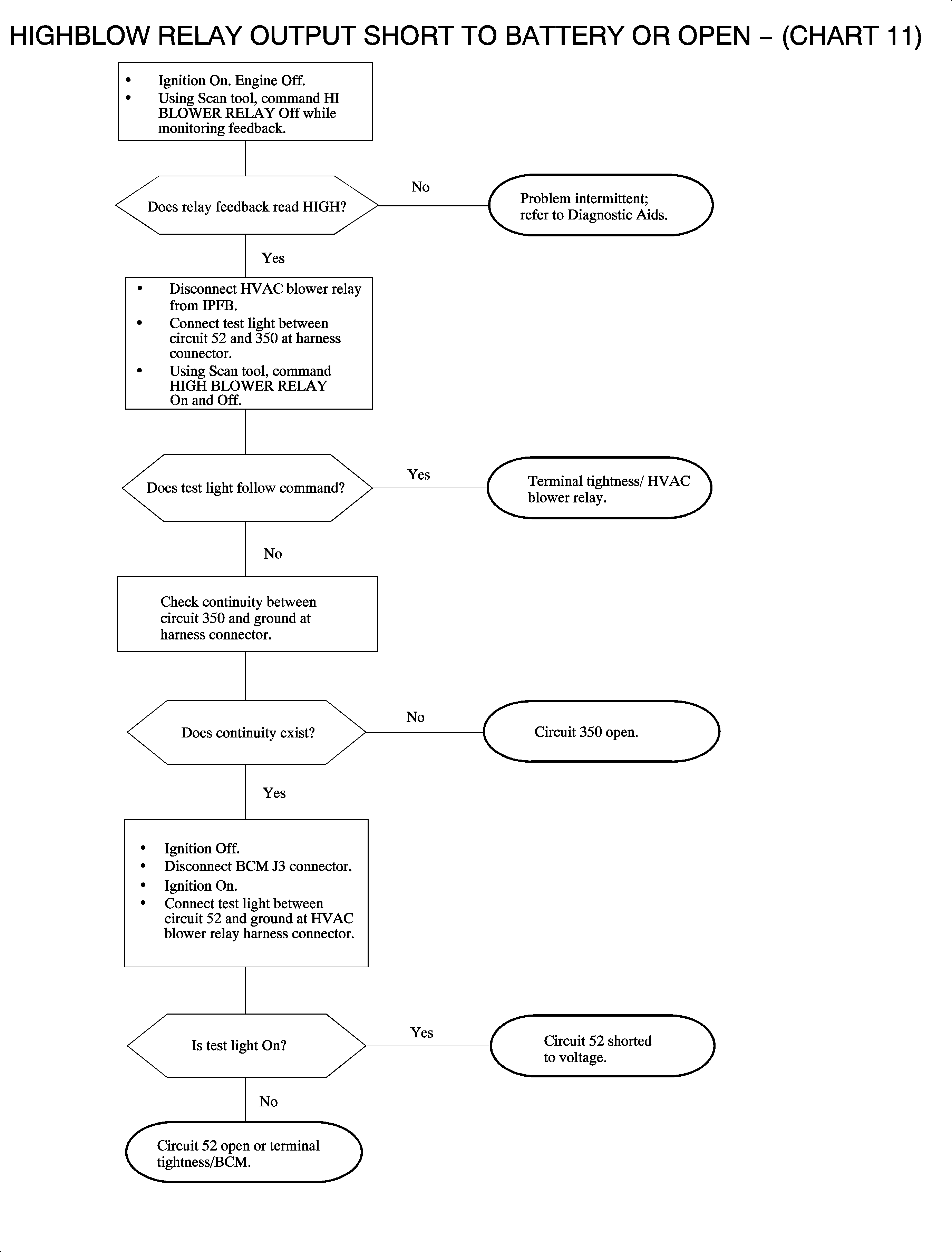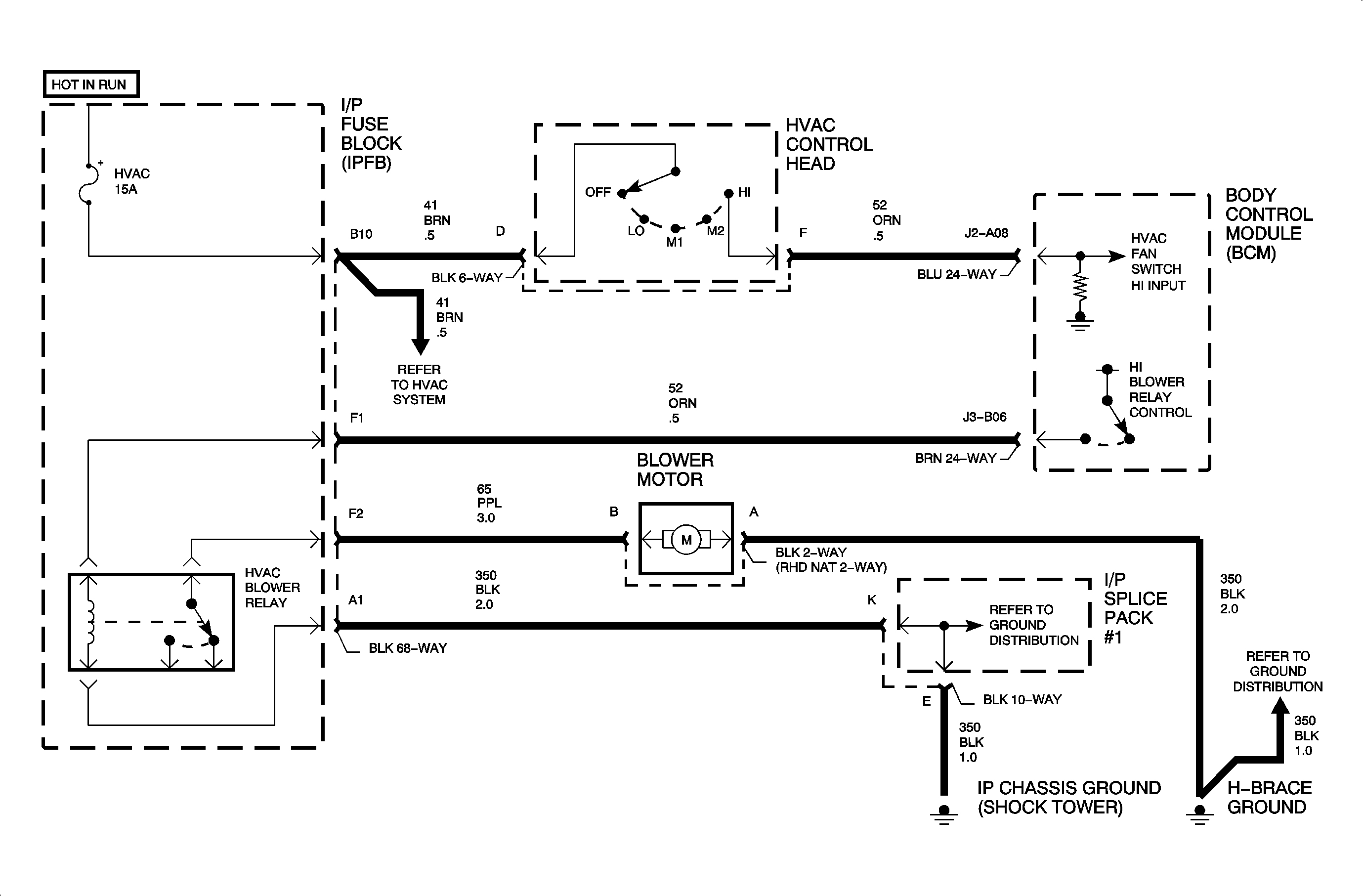
The HVAC HI Blower Fan Output can be requested by either the HI Blower Switch Input or the HVAC Afterblow function. When requested by the HI blower switch the body control module (BCM) receives the switch input over circuit 52 and switches the blower relay to battery. This energizes the blower relay coil and turns the blower motor on HI. The HVAC Afterblow function is used to eliminate the odor associated with A/C usage. The "Afterblow" is a method whereby the HVAC blower is run for a few minutes, approximately 50 minutes after the vehicle is turned OFF, in order to physically blow off excess condensation and eliminate odors. The powertrain control module (PCM) sends vehicle speed, air intake temperature (used for ambient temperature), and A/C clutch status to the BCM. When the BCM receives the above information from the PCM, and determines the A/C has been engaged during the ignition cycle, the Afterblow is requested to occur after vehicle power down.
Once the request for the Afterblow is made, the BCM monitors air intake temperature to determine the duration of the Afterblow required. A sufficiently high ambient temperature, approximately 30° C (86° F) or higher causes an Afterblow event of approximately 3 minutes. A lower ambient temperature, below 30° C (86° F), allows for a shorter duration, approximately 32 seconds. The vehicle speed must have met or exceeded 30 mph to cause an Afterblow event when all other conditions have been met. After vehicle power down, the Afterblow shall occur after a delay. In the event that the ignition is cycled ON during the delay period or the Afterblow event, the Afterblow output shall be turned OFF.
DTC Parameters
| • | The ignition is in RUN, ACC or CRANK |
| • | Circuit 52 is shorted to battery |
| • | Circuit 52 is open and HI Blower is requested |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Check for poor connection at the BCM. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper terminal mating, broken connector locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals and poor terminal to wire connection, terminal crimped over wire insulation and not conductors. |
| • | Inspect wiring harness for damage. Check for broken or chaffed insulation. |
| • | If a fault is suspected to be intermittent, wiggling harness wiring may help in locating the fault. |