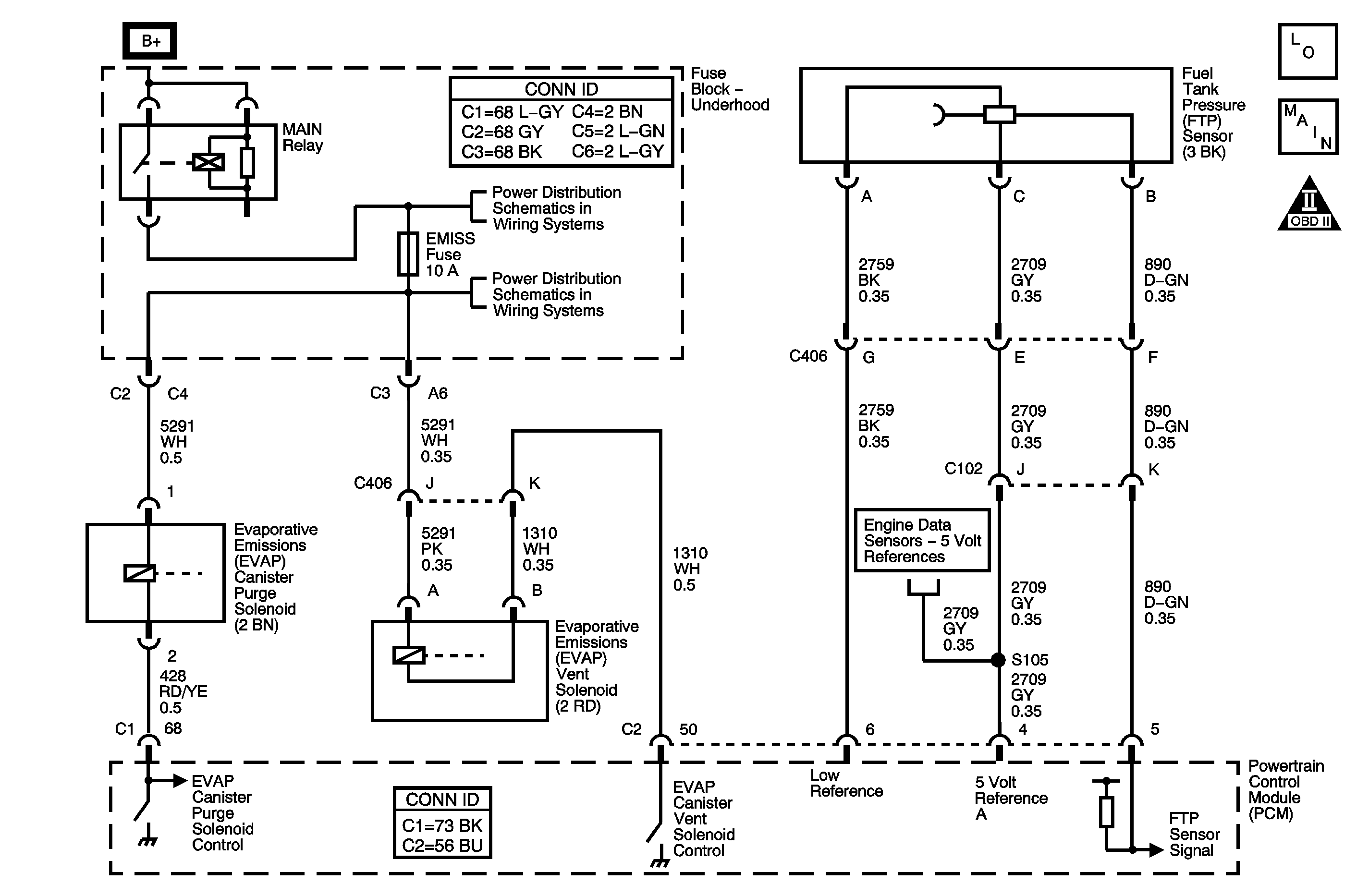
Circuit Description
The DTC P0499 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Vent Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage diagnostic detects faults in the vent solenoid electrical circuit. Battery positive voltage is supplied to the evaporative emission (EVAP) canister vent valve. The control module grounds the EVAP canister vent valve control circuit to close the valve by means of an internal switch called a driver. The scan tool displays the commanded state of the EVAP canister vent valve as ON or OFF. The control module monitors the status of the driver. If the control module detects voltage on the control circuit when the driver is commanded ON, this DTC sets.
The following table illustrates the relationship between the ON and OFF states, and the OPEN or CLOSED states of the EVAP canister vent valve.
Control Module Command | EVAP Canister Vent Valve Position |
|---|---|
ON | CLOSED |
OFF | OPEN |
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic supports the following DTC.
DTC P0499 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Vent Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The battery voltage is 10.1 volts. |
| • | The engine is running. |
| • | DTC P0499 runs continuously once the above conditions are met. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The actual state of the control circuit does not match the commanded state.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
The Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool, if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
After replacing the PCM, a new minimum throttle position and idle speed must also be established.
Step | Action | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls Connector End Views or Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views | |||
Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | Go to Step 2 | ||
2 |
Do you hear or feel a click from the EVAP vent valve when the valve is commanded ON and OFF? | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 |
3 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | Go to Step 4 | Go to Intermittent Conditions |
4 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 6 |
5 | Test the control circuit of the EVAP vent valve for a short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 7 |
6 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the EVAP vent valve. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 8 |
7 | Test for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the control module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 9 |
8 | Replace the EVAP vent valve. Refer to Evaporative Emission Canister Vent Solenoid Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 10 | -- |
Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 10 | -- | |
10 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 11 |
11 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | System OK | |
