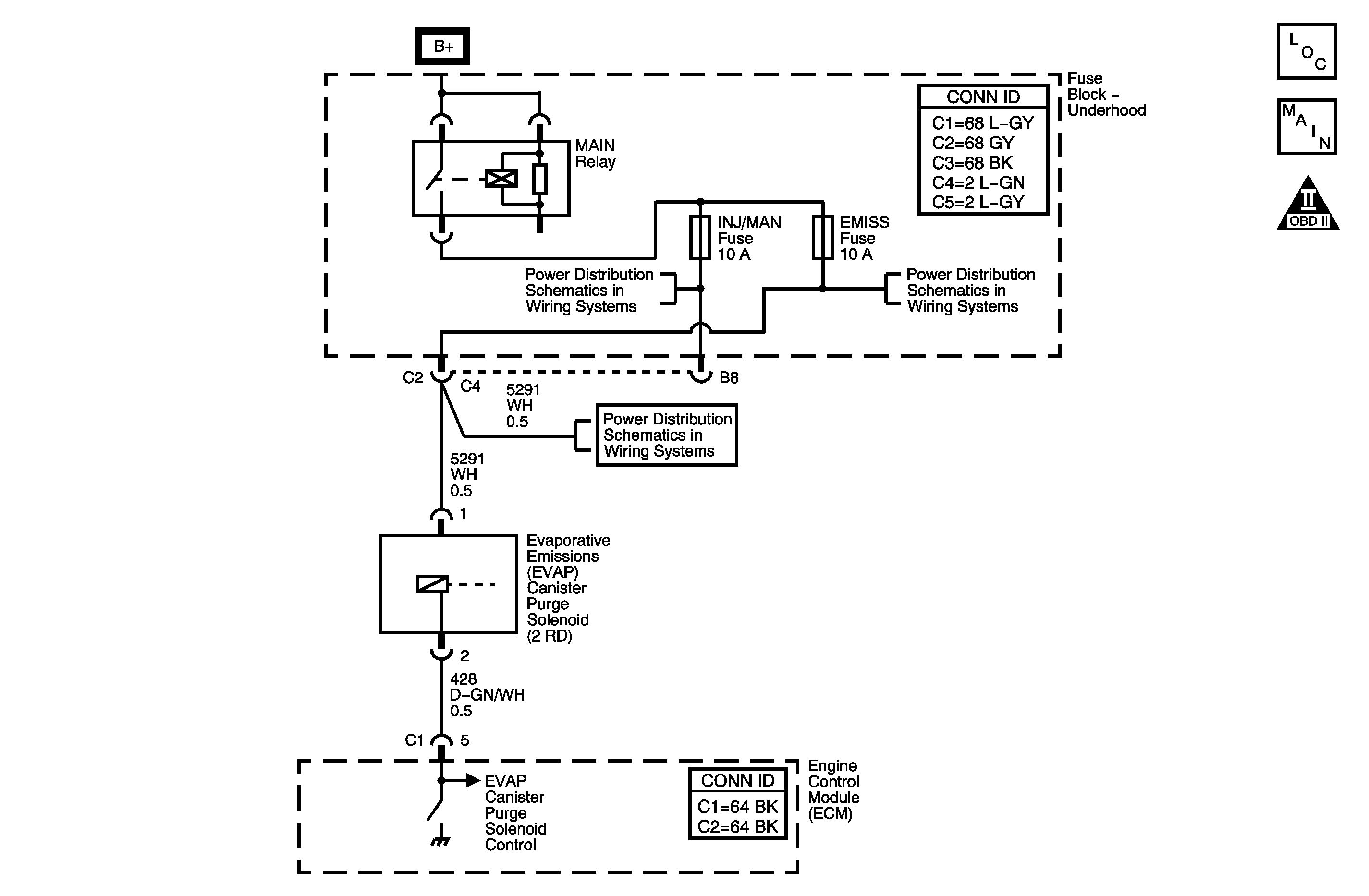
Circuit Description
The Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System is used to store fuel vapors as to reduce the amount of unburned fuel from escaping into the atmosphere. The EVAP purge solenoid is used to control the flow of fuel vapor from the EVAP canister to the intake manifold. The engine control module (ECM) controls the solenoid by supplying it ground whenever the EVAP system is in purge mode. Fuel vapors can be purged anytime the ECM is in Closed Loop and the vehicle is not in deceleration. When the solenoid is commanded OFF, circuit not grounded, the voltage level at the ECM should be high, ignition voltage. When the driver is commanded ON, circuit grounded, the voltage level at the ECM should be low. The ECM EVAP purge solenoid feedback circuit uses a pull-up voltage (2.6-4.6 volts), which allows the ECM to individually differentiate between an open, short to ground or short to voltage. DTC P0444 will set if the ECM detects lower than normal feedback voltage when EVAP purge solenoid is commanded OFF with engine cranking/running.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine speed is more than 40 RPM. |
| • | The battery is between 8-18 volts. |
DTC P0444 runs continuously once the above conditions have been met.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0444 will set if the EVAP purge solenoid feedback voltage is less than 2.6 volts, ECM pull-up voltage indicating an open circuit, when EVAP purge solenoid is commanded OFF and the condition exists for longer than 0.5 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | A current DTC Last Test Failed clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other non-emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | The EVAP purge solenoid resistance is 23-32 ohms. |
| • | The EVAP purge solenoid is pulse width modulated (PWM). An audible clicking should be heard when the purge solenoid is commanded to 50 percent. The rate at which the solenoid cycles should increase as the commanded state is increased and decreased as the commanded state is decreased. Repeat the commands as necessary. |
| • | For intermittent conditions, refer to Intermittent Conditions |
Step | Action | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics Connector End View Reference: Engine Control Module Connector End Views or Engine Controls Connector End Views | |||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | Go to Step 2 | |
2 |
Do you hear or feel a clicking from the EVAP purge solenoid when the solenoid is commanded to 50 percent? | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 |
3 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | Go to Step 4 | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
4 | Test the control circuit of the EVAP canister purge valve for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 5 |
5 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the control module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 6 |
6 | Replace the control module. Refer to Engine Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 7 | -- |
7 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 8 |
8 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | System OK | |
