastener, test lab evaluations are conducted to determine the torque specification for the joint. Once this specification is determined to be adequate for the application, it is then published in the service manual. If the technician was to replace the fastener with a finish or plating that was not tested, it is very possible the joint could be either under torqued or over torqued which could cause joint failure. Replacement fasteners should be Saturn approved for the specific application.
Electrical Grounding

Electrical grounding specifications on fasteners are required when the fastened component has a grounding requirement. In many attachments, fasteners are the only way to insure proper grounding of the electrical component and therefore any improper substitutions could cause component failure.
Saturn fastener engineering recommends that all electrical attachments should have a finish of GM-4345M (Code 12U96/0 which is a 12 micrometers zinc). This finish was selected because of its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. If electrical grounding fasteners become corroded and are removed, they must be replaced. Undisturbed corroded fasteners typically have a good ground. Any fasteners that are replaced and are intended to have grounding potential, must be replaced with a fastener coated with GM-4345M to insure proper grounding.
GM-4345M finish can be identified by a silver or gold high luster finish. If in doubt, measure the resistance of the fastener to verify that there is zero resistance.
Fasteners, both stud and bolts, that are used for grounding in conjunction with ring terminals must follow specific Saturn guidelines for proper grounding.
Corrosion
Corrosion protection has never been more important in the automotive industry that it is today. With customer satisfaction being number one priority, much emphasis has been put on exotic finishes that will enhance the life of metallic parts. Fasteners are no exception. Saturn is specifying platings and finishes for fasteners that have proven long term corrosion resistance. Not only will corroded fasteners cause an appearance problem, but in time, corrosion of the fasteners will weaken the structural integrity of the joint.
The majority of fasteners on the Saturn vehicle have a black organic phosphate finish unless a beauty appearance or grounding specification is required. After-Market replacement fasteners must have the corrosion resistance specifications as required by Saturn. Using Saturn original equipment replacement parts, guarantees the corrosion protection the customer deserves.
