Circuit Description
The Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid is inside of the transmission adapter case. The PC solenoid valve is an electronic device that regulates transmission line pressure based on the current flow through its coil winding. The magnetic field produced by the coil moves the solenoid's internal valve which varies pressure to the pressure regulator valve. The transmission control module (TCM) controls the PC solenoid valve by applying a varying amount of amperage to the solenoid.
The PC Solenoid is supplied power via the Transmission Power Relay (internal to the TCM). The TCM controls the solenoid by grounding the control circuit via an internal solid state device called a driver. The applied amperage can vary from 0.1 to 1.1 amps. Low amperage (0.1 amp) indicates high line pressure. High amperage (1.1 amps) indicates low line pressure. The duty cycle of the PC solenoid valve is expressed as a percentage of energized ON time. Zero percent indicates zero ON time (non-energized) or no current flow. Approximately 60% at idle indicates maximum ON time (energized) or high current flow. The TCM determines the appropriate line pressure for a given load by comparing the throttle position (TP) voltage, the engine speed and other inputs from the engine control module (ECM).
When the TCM detects a continuous open, short to power or a short to ground in the PC solenoid valve circuit or the PC solenoid valve, then DTC P0748 sets. DTC P0748 is a type B DTC.
Conditions For Running The DTC
| • | The ignition switch is in the RUN position. |
| • | High side driver is closed. |
| • | TCM is commanding PC solenoid current. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The TCM detects any one of the two conditions for 0.54 seconds.
| • | Open or short to ground (feedback voltage is low). |
| • | Short to power (feedback voltage remains high). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | Early production - The TCM illuminates the service transmission lamp (STL) and sends a MIL request to the ECM on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. The ECM then illuminates the MIL. |
| • | Late production - The TCM flashes the Sport Mode Lamp and sends a MIL request on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. The TCM then illuminates the MIL. |
| • | The ECM records the operating conditions in the Freeze Frame at the time of the MIL request from the TCM. |
| • | The transmission operates in the default mode (maximum line pressure, command 4th gear, inhibit TCC, freeze shift adapts). |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | Early production - The TCM turns off the STL as soon as the fault is no longer present. |
| • | Late production - The TCM stops flashing the sport mode lamp as soon as the fault is no longer present. |
| • | The ECM turns off the MIL after three consecutive drive trips during which the TCM sends no MIL request. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are present by this diagnostic or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | The scan tool clears the MIL/DTC. |
| • | The TCM cancels the DTC default mode actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is Off long enough in order to power down the TCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
Vehicles equipped with Fuel Cap Lamps utilize the Sport Mode lamp to indicate a transmission malfunction. In these vehicles, the Sport Mode Lamp flashes at 200 millisecond intervals when the TCM commands the lamp ON.
Vehicles not equipped with Fuel Cap Lamps are equipped with a dedicated Service Transmission Lamp (STL) on the Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC). The STL illuminates steadily when the TCM commands the lamp ON.
Use the J 35616-A connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the TCM harness connector or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connections at the TCM or at the component. Inspect the harness connectors for any backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems for proper procedure. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving any related connectors and any wiring harnesses. A change in the display may help to locate the fault. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step will determine if the adapter case connector is disconnected or possibly loose.
-
Listen for an audible click when the solenoid operates. Ground the circuit repeatedly if necessary.
-
If the PC solenoid valve checks out OK and no condition is found with the connections at the TCM, check the wiring and connections closely. If no condition is found, the TCM may be the cause of the condition.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
Important: Before clearing the DTC, use the Scan Tool in order to record the Failure Records. Using the Clear Info function erases the Failure Records from the ECM/TCM. Is the resistance lower than the specified value? | 1.5 ohms | |||
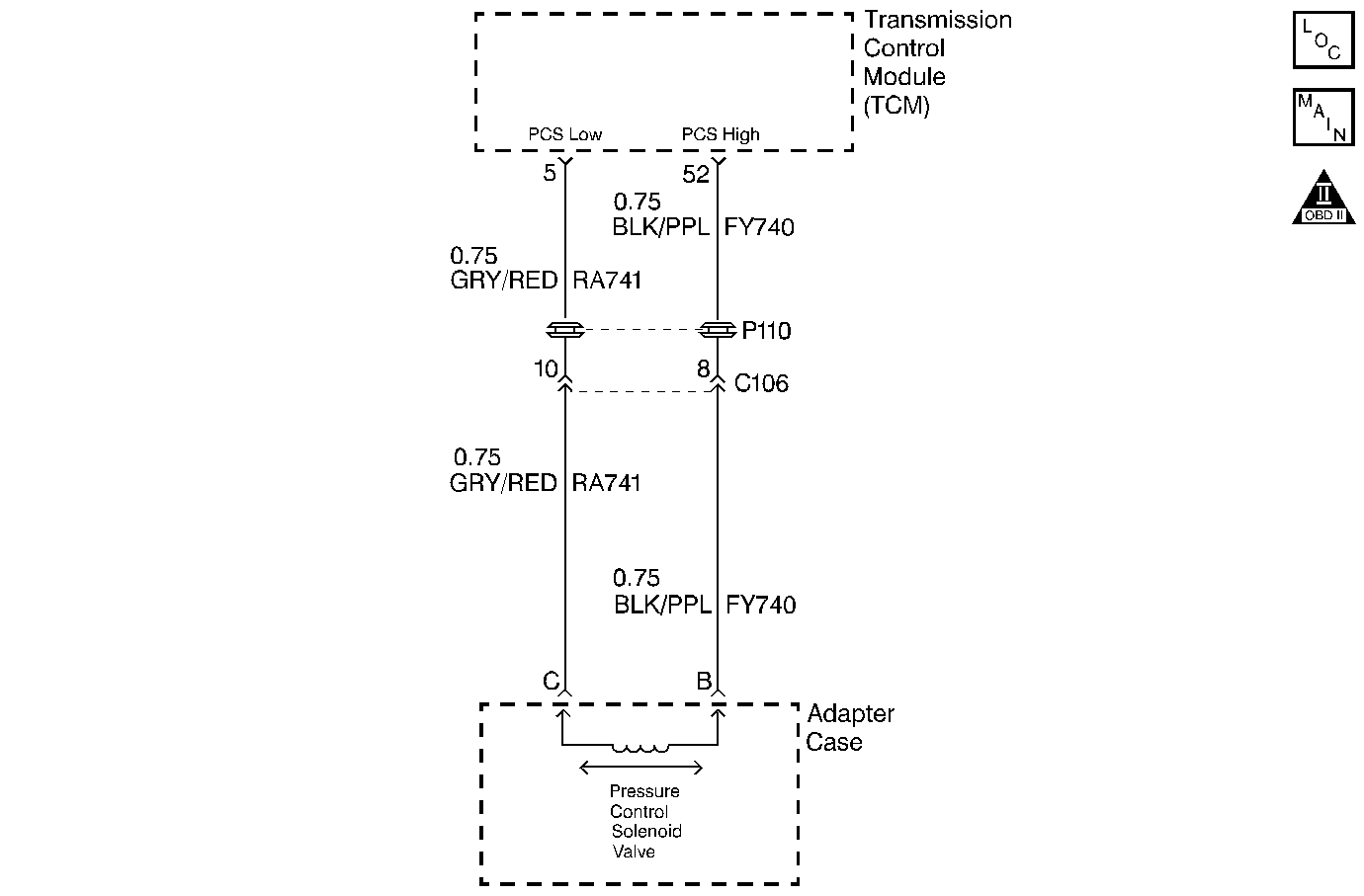
Measure the resistance from terminal 52 of the TCM connector to ground. Is the resistance greater than the specified value? | 250K ohms | |||
4 | Measure for the presence of voltage at terminal 52 of the TCM connector. Is voltage measured? | -- | ||
5 | Measure the resistance between terminal 5 of the TCM connector and terminal C of the 4-way transmission adapter case connector. Is the resistance lower than the specified value? | 1.5 ohms | ||
6 | Measure the resistance from terminal 5 of the TCM connector to ground. Is the resistance greater than the specified value? | 250K ohms | ||
7 | Measure for the presence of voltage at terminal 5 of the TCM connector. Is voltage measured? | -- | ||
8 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find an open? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a short to ground condition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
10 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a short to voltage condition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
11 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find an open condition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
12 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a short to ground condition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
13 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a short to voltage condition? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
14 | Measure the resistance between terminal B and terminal C at the transmission side of the 4-way transmission adapter case connector. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 3.5-5.5 ohms | ||
15 | Is the resistance greater than the specified value? | 5.5 ohms | ||
16 | Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 3.5 ohms | -- | |
17 | Measure the resistance between terminal B to ground. Is the resistance greater than the specified value? | 250K ohms | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
18 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find an open condition? | -- | ||
19 |
Refer to General Electrical Diagnosis in Wiring Systems. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a shorted condition? | -- | ||
20 | Replace the internal transmission wiring harness Refer to Control Valve Body . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
21 | Replace the pressure control solenoid valve. Refer to Converter Clutch Solenoid . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |
22 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair.
Is DTC P0748 set? | -- | System OK |
