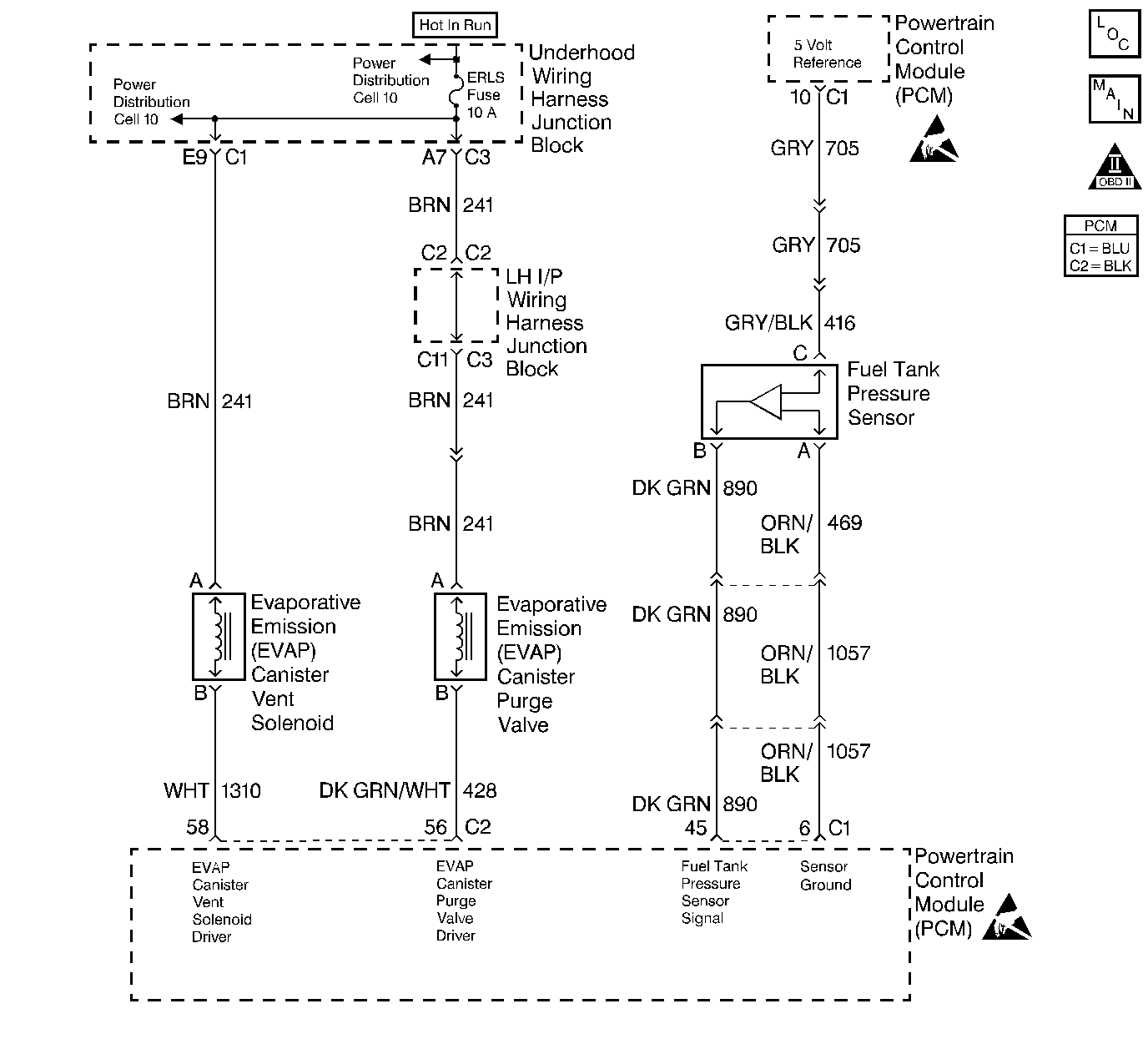
Circuit Description
The evaporative system includes the following components:
| • | The fuel tank |
| • | The EVAP vent solenoid |
| • | The fuel tank pressure sensor |
| • | The fuel pipes and hoses |
| • | The fuel vapor lines |
| • | The fuel cap |
| • | The EVAP canister |
| • | The purge lines |
| • | The EVAP canister purge valve |
| • | The EVAP service port |
The evaporative emission system is checked by applying vacuum to the EVAP system and by monitoring for a vacuum decay. The PCM monitors the vacuum level through the fuel tank pressure sensor signal. At an appropriate time, the EVAP canister purge valve and the EVAP vent solenoid are turned ON, allowing the engine to draw a small vacuum on the entire evaporative emission system. Once the desired vacuum level has been achieved, the EVAP canister purge valve turns OFF, sealing the system. Detect for any leaks by monitoring for a decrease in the vacuum level over a given time period when all of the other variables remain constant. A small leak in the system will cause DTC P0442 to set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134 and P1133 are not set. |
| • | The BARO is greater than 75 kPa. |
| • | The intake air temperature is between 5°C and 29°C (41°F and 84°F) at the engine start up. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature is between 5°C and 29°C (41°F and 84°F) at the engine start up. |
| • | The Intake Air Temperature is not more than 1°C (2°F) greater than the Engine Coolant Temperature at the engine start up. |
| • | The Engine Coolant Temperature is not more than 7°C (12°F) greater than the Intake Air Temperature at the engine start up. |
| • | The fuel tank level is between 26 percent and 74 percent. |
| • | The TP sensor is between 9 percent and 35 percent. |
| • | The EVAP solenoid is at 50 percent PWM within 65 seconds of the engine run time. |
| • | A vacuum decay condition indicating a small leak is detected during the diagnostic test. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) illuminates. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time when the diagnostic fails. This information stores in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
| • | The coolant fan turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
Although this DTC is considered a type A diagnostic (refer to Powertrain Control Module (Serial Data Communication) ), this DTC acts like a type B diagnostic under certain conditions. Whenever this diagnostic reports that the system has passed, or if the battery is disconnected, the diagnostic must fail twice before setting a DTC. The initial failure does not report to the diagnostic executive or display on a scan tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic executive immediately.
If a DTC P0460 is set along with an EVAP System DTC, the EVAP DTC cannot be considered valid until you repair and clear DTC P0460.
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Any missing or damaged O-rings at the fuel vapor and the EVAP purge line canister fittings. |
| • | A cracked or a punctured EVAP canister. |
| • | A damaged source vacuum line, EVAP purge line, EVAP vent hose, or fuel tank vapor line. |
| • | A poor connection at the PCM. Inspect the harness connectors for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed connectors |
| - | Damaged terminals |
| - | A poor terminal to wire connection |
| • | A damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness to the EVAP vent solenoid EVAP canister purge valve and the fuel tank pressure sensor for an intermittent open or short circuit. |
| • | Refer to Carbon Particle Removal from Evaporative Emission System for further procedure. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer(s) to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the fault occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
If a vent solenoid or an EVAP canister purge valve electrical fault is present, the purge system will not operate correctly. Repairing the electrical fault will very likely correct the condition that set DTC P0442.
-
This step checks the fuel tank pressure sensor at the ambient pressure.
-
This step forces the fuel tank pressure sensor to re-zero.
-
This step verifies that the fuel tank pressure sensor accurately reacts to the EVAP system pressure changes.
-
This step insures proper system integrity.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||
2 | Is DTC P0460 also set? | -- | ||||||||
Does the purge valve and vent solenoid click ON and OFF? | -- | |||||||||
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 0 in. H2O (±1 in. H2O) | |||||||||
5 | Did you disconnect the battery? | -- | ||||||||
Disconnect the battery. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||
|
Important: : Before continuing with this diagnosis, zero the EVAP Pressure and Vacuum gauges on the EVAP pressure/purge cart J 41413. Then, read the temperature variation instructions (refer to the tool operating instructions).
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 5 in. H2O 5 in. H2O (±2 in. H2O) | |||||||||
8 |
Important: Review the temperature variation instructions included with the J 41413 before performing this step.
Does the pressure decrease to less than the specified value within 2 minutes? | 15 in. H2O 10 in. H2O | Refer to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||
9 |
Can the specified vacuum be maintained? | 5 in. Hg | ||||||||
10 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
11 | Replace the EVAP vent solenoid. Refer to Diagnostic Aids . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
12 |
Were there any necessary repairs? | -- | ||||||||
13 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
|
Important: Review the temperature variation instructions included with the J 41413 before performing this step.
Does the pressure decrease to less than the specified value within 2 minutes? | 15 in. H2O 10 in. H2O | System OK |
