Tools Required
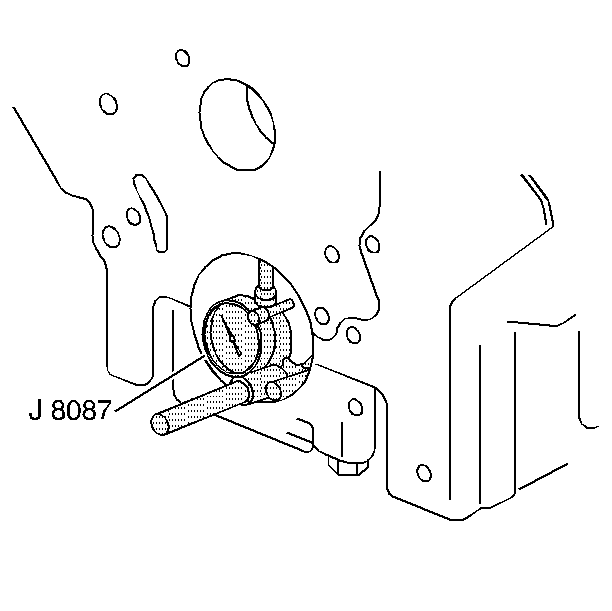
| • | J 8087 Cylinder Bore
Checking Gauge |
Important: If crankshaft bearing failure is due to other
than normal wear, investigate the cause. Inspect the crankshaft or connecting rod
bearing bores.
Inspect the connecting rod bearing bores or crankshaft main bearing bores using
the following procedure:
| • | Tighten the bearing cap to specification using the J 45059
. |
| • | Measure the bearing bore for taper and out-of-round using
the J 8087
. |
| • | No taper or out-of-round should exist. |
Bearing Selection
- Measure the bearing clearance to determine the correct replacement bearing
insert size. There are two methods to measure bearing clearance. Method A
gives more reliable results and is preferred.
| • | Method A yields measurement from which the bearing clearance can
be computed. |
| • | Method B yields the bearing clearance directly. Method B
does not give any indication of bearing run-out. |
Important: Do not mix inserts of different nominal size
in the same bearing bore.
- To measure bearing clearance using Method A, use the following procedure:
| 2.1. | Measure the crankshaft bearing journal diameter with a micrometer in
several places, 90 degrees apart. Average the measurements. |
| 2.2. | Measure the crankshaft bearing journal taper and runout. |
| 2.3. | Install the lower crankcase and tighten the bearing cap bolts to specification. |
| 2.4. | Measure bearing I.D. in several places 90 degrees apart, average
measurements. |
| 2.5. | Subtract journal measurement from bearing I.D. measurement to determine
clearance. |
| 2.6. | Determine whether clearance is within specification. |
| 2.7. | If out of spec choose different inserts. |
| 2.8. | Measure the connecting rod inside diameter in the same direction as the
length of the rod with an inside micrometer. |
| 2.9. | Measure the crankshaft main bearing inside diameter with an inside micrometer. |
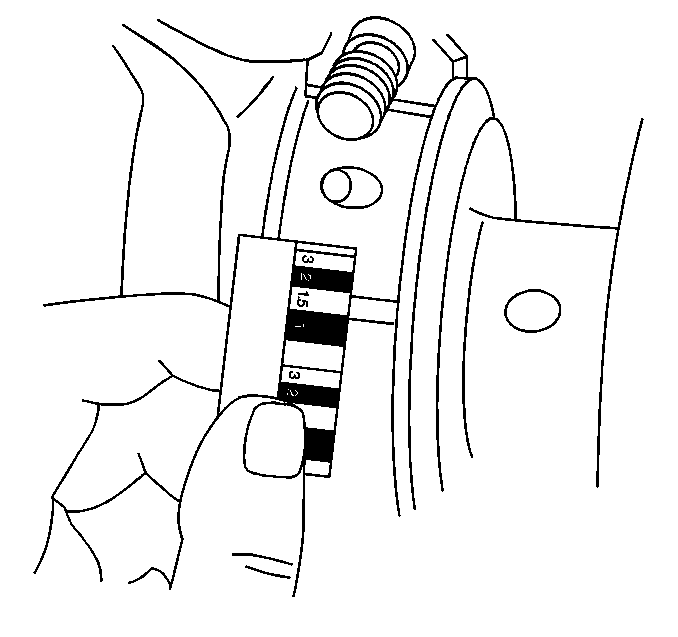
- To measure bearing clearance using Method B, use the following procedure:
| 3.1. | Clean the used bearing inserts. |
| 3.2. | Install the used bearing inserts. |
| 3.3. | Place a piece of gaging plastic across the entire bearing width. |
| 3.4. | Install the bearing caps. |
| | Notice: In order to prevent the possibility of cylinder block or
crankshaft bearing cap damage, the crankshaft bearing caps are tapped into
the cylinder block cavity using a brass, lead, or a leather mallet before
the attaching bolts are installed. Do not use attaching bolts to pull the
crankshaft bearing caps into the seats. Failure to use this process may damage
a cylinder block or a bearing cap.
|
| 3.5. | Install the bearing cap bolts to specification. |
| | Important: Do not rotate the crankshaft.
|
| 3.6. | Remove the bearing cap, leaving the gaging plastic in place. It does not matter
whether the gaging plastic adheres to the journal or to the bearing cap. |
| 3.7. | Measure the gaging plastic at its widest point with the scale printed
on the gaging plastic package. |
| 3.8. | Remove the gaging plastic. |
Tools Required
| • | J 8087 Cylinder Bore Checking
Gauge |

Important: If crankshaft bearing failure is due to other than normal wear, investigate
the cause. Inspect the crankshaft or connecting rod bearing bores.
Inspect the connecting rod bearing bores or crankshaft main bearing
bores using the following procedure:
| • | Tighten the bearing cap to specification using the J 36660-A
. |
| • | Measure the bearing bore for taper and out-of-round
using the J 8087
. |
| • | No taper or out-of-round should exist. |
Bearing Selection
- Measure the bearing clearance to determine the correct replacement
bearing insert size. There are two methods to measure bearing clearance.
Method A gives more reliable results and is preferred.
| • | Method A yields measurement from which the bearing clearance
can be computed. |
| • | Method B yields the bearing clearance directly. Method B
does not give any indication of bearing run-out. |
Important: Do not mix inserts of different nominal size in the same bearing bore.
- To measure bearing clearance using Method A, use the following
procedure:
| 2.1. | Measure the crankshaft bearing journal diameter with a micrometer
in several places, 90 degrees apart. Average the measurements. |
| 2.2. | Measure the crankshaft bearing journal taper and runout. |
| 2.3. | Install the lower crankcase and tighten the bearing cap bolts
to specification. |
| 2.4. | Measure bearing I.D. in several places 90 degrees apart,
average measurements. |
| 2.5. | Subtract journal measurement from bearing I.D. measurement to
determine clearance. |
| 2.6. | Determine whether clearance is within specification. |
| 2.7. | If out of spec, choose different inserts. |
| 2.8. | Measure the connecting rod inside diameter in the same direction
as the length of the rod with an inside micrometer. |
| 2.9. | Measure the crankshaft main bearing inside diameter with an inside
micrometer. |

- To measure bearing clearance using Method B,
use the following procedure:
| 3.1. | Clean the used bearing inserts. |
| 3.2. | Install the used bearing inserts. |
| 3.3. | Place a piece of gaging plastic across the entire bearing width. |
| 3.4. | Install the bearing caps. |
| | Notice: In order to prevent the possibility of cylinder block or
crankshaft bearing cap damage, the crankshaft bearing caps are tapped into
the cylinder block cavity using a brass, lead, or a leather mallet before
the attaching bolts are installed. Do not use attaching bolts to pull the
crankshaft bearing caps into the seats. Failure to use this process may damage
a cylinder block or a bearing cap.
|
| 3.5. | Install the bearing cap bolts to specification. |
| | Important: Do not rotate the crankshaft.
|
| 3.6. | Remove the bearing cap, leaving the gaging plastic in place. It does
not matter whether the gaging plastic adheres to the journal or to the bearing
cap. |
| 3.7. | Measure the gaging plastic at its widest point with the scale
printed on the gaging plastic package. |
| 3.8. | Remove the gaging plastic. |