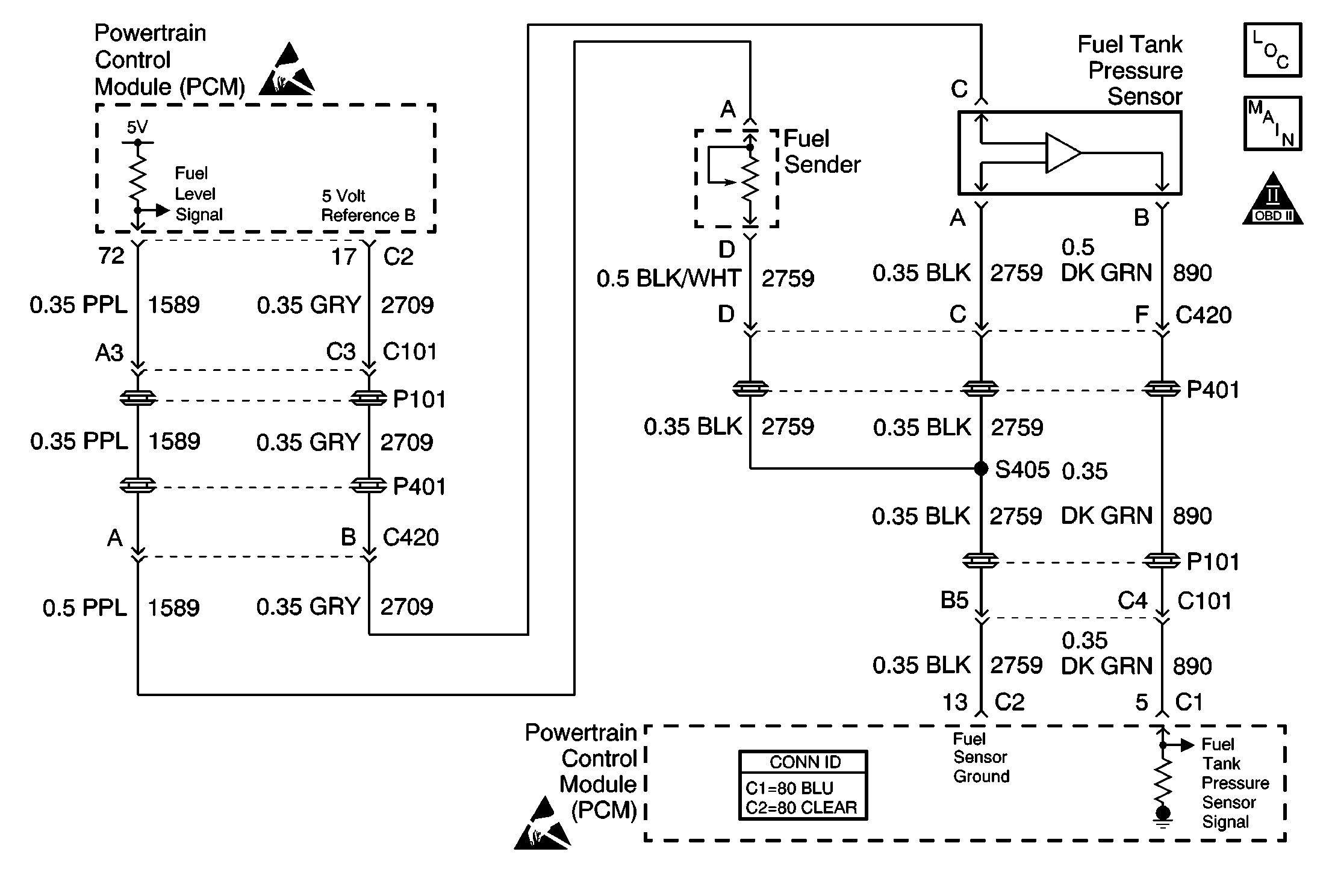
Circuit Description
The fuel level sensor is device used to determine the level of fuel in the tank. The PCM applies an ignition voltage to the sensor. The sensor varies the voltage based on the level of fuel in tank. The sensor resistance is high when the tank is full, and the PCM senses a high signal voltage. As the fuel level in the tank decreases, the sensor resistance drops, and the signal voltage at the PCM is pulled low. The PCM uses the fuel level input run certain system tests. Some of these system tests include the following:
| • | EVAP system |
| • | Misfire |
| • | Oxygen sensor |
The PCM also sends the fuel level information via class 2 serial data to the IPC. The IPC uses the information to control the fuel gauge.
The PCM requires an accurate indication of fuel level for EVAP system diagnosis. The PCM monitors the fuel level sensor for signal voltages outside the normal range of the sensor. If the PCM detects a signal voltage below the calibrated range of the sensor, DTC P0462 will set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The ignition is ON. |
| • | System voltage is between 11 and 16 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM detects a fuel level sensor voltage that is less than 0.4 volt for at least 10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The PCM will store the conditions present when the DTC set as Failure Records data only. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
Important: Fuel level is used to determine EVAP system diagnosis. Always diagnose the fuel level sensor before any other EVAP system components or DTCs.
For additional diagnostic information, refer to Diagnostic System Check - Instrument Cluster in Instrument Panel, Gauges, and Console.
| • | Check for poor connections at the PCM and/or the fuel level sensor. |
| Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Damage harness--Inspect the wiring harnesses for damage. |
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may assist in diagnosing the condition. The information may help determine how often the condition that set the DTC occurs.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 | Are there any Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC) DTCs set? | -- | Diagnose the IPC DTCs first | |
3 |
Does the fuel level gauge indicate FULL? | -- | ||
4 |
Does the fuel gauge indicate EMPTY? | -- | ||
5 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||
6 | Replace the fuel level sensor. Refer to Fuel Level Sensor Replacement . Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
7 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 |
Does the scan tool indicate that DTC P0462 failed this ignition? | -- | System OK |
