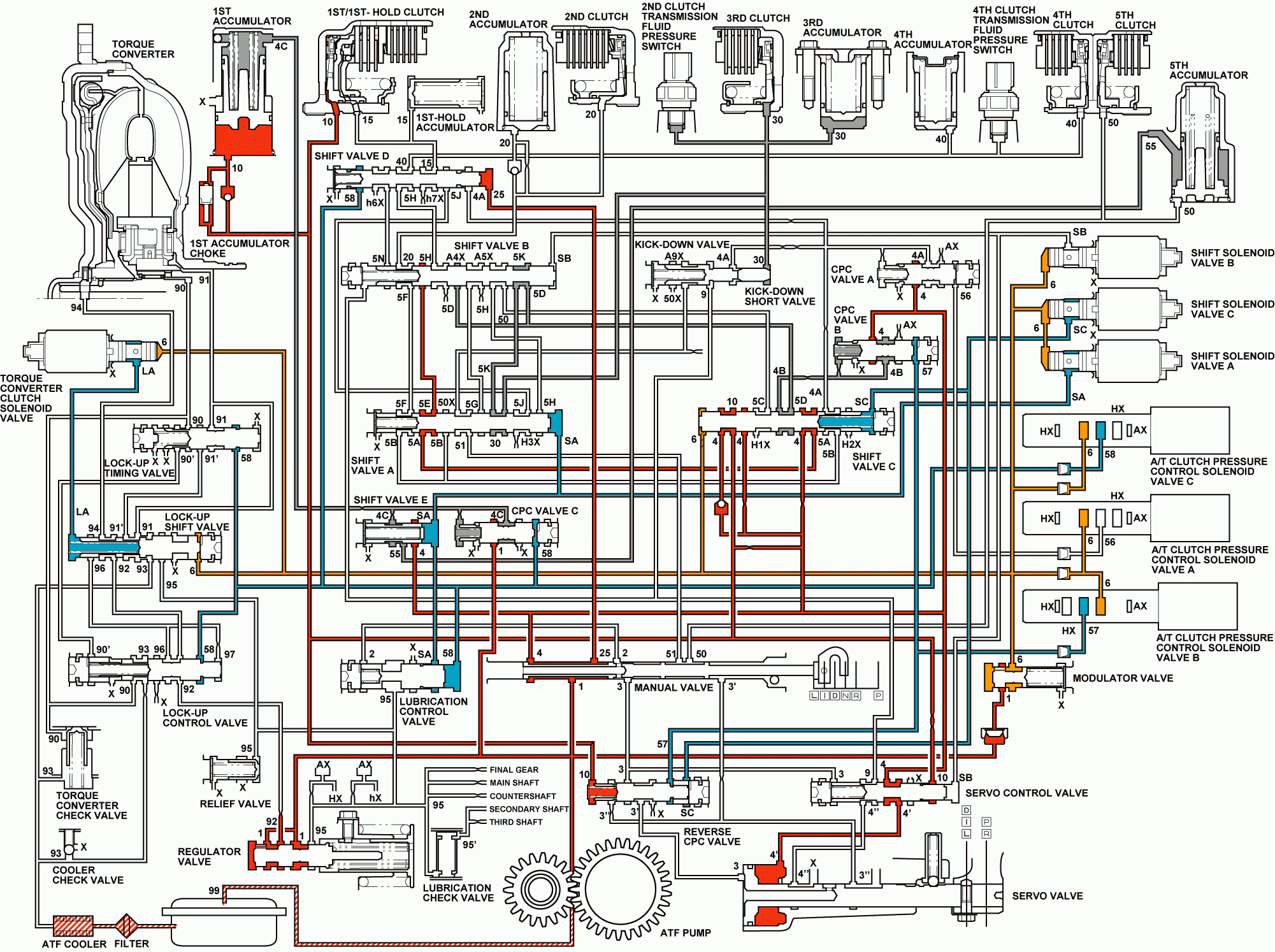
Distribution of Hydraulic Pressure
As the engine turns, the automatic transmission fluid (ATF) pump starts to operate. ATF is drawn through the ATF filter and discharged into the hydraulic circuit. ATF flowing from the ATF pump becomes line pressure that is regulated by the regulator valve. Torque converter pressure, from the regulator valve, enters the torque converter through the lock-up shift valve and is discharged from the torque converter. The torque converter check valve prevents torque converter pressure from rising.
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the shift solenoid valves ON and OFF. The shift solenoid valves control shift solenoid pressure to the shift valves. Applying shift solenoid pressure to the shift valves moves the position of the shift valve, and switches the port of hydraulic pressure. The PCM also controls the automatic transmission clutch pressure control (AT CPC) solenoid valves A and B.
The AT CPC solenoid valves A and B regulate the AT CPC solenoid pressure and apply the AT CPC solenoid pressure to CPC valves A and B. When shifting between upper gear and lower gear, the clutch is engaged by pressure from the CPC pressure mode.
The PCM controls one of the shift solenoid (SS) valves to move the position of the shift valve. This movement switches the port of the CPC and line pressure. Line pressure is then applied to the clutch, and the CPC pressure is intercepted.
When shifting is completed, the clutch is engaged with line pressure.
Port No. | Type of Pressure | Port No. | Type of Pressure | Port No. | Type of Pressure | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Line | 5N | CPC A or Line | 56 | LS A | ||||||||||||
2 | Line | 5D | CPC B or Line | 57 | LS B | ||||||||||||
3 | Line | 5G | CPC B or Line | 58 | LS C | ||||||||||||
3' | Reverse CPC or Line | 5K | CPC B or Line | 90 | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
3" | Reverse CPC or Line | 6 | Modulate | 90' | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
4 | Line | SA | SH A | 91 | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
4' | Line | SB | SH B | 91' | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
4" | Line | SC | SH C | 92 | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
4A | CPC A | LA | LC A | 93 | ATF cooler | ||||||||||||
4B | CPC B | 9 | Line | 94 | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
4C | CPC C | 10 | 1st Clutch | 95 | Lubrication | ||||||||||||
5B | CPC A | 15 | 1st Hold Clutch | 95' | Lubrication | ||||||||||||
5C | CPC B | 20 | 2nd Clutch | 96 | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
5H | CPC B | 25 | Line | 97 | Torque Converter | ||||||||||||
5J | CPC B | 30 | 3rd Clutch | 99 | Suction | ||||||||||||
5A | CPC A or Line | 40 | 4th Clutch | X | Drain | ||||||||||||
5E | CPC A or Line | 50 | 5th Clutch | HX | High Position Drain | ||||||||||||
5F | CPC A or Line | 51 | 5th Clutch | hX | High Position drain | ||||||||||||
5M | CPC A or Line | 55 | CPC C or Line | AX | Air Drain | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
N Position
The PCM controls the shift solenoid valves. The condition of the shift solenoid valves and position of the shift valves is as follows:
| • | Shift solenoid valve A is turned OFF, and shift valve A is moved to the left side. |
| • | Shift solenoid valve B is turned ON, and shift valve B remains in the right side. |
| • | Shift solenoid valve C is turned OFF, and shift valve C remains in the left side. |
Line pressure (1) passes through the manual valve and becomes line pressure (25). Line pressure (25) stops at shift valve D. Line pressure (1) also flows to the modulator valve and becomes modulator pressure (6). Modulator pressure (6) flows to the SS valves, the AT CPC solenoid valves A and B, and the AT CPC solenoid valve C. Under this condition, hydraulic pressure is not applied to the clutches.
When used, ''left'' or ''right'' indicates direction on the hydraulic circuit.
Neutral - Engine Running