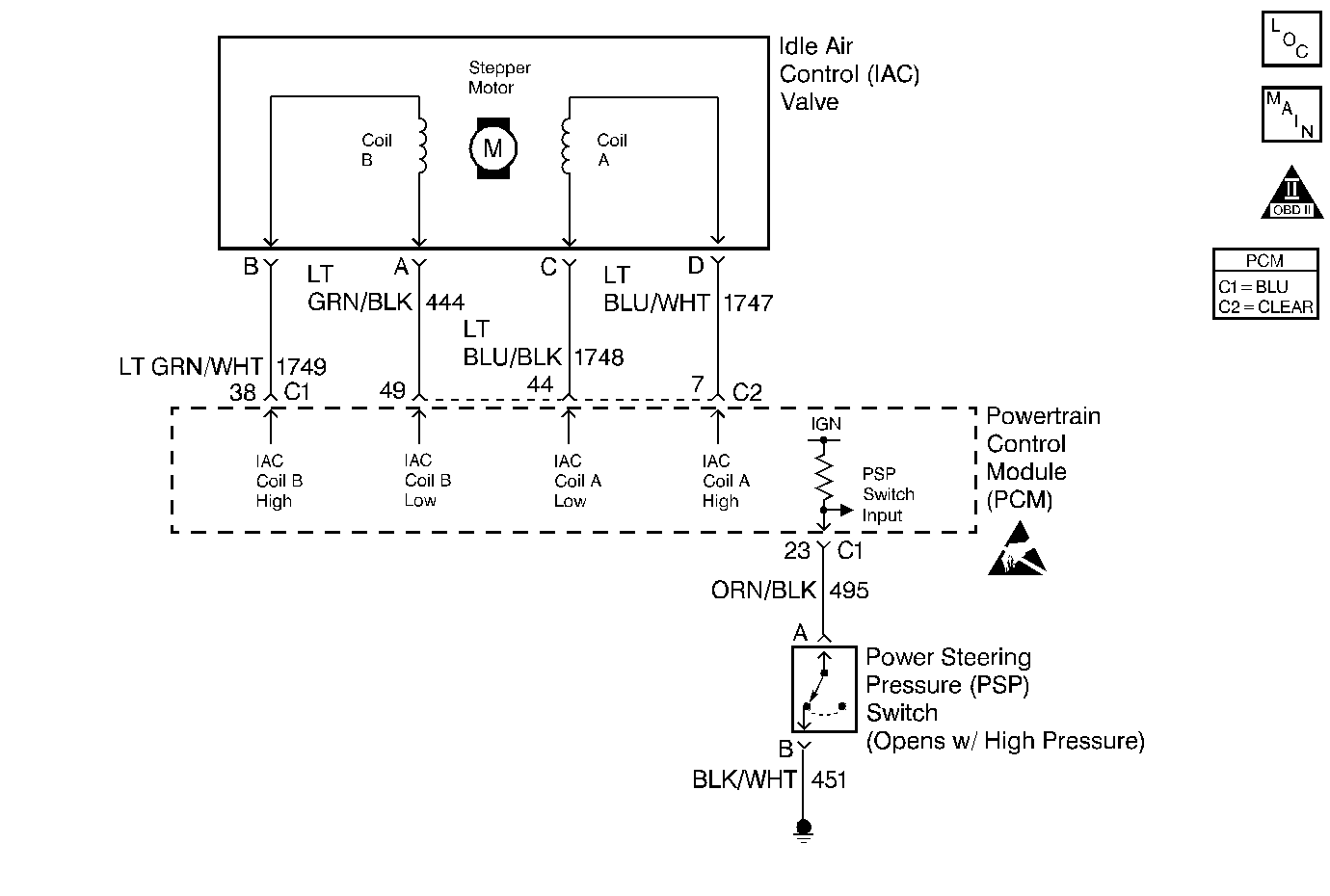
Circuit Description
The PCM controls engine idle speed by adjusting the position of the Idle Air Control (IAC) motor pintle. The IAC is a bi-directional motor driven by two coils. The PCM sends pulses (steps) to the IAC to extend or retract the IAC pintle into a passage in the throttle body to decrease or increase air flow. The commanded IAC position (displayed in counts) can be monitored on the scan tool; a higher number of counts indicates more commanded airflow (pintle retracted) This method allows highly accurate control of idle speed and quick response to changes in engine load. If the PCM detects a condition where too low of an idle speed is present and the PCM is unable to adjust idle speed by increasing the IAC counts, DTC P0506 will set indicating a problem with the idle control system.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No Fuel injector faults, Misfire, Fuel Trim, EVAP, EGR, VSS, TP, IAT, MAP, ECT, CKP or MAF sensor DTCs set. |
| • | BARO is greater than 65 kPa. |
| • | Engine has been running for at least 3 minutes. |
| • | System voltage is between 9 and 18 volts. |
| • | Engine Coolant Temperature is greater than 70°C (158°F). |
| • | Vehicle Speed is less than 3 MPH. |
| • | Intake Air Temperature is greater than -18°C (0°F). |
| • | The throttle is closed. |
| • | Conditions stable for at least 15 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
Engine Speed is more than 100 RPM lower than Desired Idle (negative idle speed error greater than 100 RPM).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL Off after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed (current DTC) clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if this or any other emission related diagnostic does not report any failures. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL/DTC. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM or IAC motor. Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. |
| • | Restricted air intake system. Check for a possible collapsed air intake duct, restricted air filter element, or foreign objects blocking the air intake system. |
| • | Throttle body. Check for objects blocking the IAC passage or throttle bore, excessive deposits in the IAC passage and on the IAC pintle, and excessive deposits in the throttle bore and on the throttle plate. |
| • | Large vacuum leak. Check for a condition that causes a large vacuum leak, such as a incorrectly installed or malfunctioning crankcase ventilation valve or brake booster hose disconnected. |
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||
2 | Are any other DTC(s) set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table. | |||||||||
3 |
Does Engine Speed remain within the specified value of Desired Idle for each RPM command? | ± 100 RPM | Refer to Diagnostic Aids. | |||||||||
4 |
Does each node light cycle red and green (never OFF)? | -- | ||||||||||
5 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||||
6 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||||
7 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||||
8 | Replace the IAC valve. Refer to Idle Air Control Valve Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||
9 |
Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||||
Replace the PCM. Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||
11 |
Does Engine Speed remain within the specified value of Desired Idle for each RPM command? | ± 100 RPM | ||||||||||
12 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
