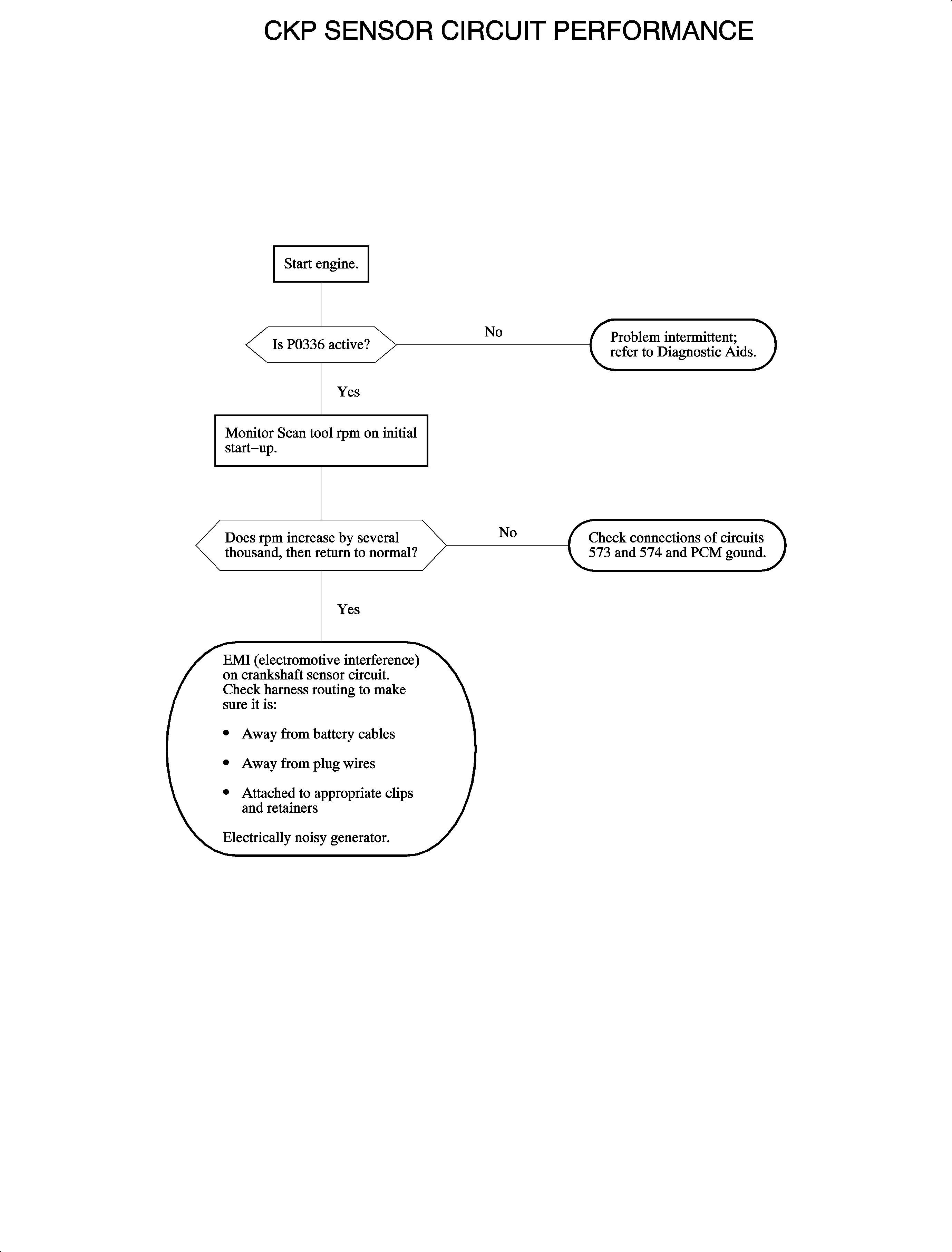
Circuit Description
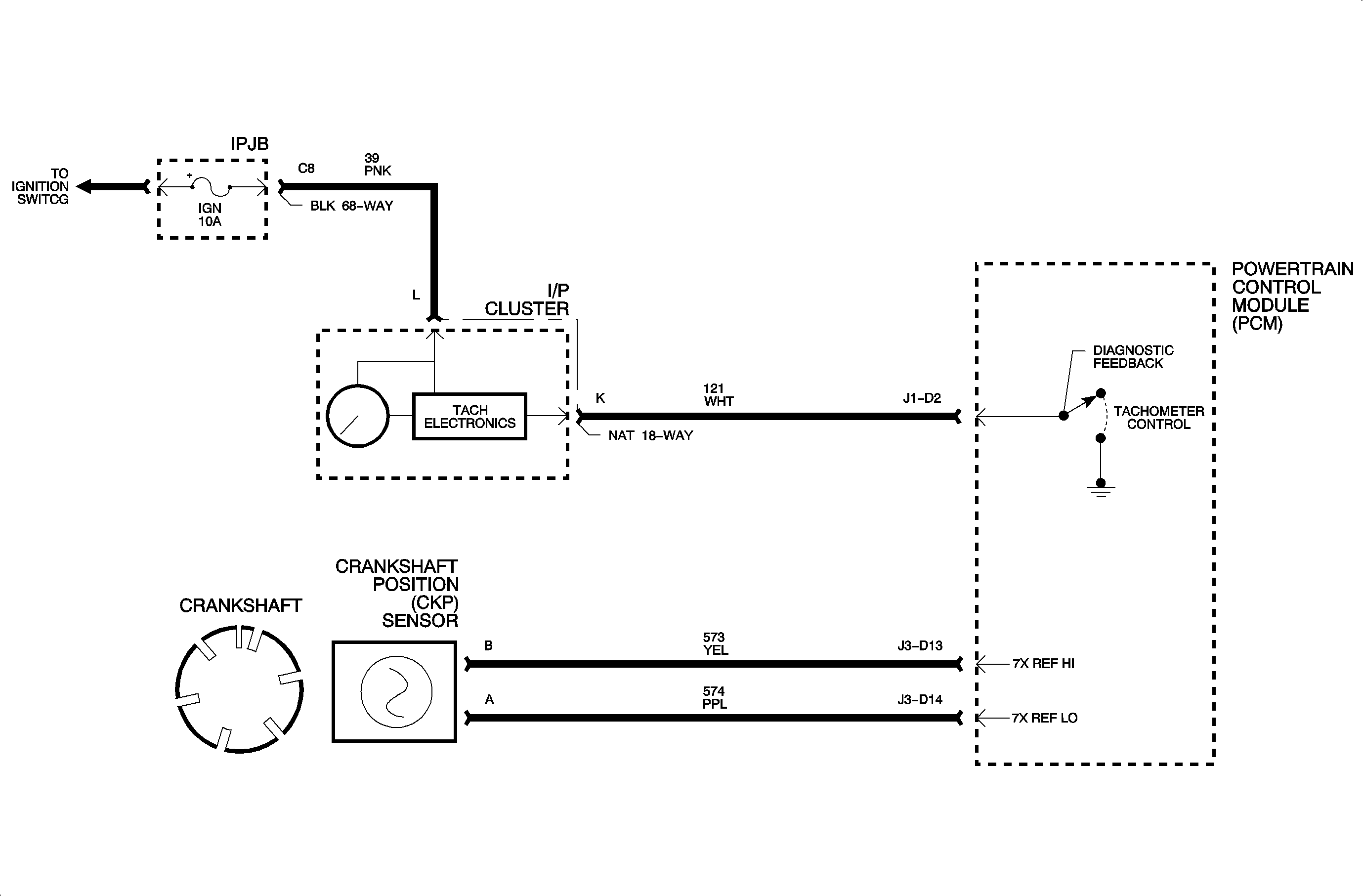
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor defines engine position by generating an electrical pulse each time it passes by a notch of the crankshaft reluctor wheel. The PCM uses crankshaft sensor pulses for fuel delivery and spark timing.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Important: The CKP signal is continuously checked after the above conditions have been met.
Important: Any time a crankshaft position sensor is replaced, the crankshaft learn procedure must be performed. Failure to relearn may result in false misfire DTCs.
DTC P0336 will set if extra or missing crankshaft sensor pulses are detected or time between reference pulses is too long or too short when:
| • | RPM is over 3,600 RPM or under 2,600 RPM. |
| • | Engine run time is greater than 10 seconds. |
| • | Engine coolant temperature is greater than 65°C (149°F). |
| • | TP is greater than 9.8 percent open. |
| • | No ECT, TP sensor, or P0125 DTCs have been set. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Make sure the crankshaft position sensor circuit wires are clear of other voltage interfering wires. Electromotive interference (EMI) waves may offset a crank signal to the PCM, thus setting a DTC.
Verify that the secondary leads are not in close proximity to the signal wires, e.g. IC, REF, etc.