The throttle actuator control (TAC) system delivers improved throttle response
and greater reliability and eliminates the need for mechanical cable. The TAC system
performs the following functions:
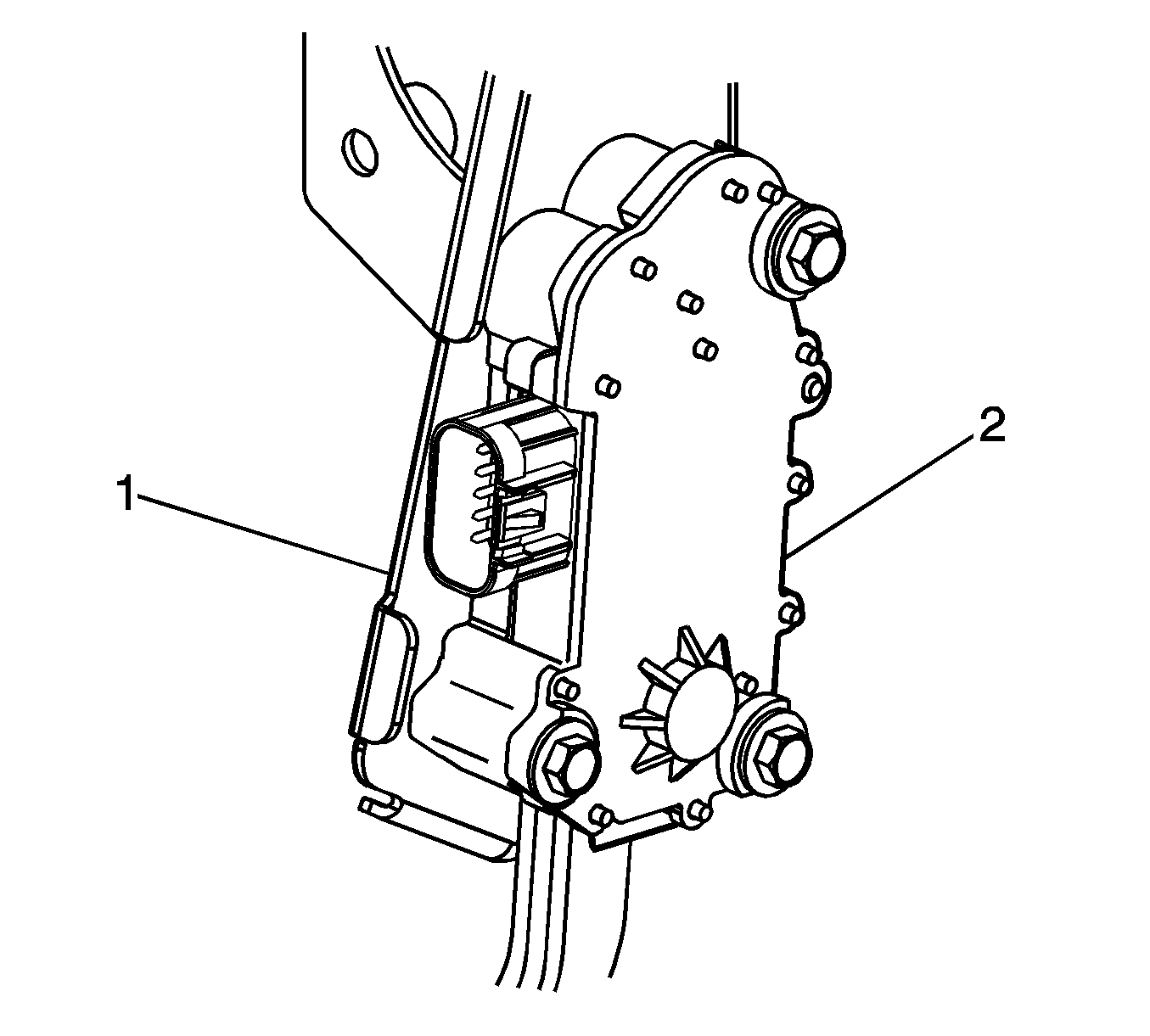
The accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor assembly (2) is fastened
to the accelerator pedal assembly and attached to the brake pedal bracket (1).
The APP sensor assembly contains two APP sensors that are operated by the accelerator
pedal movement. The APP sensors 1 and 2 are potentiometer type sensors each
with 3 circuits:
The APP sensors are used to determine the pedal angle. The powertrain control
module (PCM) provides each APP sensor a 5-volt reference circuit and a low reference
circuit. The APP sensors provide the PCM with signal voltage proportional to the pedal
movement. APP sensor 1 signal voltage is low at the rest position and increases
to near the 5-volt reference as the pedal is applied. APP sensor 2 signal is
low at rest and also increases as the accelerator pedal is applied. APP sensor 2
increases at a different rate to approximately half the reference voltage. The APP
sensor 1 is responsible for providing the actual pedal position to the PCM.
The PCM then sends a throttle position target value to the TAC control module. APP
sensor 2 provides a backup value to the APP sensor 1.