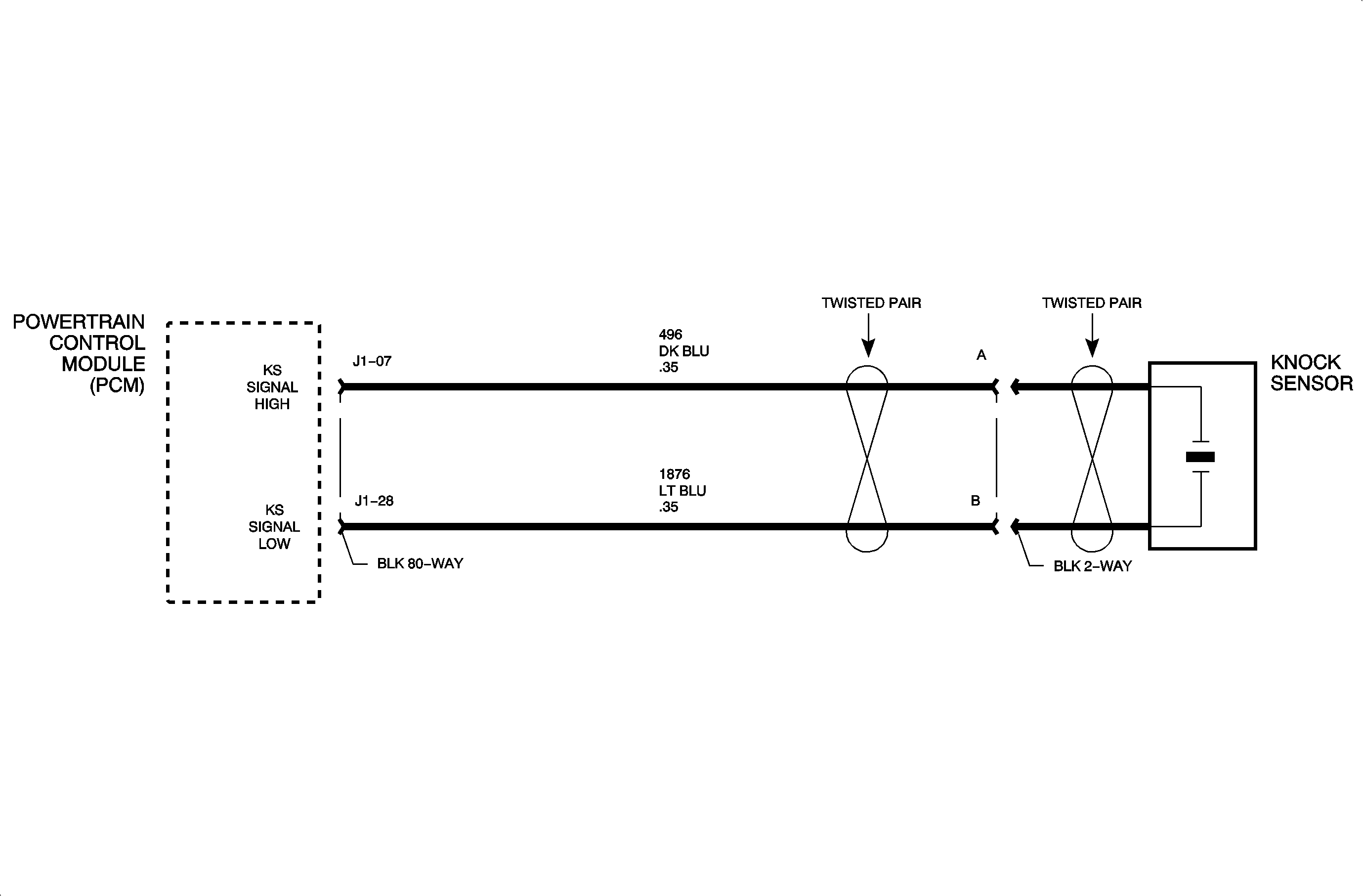
The knock sensor is a piezoelectric device that produces an AC voltage of different amplitude and frequency based on engine mechanical vibration. The amplitude and frequency are dependant on the level of knock the sensor detects. The powertrain control module (PCM) learns a minimum noise level at idle from the knock sensor and uses stored normal noise level calibration values for the rest of the RPM band. The knock sensor signal is only used during the top dead center combustion event of the firing cylinder. When in a combustion event, the PCM filters the knock signal and compares it to the normal calibration noise level for that RPM. If the PCM has determined that knock is present during the combustion event, it will retard timing on the next firing cylinders until the knock is eliminated. The PCM will always try to work back to a zero compensation level or no spark retard. DTC P0326 sets when the PCM cannot eliminate spark knock by retarding spark timing which most likely is caused by engine noise.
DTC Parameters
DTC P0326 will set if the PCM cannot reduce spark knock (as seen by the knock sensor) by retarding timing. The knock sensor activity is probably due to engine noise and not spark knock.
DTC P0326 diagnostic is run with engine running and a cylinder in a combustion event window.
DTC P0326 is a type D DTC.
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0326 indicates excessive engine noise and not excessive spark knock. This code does not indicate a problem in the knock sensor circuit subsystem.
Possible causes for engine noise:
| • | Valve train |
| • | Belt tensioner |
| • | Bracket loose |
| • | Low octane fuel in high altitude with engine under high load. |
The PCM learns spark retard. The PCM uses low (low RPM), mid (mid RPM), and hi (high RPM) spark compensating cells that fill up when spark knock is present under those conditions. The PCM will automatically adjust spark retard based on these cells and will learn back to 0 compensation when the noise condition is corrected.
The compensating cells found on the scan tool are adjusted according to start-up engine coolant temperature (ECT). If the start-up ECT is:
| • | Less than 8°C (46°F), the cells are set to 0. |
| • | Less than 56°C (133°F), the cells are set to 75 percent of the stored learned values. |
| • | Greater than 104°C (219°F), the stored values are used. |
| • | Temperatures in between are adjusted on a percentage value. |
A reduced engine power condition may result due to excessive spark retarding.
