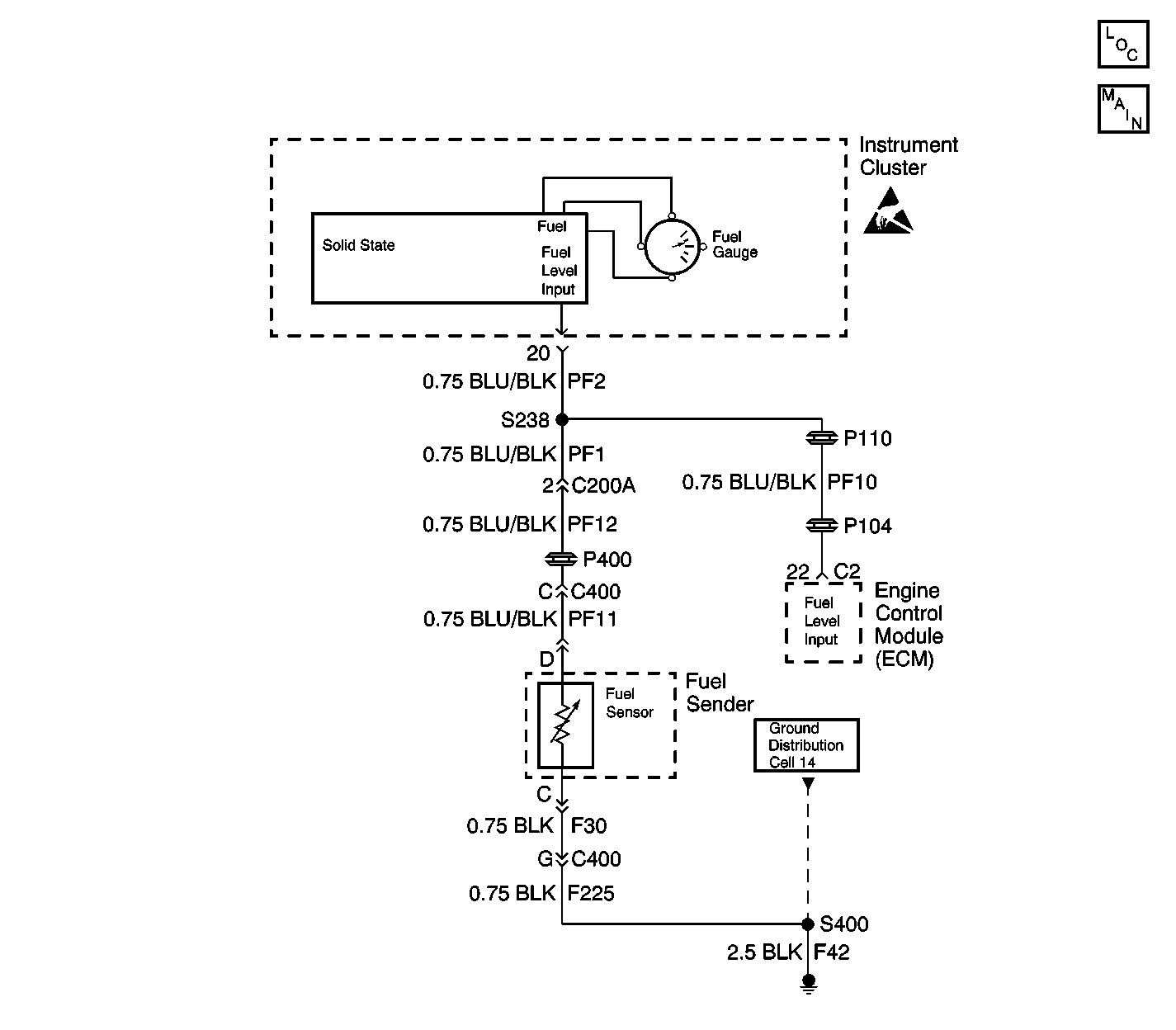
Circuit Description
A microprocessor in the instrument cluster sends voltage to the fuel tank sensor contained inside the fuel tank. A float arm attached to the sensor changes position with the fuel level in the tank. The fuel sensor is a variable resistor. As the fuel level changes, the resistance of the fuel sensor changes. The instrument cluster monitors changes in the voltage caused by the changes in the resistance of the sensor in order to determine the fuel level.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The fuel gauge circuit is tested every 100 ms. DTC 168 will set in the following ways:
| • | When the circuit is open. |
| • | Shorted to battery |
| • | The resistance of the fuel sensor is out of range (more than 350 ohms) for more than 8 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Stores a DTC 168 in memory. |
| • | The fuel gauge pointer will return to the zero position. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The resistance must be greater than 350 ohms for 4 seconds to clear the fault in the next monitoring cycle. |
| • | Conditions for the fault are no longer present. |
| • | Using a scan tool |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the DTC is a history or an intermittent DTC, perform the tests shown while moving related wiring harnesses and connectors. This can often cause the malfunction to appear. Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Visually inspect the harness and harness connectors for the following conditions: |
| - | Damage |
| - | Corrosion |
| - | Water intrusion |
| - | Adequate terminal tension |
| - | Mis-routed harness |
| - | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| - | Broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Before replacing the instrument cluster, test all power and ground circuits to the cluster. Refer to Measuring Voltage Drop in Wiring Systems. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This test determines if the fuel tank sensor has high resistance.
-
This test determines if system voltage is present. No voltage may indicate an open circuit.
-
After making a circuit repair, test the system again in order to see if the DTC resets. If the DTC resets, the instrument cluster most likely has an internal failure.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perfrorm the Instrument Cluster Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Is the resistance reading greater than the indicated value? | 350 ohms | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | |
3 | Replace the fuel tank sender. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 11 | -- |
Is the voltage within the specified range? | B+ | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 6 | |
5 |
Is the voltage less than the indicated value? | 0.1 V | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 |
6 |
Is the voltage reading within the specified range? | B+ | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 10 |
7 |
Is the voltage less than the indicated value? | 0.1 V | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 14 |
8 | Locate and repair the short to B+ in CKT PF12. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 11 | -- |
9 | Locate and repair the open circuit in CKT PF12. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 11 | -- |
10 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-5 ohms | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 13 |
Is a current DTC 168 set? | -- | Go to Step 12 | System OK | |
12 | Replace the instrument cluster. Refer to Instrument Cluster Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Locate and repair the open circuit between instrument cluster connector terminal 20 and C200A terminal 2. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 11 | -- |
14 | Locate and repair the short to B+ in CKTs PF1 or PF10. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Step 11 | -- |
