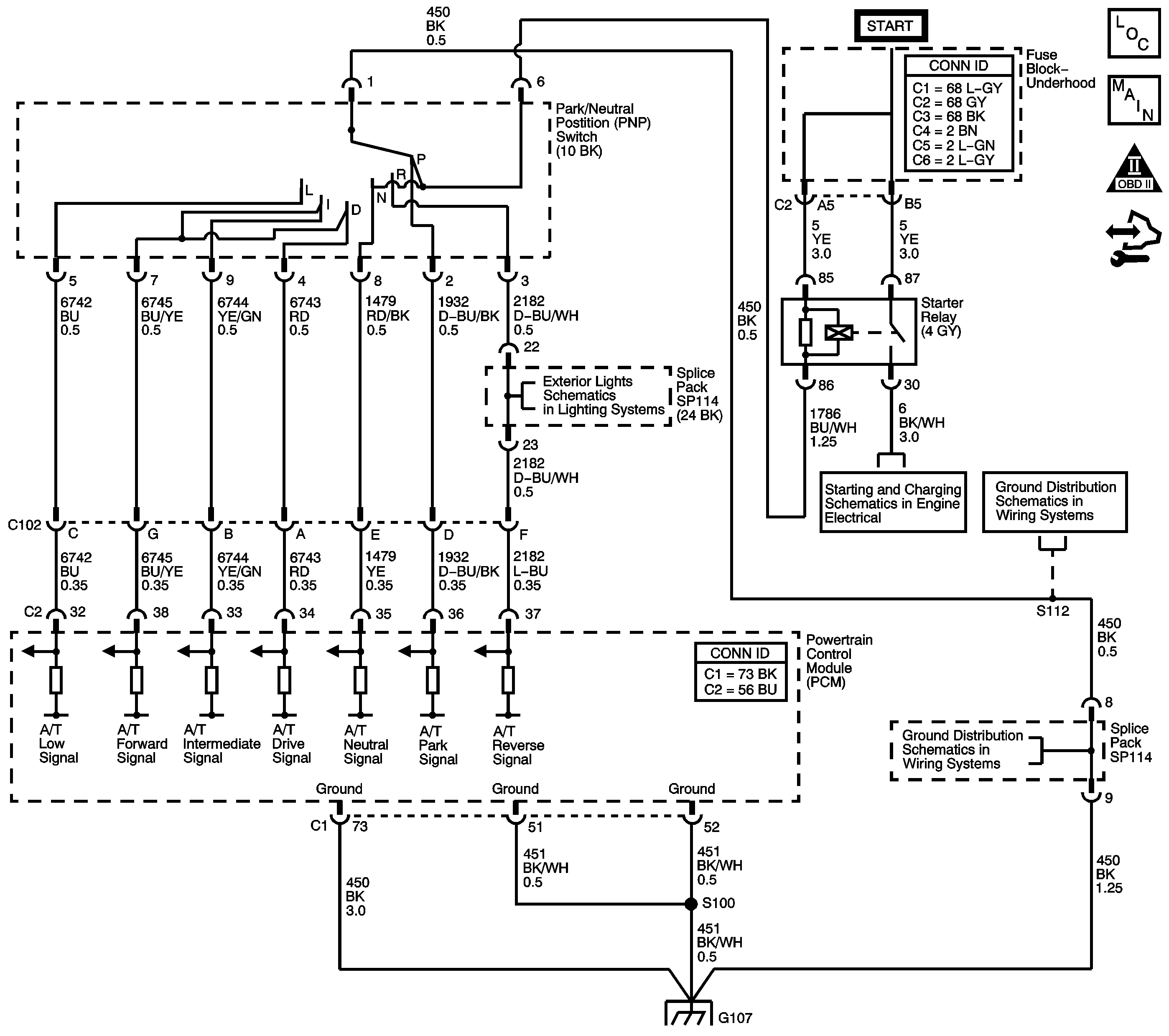
Circuit Description
The transmission range (TR) switch is part of the park/neutral position switch assembly and is mounted on the transmission manual shaft. The TR switch is a multi-signal switch. The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies ignition voltage to the TR switch on 7 signal circuits, P, R, N, D, I, L, and Forward Range. Each gear selector lever position grounds one or more of the signal circuits in a unique pattern. In order to determine the gear range selected by the driver, the PCM compares the voltage combination on the signal circuits to a TR switch combination table stored in memory. Refer to Transmission Range Switch Logic .
When the PCM detects an invalid combination of TR switch signals, DTC P0705 sets. DTC P0705 is a type A DTC.
Refer to Range Reference .
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC P0705 Transmission Range (TR) Switch Circuit
Conditions for Running the DTC
System voltage is 11 volts or greater.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Incorrect combination of 2 or more transmission range switch signals, with the TR Sw. Forward Range signal input LOW at the same time, for 1 second or greater. |
| • | The TR Sw. Forward Range signal input is LOW when P, R, N or L gear range is selected, for 1 second or greater. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The PCM limits the transmission shift to 2nd and 3rd gears. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions when the Conditions for Setting the DTC are met. The PCM stores this information as Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
| • | The PCM stores DTC P0705 in PCM history. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test runs and passes. |
| • | A scan tool can clear the MIL/DTC. |
| • | The PCM clears the DTC from PCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without an emission related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The PCM cancels the DTC default actions when the ignition switch is OFF long enough in order to power down the PCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | Inspect the connectors at the PCM, the output speed sensor, and all other circuit connecting points for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the circuit wiring for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect for a shorted TR switch wire. |
| • | Inspect for a faulty TR switch. |
| • | Inspect for an internal fault of the PCM. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
By disconnecting the TR switch, the ground path for all TR switch circuits are removed and the PCM should recognize all circuits as open. The scan tool should display HI for all range signals.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring for an open or lack of signal voltage from the PCM.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring and the PCM by providing a ground path through a fused jumper wire. When grounded, the scan tool range signal park should change to LOW.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring and the PCM by providing a ground path through a fused jumper wire. When grounded, the scan tool range signal reverse should change to LOW.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring and the PCM by providing a ground path through a fused jumper wire. When grounded, the scan tool range signal neutral should change to LOW.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring and the PCM by providing a ground path through a fused jumper wire. When grounded, the scan tool range signal drive should change to LOW.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring and the PCM by providing a ground path through a fused jumper wire. When grounded, the scan tool range signal intermediate should change to LOW.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring and the PCM by providing a ground path through a fused jumper wire. When grounded, the scan tool range signal forward should change to LOW.
-
This step tests the TR switch wiring and the PCM by providing a ground path through a fused jumper wire. When grounded, the scan tool range signal low should change to LOW.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle in Vehicle DTC Information | ||||||||||||
2 |
Does TR Sw. parameter display match each transmission range selection? | -- | Go to Intermittent Conditions in Engine Controls - 3.5L (L66) | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||||
3 |
Did you find and correct a condition? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||||||
4 | With the scan tool, observe the TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. Do the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters indicate HI for all range signal states? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||||||
Do the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters indicate HI for all range signal states? | -- | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 14 | |||||||||||||
Does the voltage measure within the specified range at all circuits? | 10-12 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 15 | |||||||||||||
Connect a 3 amp fused jumper wire from the TR switch park signal circuit 10-way connector to ground, while monitoring the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. When the TR switch park signal circuit is grounded, do any other signal circuits indicate LOW? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 8 | |||||||||||||
Connect a 3 amp fused jumper wire from the TR switch reverse signal circuit 10-way connector to ground, while monitoring the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. When the TR switch reverse signal circuit is grounded, do any other signal circuits indicate LOW? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 9 | |||||||||||||
Connect a 3 amp fused jumper wire from the TR switch neutral signal circuit 10-way connector to ground while monitoring the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. When the TR switch neutral signal circuit is grounded, do any other signal circuits indicate LOW? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 10 | |||||||||||||
Connect a 3 amp fused jumper wire from the TR switch drive signal circuit 10-way connector to ground while monitoring the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. When the TR switch drive signal circuit is grounded, do any other signal circuits indicate LOW? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 11 | |||||||||||||
Connect a 3 amp fused jumper wire from the TR switch intermediate signal circuit 10-way connector to ground while monitoring the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. When the TR switch intermediate signal circuit is grounded, do any other signal circuits indicate LOW? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 12 | |||||||||||||
Connect a 3 amp fused jumper wire from the TR switch forward signal circuit 10-way connector to ground while monitoring the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. When the TR switch forward signal circuit is grounded, do any other signal circuits indicate LOW? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 | |||||||||||||
Connect a 3 amp fused jumper wire from the TR switch low signal circuit 10-way connector to ground, while monitoring the scan tool TR Sw. P/R/N, TR Sw. D/I/L and the TR Sw. Forward Range parameters. When the TR switch low signal circuit is grounded, do any other signal circuits indicate LOW? | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||||||||
14 | Test the TR switch signal circuits that did not indicate HI for a short to ground. Refer to Testing for Short to Ground and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||||
15 | Test the TR switch signal circuits that did not indicate proper voltage for an open. Refer to Testing for Continuity and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||||
16 | Test the affected signal circuits of the TR switch for a shorted together condition. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||||
17 | Test the TR switch ground circuit for an open. Refer to Testing for Continuity and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||||||
18 | Replace the TR switch. The TR switch is part of the park/neutral position switch. Refer to Park/Neutral Position Switch Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||||||||
19 |
Important: Always perform the PCM set up procedure.
Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 20 | -- | ||||||||||||
20 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Has the test run and passed? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||||
21 | With the scan tool, observe the stored information, capture info and DTC info. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle in Vehicle DTC Information | System OK |
