Circuit Description
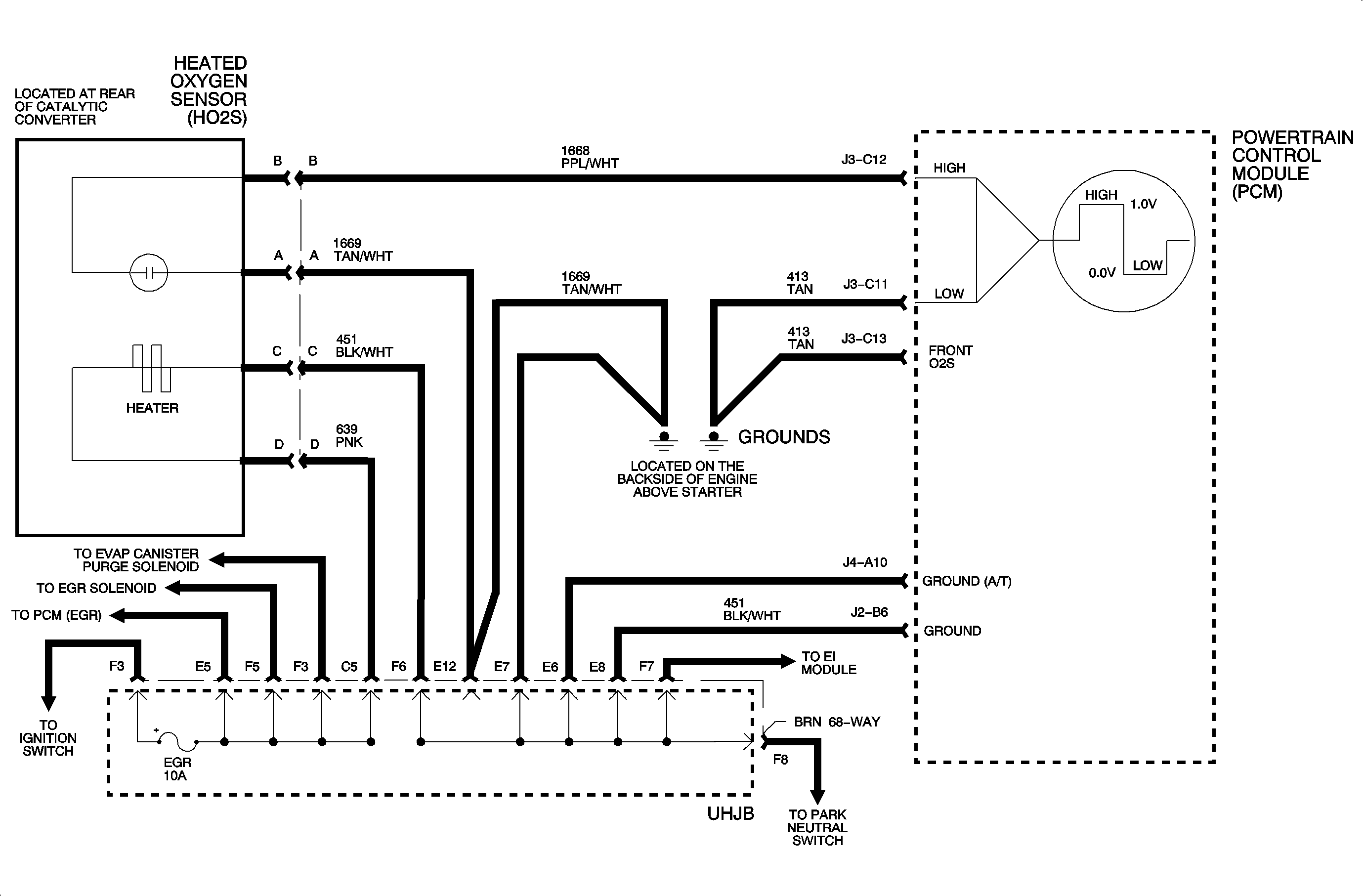
The catalyst monitor test is performed once per drive cycle if all test conditions are met. The main enable criteria to enable a catalyst test are: a steady TP sensor reading and calculated temperature of catalytic converter, using the ECT sensor, IAT sensor, load, and run time, indicating the system is fully warmed up. Once the enable criteria are met, 50 samples of the sensor voltage amplitudes are collected. The results of the 50 samples are averaged and converted to a millivolt (mV) reading which indicates the efficiency of the converter. The catalyst monitor tests consist of 2 stages. Stage 1 voltage ranges from -555 to +550 mV. When this value goes above 0 mV indicating stage 1 has failed, the stage 2 test will start to be used in determining the efficiency. When stage 2 reaches the fail threshold, the MIL, service engine soon, lamp will be illuminated and a DTC P0420 will be set. The scan tool can display the current value in millivolts for stage 1 as well as indicate if the stage 1 test has passed or failed. Whenever DTCs are cleared or the battery has been disconnected, the results of stage 1 will be reset to -555 mV. For more information on the catalyst test, refer to Description and Operations.
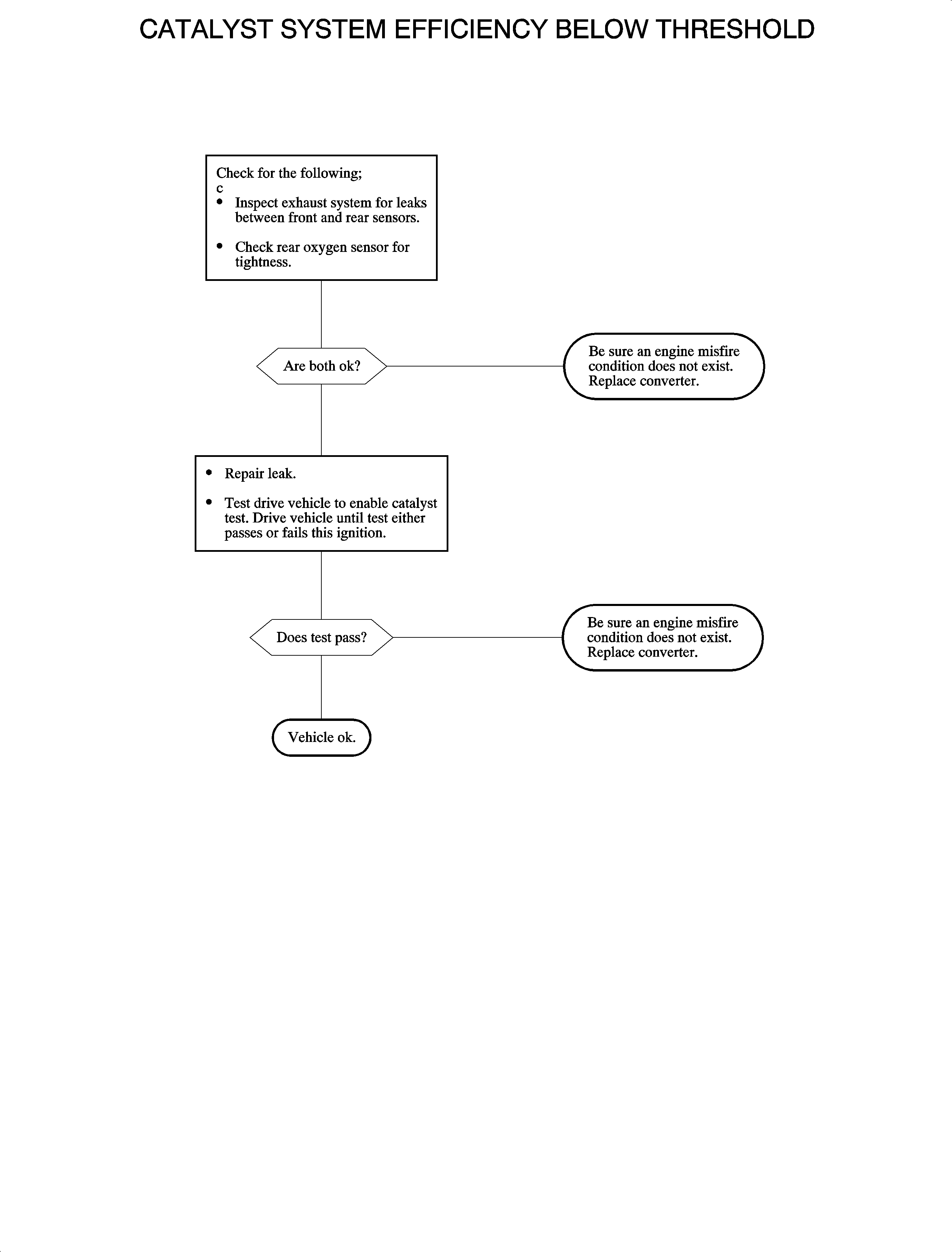
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The stage 1 will fail when the catalyst efficiency becomes less than 75 percent efficient. After stage 1 fails, the 50 sample test results are used by stage 2. When the results of stage 2 are greater than the fail threshold mV, catalyst efficiency below about 70 percent, the MIL, service engine soon, telltale lamp will be illuminated and a DTC P0420 will be set.
Important: A catalyst monitor test will not be performed if a fault exists in the rear or front oxygen sensor circuits.
Probable causes of a DTC P0420 are:
| • | Exhaust system leaks between the front and rear sensors or rear sensor leaking |
| • | Catalyst deteriorated due to excessive time operating the vehicle with a catalyst damaging misfire |
| • | Contamination of the converter due to incorrect sealant, fuel, or fuel additives. |
Diagnostic Aids
DTC P0420, once set, should remain active. However, under certain driving conditions, the catalyst monitor test may pass. This condition may occur if driving the vehicle at highway speeds, high air flow, but if DTC P0420 is set and no exhaust leaks are found, the catalytic converter should be replaced. If a misfire DTC P0300 is detected, the DTC P0420 test will not run. Be sure to correct a misfire condition before replacing the converter.