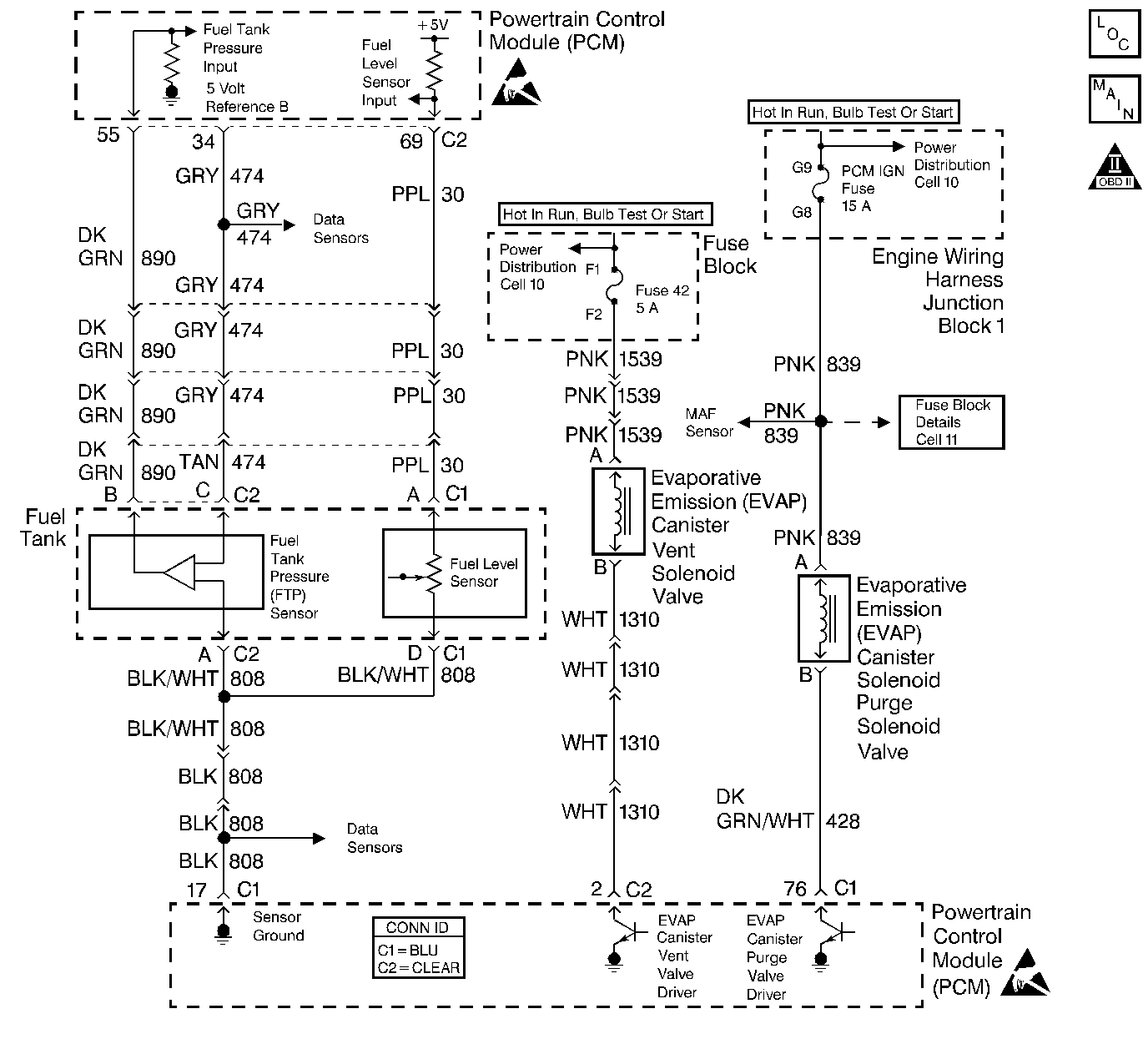
Circuit Description
The PCM uses the fuel level input in order to calculate the expected vapor pressures within the fuel system. These vapor pressures vary as the fuel level changes. The vapor pressure is critical in determining if the Evaporative Emissions System is operating properly. The PCM also uses the fuel level in order to determine if the fuel level is too high or too low to be able to accurately detect EVAP system malfunction.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The Fuel Level Sensor should be greater than 98% for greater than 25 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will not illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The PCM will store conditions which were present when the DTC set as Failure Records data only. This information will not be stored as Freeze Frame data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | A History DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear Info function. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | An intermittent problem may be caused by the following conditions: |
| - | Poor electrical connection |
| - | Rubbed through wire insulation |
| - | A wire that is broken inside the wire insulation |
| • | Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wire connection |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table:
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the malfunction occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step simulates a DTC P0462. If the PCM senses the change, then the PCM and the Fuel Level Sensor wiring are OK.
-
Replacement PCMs must be reprogrammed and the crankshaft position system variation procedure must be performed. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM reprogramming and also refer to the CKP System Variation Learn Procedure for the Crankshaft Position System Variation Procedure.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain on-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | |||
2 |
Is the Fuel Level sensor value greater than the specified value? | 98% | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
Is the Fuel Level sensor value less than the specified value? | 3.5% | |||
4 | Jumper the Fuel Level sensor signal circuit at the Fuel Level sensor electrical connector to chassis ground. Is the Fuel Level sensor value greater than the specified value? | 3.5% | ||
5 | Test for poor connections at the Fuel Level sensor and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
6 | Test the Fuel Level sensor ground circuit for an open and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
7 | Test the Fuel Level sensor signal circuit for an open and repair as necessary. Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
8 | Test for a poor Fuel Level sensor ground or a poor Fuel Level sensor signal circuit terminal connection at the PCM and replace the terminals if necessary. Did any of the terminal(s) need to be replaced? | -- | ||
9 | Replace the Fuel Level sensor. Refer to Fuel Level Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
|
Important: : The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Replace the PCM. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
11 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has ran and passed? | -- | ||
12 | Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTCs | System OK |
