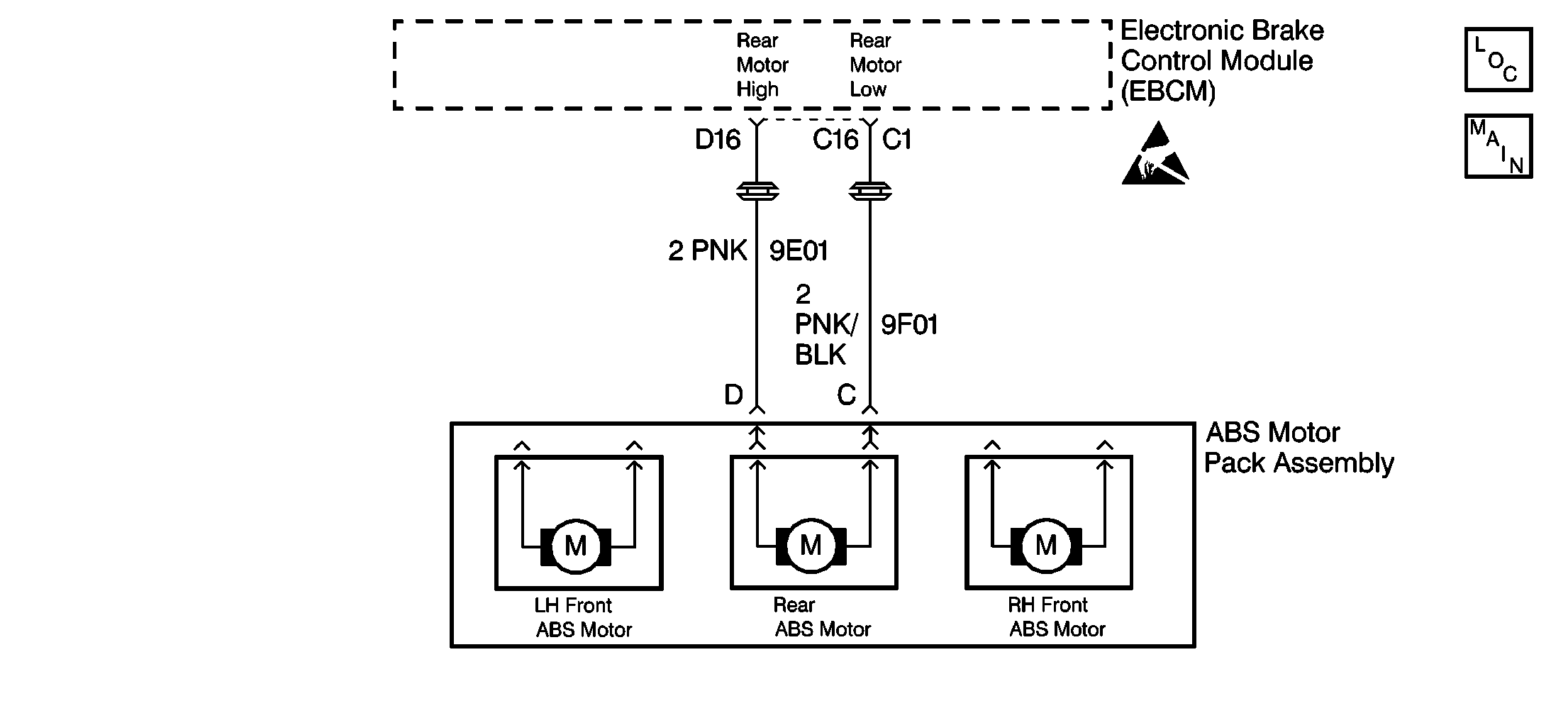
Circuit Description
DTC C1266 identifies an ABS motor circuit that shorts to voltage or an ABS motor that has low or zero resistance. The malfunction will cause one of the following conditions to occur:
| • | The ABS motor will not be controlled at the commanded current rate. |
| • | The ABS motor will turn in the opposite direction or not at all. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTC C1266 can set only when the ABS motor is commanded off. |
| • | A malfunction exists if The EBCM detects an out of range voltage on either of the rear ABS motor circuits. |
| • | An out of range voltage on either circuit indicates one of the following conditions: |
| - | A circuit is shorted to voltage. |
| - | An ABS brake motor is shorted internally. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC stores. |
| • | The ABS disables. |
| • | The ABS warning indicator turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition responsible for setting the DTC no longer exists and the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function is used. |
| • | 100 drive cycles pass with no DTCs detected. A drive cycle consists of starting the vehicle, driving the vehicle over 16 km/h (10 mph), stopping and then turning the ignition off. |
Diagnostic Aids
Use the Scan Tool Manual Control function to exercise ABS motor movement of affected channel in both directions while applying light pressure on the brake pedal.
An intermittent malfunction may be indicated if erratic or jumpy brake pedal movement is detected while performing an apply or release function of the ABS monitor.
If the malfunction is not current, use the following procedure to pinpoint an intermittent malfunction in the motor circuitry or connections:
- Wiggle the wires of the affected channel.
- Inspect if the DTC resets.
Use the enhanced diagnostic function of the Scan Tool in order to measure the frequency of the malfunction.
Clear the DTCs after completing the diagnosis. Test drive the vehicle for three drive cycles in order to verify that the DTC does not reset. Use the following procedure in order to complete one drive cycle:
- Start the vehicle.
- Drive the vehicle over 16 km/h (10 mph).
- Stop the vehicle.
- Turn the ignition to the OFF position.
Important: Zero the J 39200 test leads before making any resistance measurements. Refer to the J 39200 user's manual.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | |||||||||||||
2 | Does DTC C1266 occur intermittently? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||||
3 |
Do not start the engine. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 0-1 V | ||||||||||||||
4 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the voltage between the 6-way ABS brake motor pack harness connector terminal C and ground. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 0-1 V | ||||||||||||||
5 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||
6 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the 6-way ABS motor pack connector terminal C and the 6-way ABS motor pack connector terminal D. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0.2-1.5 ohms | ||||||||||||||
7 |
Is there damage that may cause a short to voltage? | -- | ||||||||||||||
8 |
Did DTC C1266 set as a current DTC in the last three drive cycles? | -- | ||||||||||||||
9 | Replace the ABS motor pack. Refer to ABS Motor Pack Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||
10 | Repair the short to voltage in CKT 9E01. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||
11 | Repair the short to voltage in CKT 9F01. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||
12 | Repair the short between CKT 9E01 and CKT 9F01. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||
13 | Replace all of the following components that are damaged:
Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||
14 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- | ||||||||||||
15 | The malfunction is intermittent or is not present at this time. Refer to Diagnostic Aids for more information. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- |
