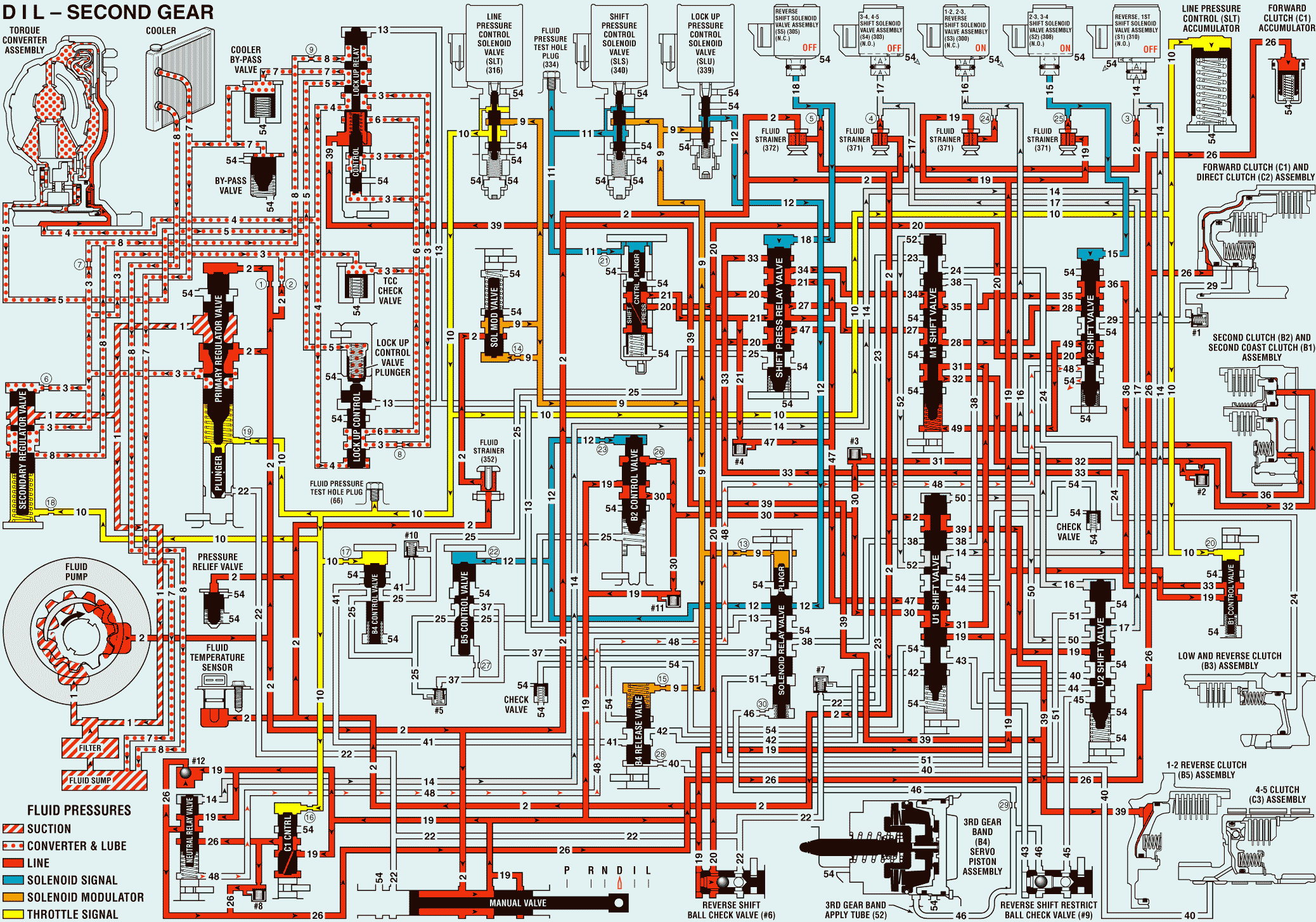
As vehicle speed increases and operating conditions become appropriate, the TCM de-energizes the reverse, 1st shift solenoid valve assembly (S1) and energizes the 2-3, 3-4 shift solenoid valve assembly (S2) to shift the transmission into Second gear. The manual valve remains in the DRIVE (D) position and line (2) pressure continues to feed the drive (19) fluid circuit.
SECOND CLUTCH (B2) ASSEMBLY APPLIES
Reverse, 1st Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Assembly (S1)
The reverse, 1st SS valve assembly is de-energized, allowing fluid pressure in the S1 signal (14) fluid circuit and the reverse inhibit (52) fluid circuit to exhaust through the solenoid.
M1 Shift Valve
When reverse inhibit (52) fluid exhausts, spring force shifts the M1 shift valve to the released position. This allows B2 control 2 (31) fluid to pass through the valve into the second clutch (32) fluid circuit.
#2 Accumulator Check Valve Assembly
Second clutch (32) fluid pressure is routed to the #2 accumulator check valve assembly and moves the check valve against spring force in order to help cushion the apply of the second clutch.
Second Clutch (B2) Assembly
Second clutch (32) fluid is routed to the second clutch piston to apply the second clutch plates.
SECOND COAST CLUTCH (B1) ASSEMBLY APPLIES
M1 Shift Valve
B1 control 2 (34) fluid is routed through the M1 shift valve into the B1 control 3 (35) fluid circuit.
2-3, 3-4 Shift Solenoid (SS) Valve Assembly (S2)
The 2-3, 3-4 SS valve assembly is energized, causing fluid pressure to build-up in the S2 signal (15) fluid circuit.
M2 Shift Valve
S2 signal (15) fluid is routed to the M2 shift valve and applies the valve against spring force, allowing B1 control 3 (35) fluid to pass through the valve into the second coast clutch (36) fluid circuit.
Second Coast Clutch (B1) Assembly
Second coast clutch (36) fluid is routed to the second coast clutch piston to apply the second coast clutch plates.
FLUID PRESSURE DIRECTED IN PREPARATION FOR A SHIFT TO THIRD GEAR
Shift Pressure Relay Valve
Drive or reverse (20) fluid passes through the shift pressure relay valve into the PN12345 (47) fluid circuit.
U1 Shift Valve
PN12345 (47) fluid is routed to the U1 shift valve where it is blocked by the valve in preparation for an upshift to third gear.
Important: Power flow for Intermediate and Low Range - Second Gear is exactly the same as Drive Range - Second Gear.
PASSAGES
- SUCTION
- LINE
- CONVERTER FEED
- RELEASE
- APPLY
- EXHAUST ENABLE
- COOLER
- LUBE
- SOLENOID MODULATOR
- THROTTLE SIGNAL (SLT)
- SHIFT CONTROL (SLS)
- LOCK UP CONTROL (SLU)
- TCC SIGNAL
- S1 SIGNAL
- S2 SIGNAL
- S3 SIGNAL
- S4 SIGNAL
- S5 SIGNAL
- DRIVE
- DRIVE OR REVERSE
- REGULATED DRIVE OR REVERSE
- REVERSE
- REVERSE CLUTCH
- LOW AND REVERSE CLUTCH
- REVERSE CONTROL
- FORWARD CLUTCH
- DIRECT CLUTCH FEED 1
- DIRECT CLUTCH FEED 2
- DIRECT CLUTCH
- B2 CONTROL 1
- B2 CONTROL 2
- SECOND CLUTCH
- B1 CONTROL 1
- B1 CONTROL 2
- B1 CONTROL 3
- SECOND COAST CLUTCH
- B5 CONTROL 1
- B5 CONTROL 2
- 1-2 REVERSE (B5) CLUTCH
- 4-5 CLUTCH
- B4 CONTROL
- B4 RELEASE
- SERVO RELEASE
- SERVO FEED
- SERVO APPLY
- 3RD GEAR BAND APPLY
- PN12345
- PRN15
- 234NCON
- 345 ENABLE
- 45 ENABLE
- REVERSE INHIBIT
- VENT
- EXHAUST
- SUMP
- VOID
- TORQUE CONVERTER SEAL DRAINBACK
Drive, Intermediate and Low Range - Second Gear