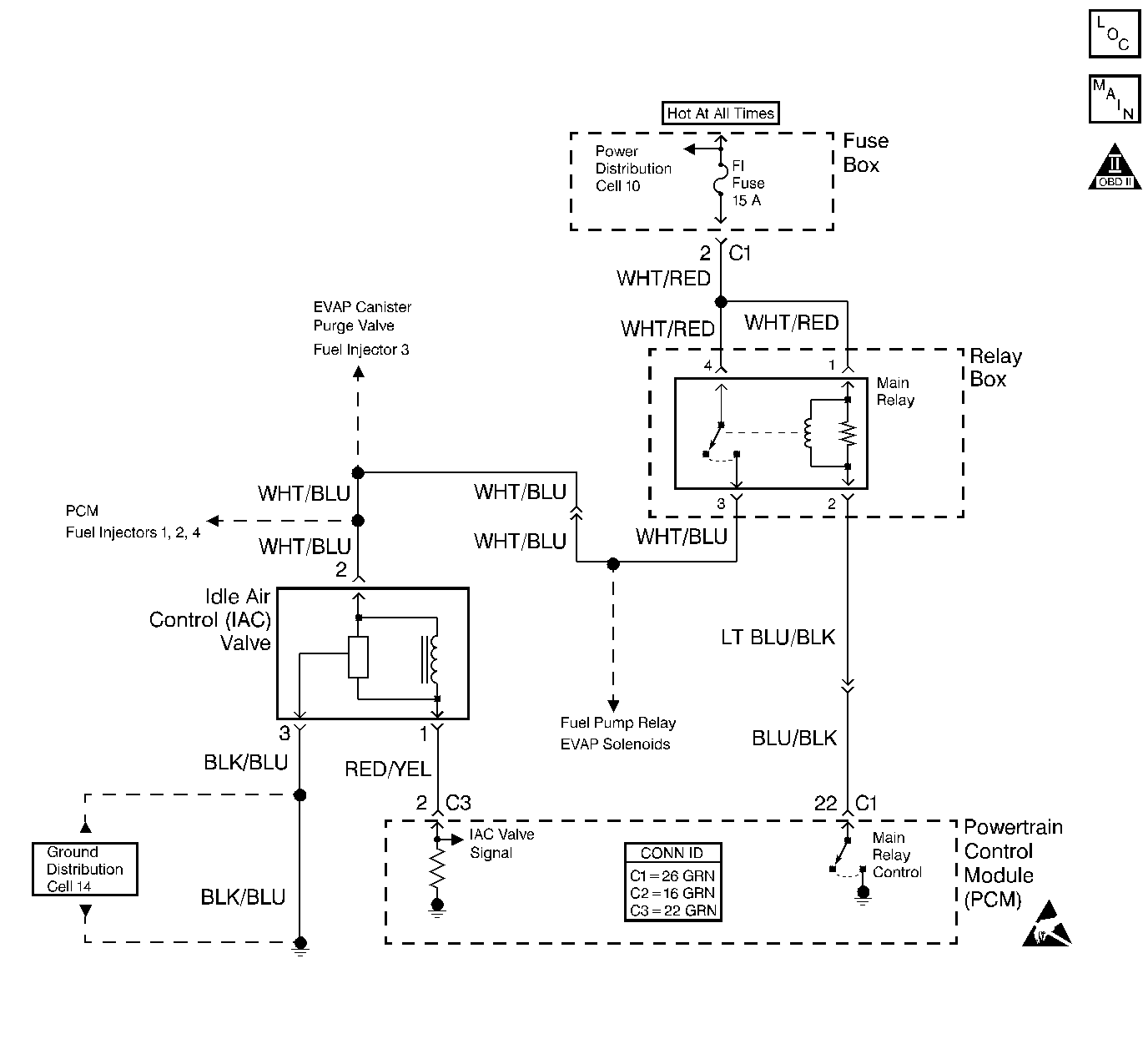
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the idle air control (IAC) valve to regulate the air flow through the idle air bypass passage. The amount of air flowing through the idle air bypass passage determines the idle speed. The IAC valve is regulated according to engine load. A stalling condition could be caused by the IAC valve not functioning properly.
Conditon for Running the DTC
| • | Engine coolant temperature is greater than 80°C (176°F). |
| • | The TP sensor indicates a closed throttle position. |
| • | The engine is running. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Engine idle speed is 100 RPM or less than the desired idle.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns off after three consecutive drive cycles without a fault present. |
| • | A DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear DTC Information function or disconnect the PCM battery feed in order to clear the DTC. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | An incorrect engine idle speed. Refer to Idle Speed Inspection . |
| • | A restricted air intake system. Check for a possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter element, or foreign objects blocking the air intake system. |
| • | Inspect the throttle body for any of the following conditions: |
| - | Check the throttle plate for smooth and even movement. |
| - | Check for excessive deposits in the IAC passage. |
| - | Check for excessive deposits in the throttle bore or on the throttle plate. |
| - | Check for objects blocking the IAC passage or the throttle bore. |
| • | Check for a large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that causes a large vacuum leak, such as a incorrectly installed or faulty crankcase ventilation valve or a disconnected brake booster hose. |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the IAC valve electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals. |
| • | Improper mating of terminals. |
| • | Broken electrical connector locks. |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals. |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connections. |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation. |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals. |
If a DTC P0506 cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining vehicle operating conditions when the DTC was first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain (OBD) System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
A visual and physical inspection may uncover a problem and reduce the diagnostic time.
-
This step checks the IAC valve battery positive voltage circuit for an open or a short.
-
This step checks the IAC valve battery positive voltage circuit for the correct voltage reading.
-
This step checks the IAC valve ground circuit.
-
This step checks the IAC valve control circuit for a short to voltage.
-
This step determines whether the fault is caused by the PCM or by the IAC valve.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||||||
2 |
Does the scan tool display indicate the IAC duty cycle is within the specified range? | 8% to 25% | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||||||
Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||||||||
Probe terminal 2 of the IAC valve electrical connector (harness side), using a DMM. Did the DMM read the specified value? | B+ | |||||||||||||
Repair the open or the short in the IAC valve battery positive voltage circuit between the IAC valve and the main relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||
7 | Probe terminal 3 of the IAC valve electrical connector (harness side), using a test lamp connected to battery positive voltage. Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||
8 | Repair the open in the IAC valve ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
Does the DMM indicate voltage? | -- | |||||||||||||
Does the engine speed fluctuate when the test lamp is contacting the terminal? | -- | |||||||||||||
11 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||||
12 | Replace the IAC Valve. Refer to Idle Air Control Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
13 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
14 |
Are any DTCs displayed on scan tool? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
