Fuse blocks provide a home for mini and maxi fuses, relays, and electronic modules, eliminating the need for separate connections and mounting attachments. They are also a central connection point for major harnesses (Engine, Forward Lamp, I/P, and Body). Inside the fuse block are layered buss plates that help reduce the number of splices in the harnesses.
With the advances in automotive electronics over the past few years, the size and complexity of wiring harnesses have increased. The fuse blocks help remove complexity from the wiring assemblies and provide a central location for circuit protection devices and relays. Fuse blocks help reduce the complexity while also reducing cost and mass. This is accomplished by reducing the number of cut leads, eliminating the need for in-line connectors and splice packs. This also helps reduce the bundle size of a wiring harness.
Splice Packs
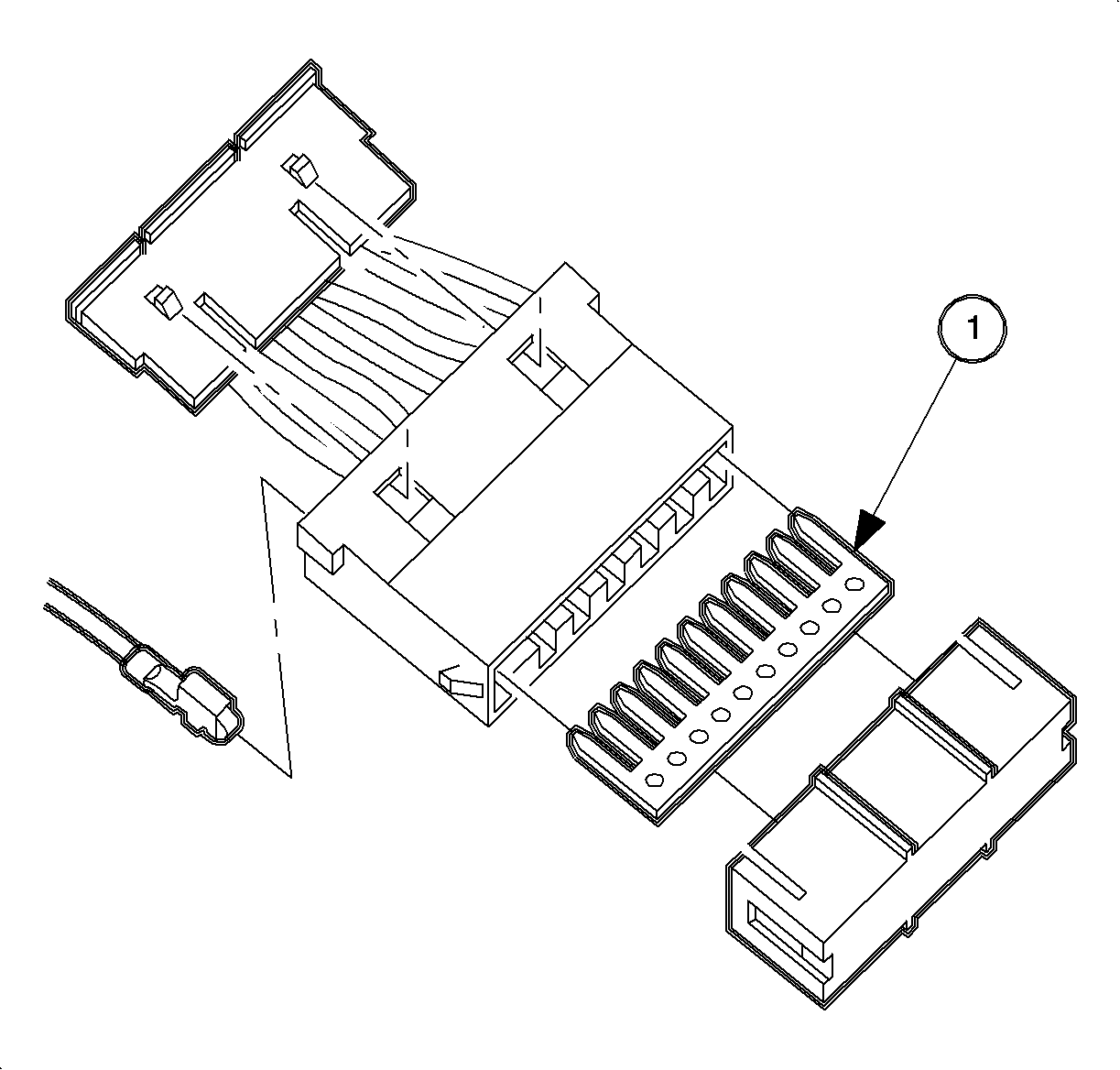
Important: Cavity references for slice packs on schematics may be different than the harness due to manufacturing constraints of the wire harness.
Splice packs are used to replace conventional soldering and clipped splices. The splice pack consists of a buss bar (1) with male blades that plug into a standard female crimp on terminal. A plastic cover is placed over the buss bar to insulate it from surrounding wires and the environment. This feature improves the reliability of splices.
Some of the grounding splice packs have an integral ring terminal as part of the buss bar. This way the splice pack can be directly connected to the vehicle body instead of using a wire to go from the splice pack to a ring terminal.
