| Table 1: | Relay Cavity Identification |
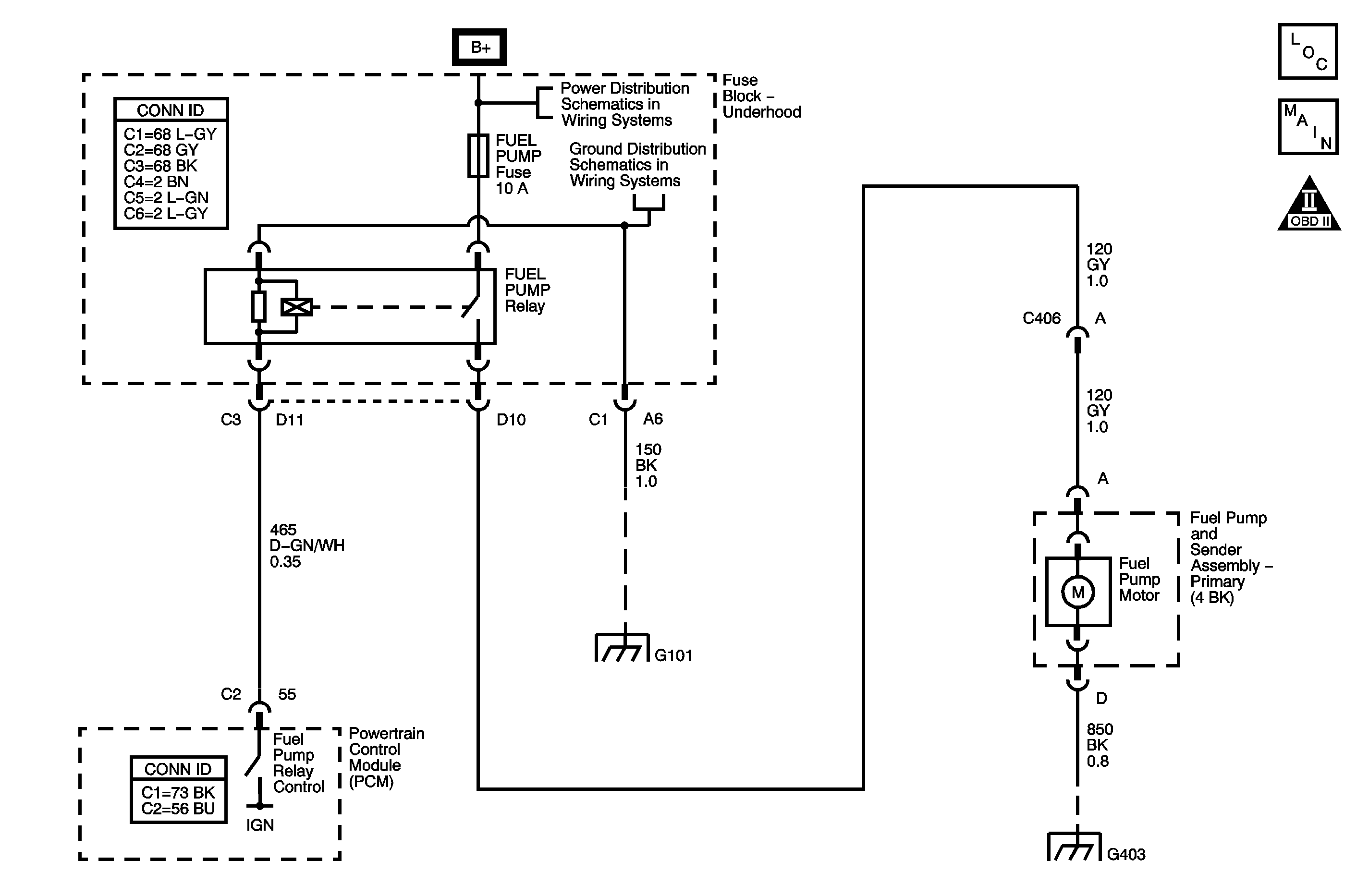
Circuit Description
The DTC P0628 Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit Low Voltage diagnostic detects an incorrect voltage on the coil control circuit. The fuel pump relay is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM energizes the relay coil for 2 seconds when the ignition switch is first turned ON and when ignition system reference pulses are detected. The fuel pump relay supplies ignition positive voltage to the fuel pump.
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC.
DTC P0628 Fuel Pump Relay Control Circuit Low Voltage
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | Battery voltage is 10.5 volts or more. |
| • | DTC P0628 runs continuously with the above condition met. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The PCM detects a lower than expected voltage on the coil control circuit . |
| • | The above condition is present for at least 1 second. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) the first time the diagnostic fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information is stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns OFF after 3 consecutively passing trips without a fault present. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Perform the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | Check the resistance of the relay. The resistance across the coil terminals is 70-95 ohms at 20°C (68°F). The resistance across the switched load terminals is infinite. |
| • | The relay electrical contacts may be pitted or sticking. Replace the relay if tapping gently on the relay or wiggling the relay causes a change in the relays operation. |
| • | The performance of the relay may be affected by temperature. Test the relay after sitting outside overnight and after running the engine 30 minutes. |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the relay electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for an intermittent condition. Refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Use the following relay cavity table in order to locate the correct cavities to probe during diagnosis. The table layout corresponds to the cavity layout of the relay block.
Front of Vehicle | |
Switch Load | Battery Power Coil |
Coil Control | Battery Power Load |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step will verify whether the PCM is providing a ground path for the relay circuit. When the coil ground circuit is grounded, the relay turns ON.
-
After replacing the PCM a new minimum throttle position and idle speed must also be established.
Step | Action | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|
Connector End View Reference: Powertrain Control Module Connector End Views or Engine Controls Connector End Views | |||
Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | Go to Step 2 | ||
2 |
Does the fuel pump relay turn ON and OFF with each command? | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 |
3 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | Go to Step 4 | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF? | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 5 | |
5 | Test the control circuit of the fuel pump relay for a short to ground. Refer Circuit Testing to and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct a condition? | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 7 |
6 | Replace the fuel pump relay. Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 8 | -- |
Did you complete the replacement? | Go to Step 8 | -- | |
8 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 9 |
9 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | System OK | |
