Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis LD9
Diagnosis
| • | EVAP canister purge valve operation is covered in this section and diagnosed in DTCs P0440, P0446, and P1441. |
| • | EVAP vent solenoid operation is covered in this section and diagnosed in DTCs P0440, P0442, and P0446. |
| • | Fuel tank vapor pressure sensor operation is covered in this section and diagnosed in DTCs P0440, P0442, P0446, P1441 and Evaporative Emission System Check. |
| • | A open or shorted circuit in the EVAP canister purge valve and EVAP vent solenoid can also be diagnosed in Powertrain Control Module Outputs Diagnosis . |
Visual Check of the EVAP Canister
If cracked or damaged, replace canister. Refer to EVAP Canister Replacement .
Circuit Description
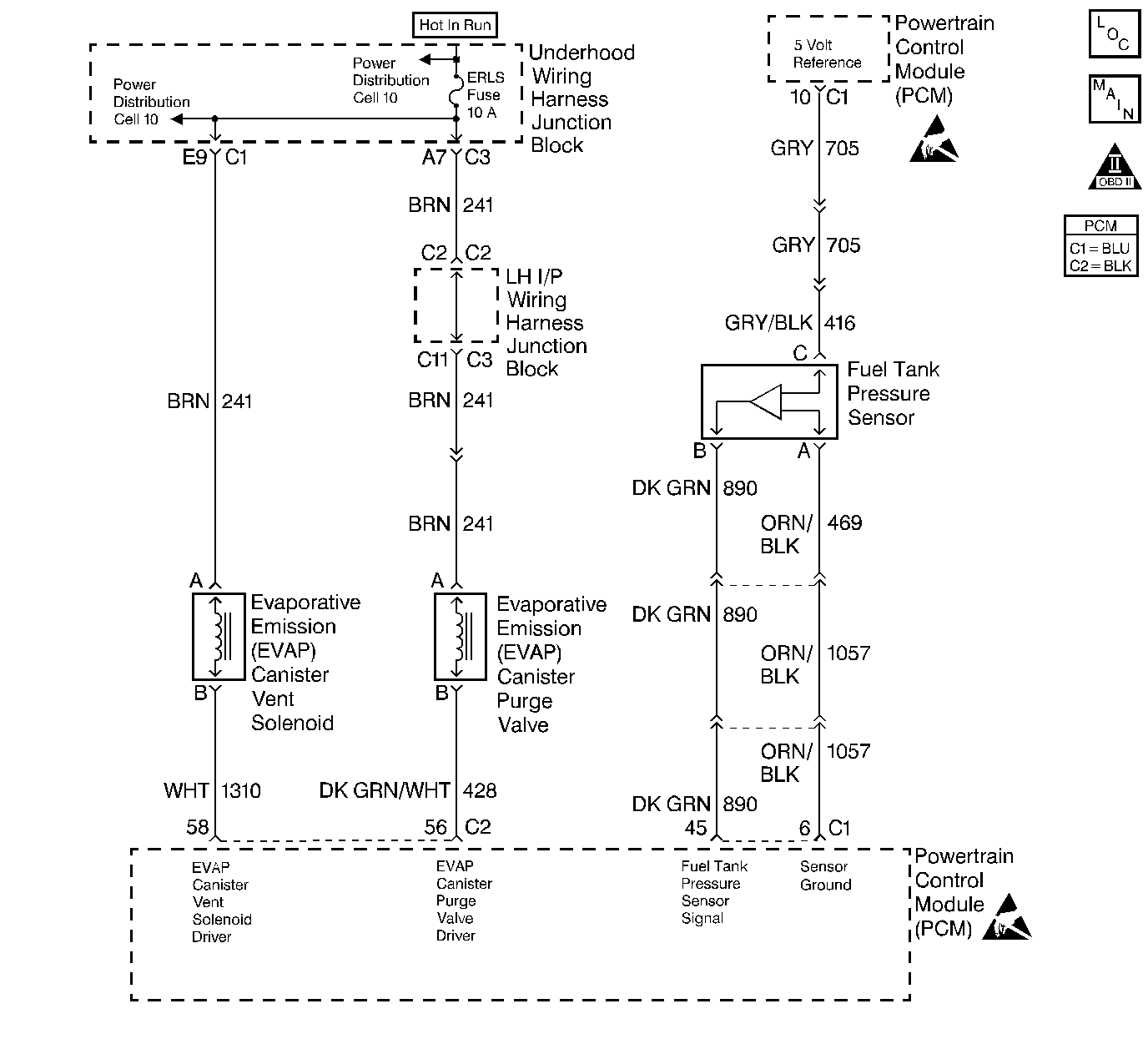
The evaporative emission system is checked by applying vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring for a vacuum decay. The PCM monitors the vacuum level through the fuel tank vapor pressure sensor signal. At an appropriate time, the EVAP canister purge valve and the EVAP vent solenoid are turned ON, allowing the engine to draw a small vacuum on the entire evaporative emission system. After the desired vacuum level has been achieved, the EVAP canister purge valve is turned OFF, sealing the system. A leak is detected by monitoring for a decrease in vacuum level over a given time period, when all other variables remain constant. A leak, blockage or faulty component in the system will cause a DTC to be set.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor electrical connection at PCM. Inspect harness electrical connectors for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed |
| - | Damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wire connection |
| • | Damaged harness--Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the Fuel Tank Vacuum Pressure display on the scan tool while moving electrical connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Incorrect purge or vacuum source line routing. Verify that the source vacuum and purge lines to the EVAP canister purge solenoid valve are not switched. |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||
2 | Are any DTCs set? | -- | Go to DTC Diagnostic Tables first | |
3 |
Is the fuel tank pressure at the specified value? | 0 in. H2O (1 in. H2O) | ||
4 |
Important:: Before continuing with diagnosis, zero the EVAP Pressure and Vacuum gauges on the EVAP pressure/purge cart J 41413 (refer to tool operating instructions).
Is the fuel tank pressure at the second specified value? | 5 in. H2O 5 in. H2O (± 2 in. H2O) | ||
5 | Observe the EVAP system Pressure on the EVAP pressure/purge cart J 41413 while commanding the vent solenoid OFF (Open). Does the EVAP system pressure decrease to the specified value within 5 seconds? | 0 in. H2O | Go to DTC P0446 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Vent System Performance | |
6 |
Is the fuel tank pressure decreasing? | 1500 RPM | Go to DTC P1441 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Flow During Non-Purge | |
7 |
Is the fuel tank pressure decreasing? | 1500 RPM | System OK If a driveability symptom exists, refer to Symptoms |
Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor

Diagnosis
| • | EVAP canister purge valve operation is covered in this section and diagnosed in DTCs P0440, P0446, and P1441. |
| • | EVAP vent solenoid operation is covered in this section and diagnosed in DTCs P0440, P0442, and P0446. |
| • | Fuel tank vapor pressure sensor operation is covered in this section and diagnosed in DTCs P0440, P0442, P0446, P1441 and Evaporative Emission System Check. |
| • | A open or shorted circuit in the EVAP canister purge valve and EVAP vent solenoid can also be diagnosed in Powertrain Control Module Outputs Diagnosis . |
Visual Check of the EVAP Canister
If cracked or damaged, replace canister. Refer to EVAP Canister Replacement .
Circuit Description
The fuel tank pressure sensor is used to detect vacuum decay and excess vacuum during the EVAP diagnostic routine. The sensor responds to changes in fuel tank pressure or vacuum. The signal voltage to the PCM varies from a minimum of about 0.2 volts with pressure in the fuel tank to above 4 volts with a high vacuum in the fuel tank.
The Fuel Tank Pressure display on the scan tool has an auto zero feature which occurs at each ignition cycle and is corrected according to barometric pressure. Because of this,Fuel Tank Pressure may not accurately reflect the actual output of the sensor or conditions within the fuel tank.
The Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Diagnosis is intended to isolate and diagnose electrical problems with the sensor wiring or the sensor.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Inspect the PCM harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and for poor terminal to wire connections. |
| • | Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the Fuel Tank Pressure display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the fault. |
Test Description
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to use the Capture Info selection on the scan tool. This creates an electronic copy of the freeze frame data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
Refer to the Fuel Tank Replacement portion of the service manual for the fuel tank removal procedure.
-
A normal fuel tank pressure sensor voltage output with no pressure or vacuum on the fuel system should be between 1.3 V and 1.7 V.
-
Reprogram the replacement PCM and perform the crankshaft position system variation learning procedure. Refer to the latest Techline procedure for the PCM reprogramming and also refer to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) for the Crankshaft variation learning procedure.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5.0 V | |||
3 | Connect the DVM to ground and probe the 5.0 volt reference circuit for the specified voltage. Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5.0 V | ||
4 | Check the 5.0 volt reference circuit for a poor electrical terminal connection at the PCM. Was a problem present? | -- | ||
5 | Check for an open or for a grounded 5.0 volt reference circuit to the fuel tank pressure sensor harness electrical connector. Was a problem present? | -- | ||
Is the voltage between the specified values? | 1.3-1.7 V | |||
7 | Check the fuel tank pressure sensor signal circuit for a poor electrical terminal connection at the PCM and repair the circuit as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
8 | Check the fuel tank pressure signal circuit between the fuel tank pressure sensor electrical connector and the PCM for an open, a short to ground, or for a short to voltage and repair the circuit as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
9 | Check the fuel tank pressure sensor ground circuit for a poor electrical terminal connection at the PCM and repair the circuit as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
10 | Check for an open in the fuel tank pressure sensor ground circuit. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
11 | Check for a poor electrical terminal connection at the fuel tank pressure sensor electrical connector and repair the connection as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
12 | Replace the malfunctioning harness connector electrical terminals as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Locate and repair an open or short to ground in the wiring harness as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
14 | Replace the fuel tank pressure sensor. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- |
