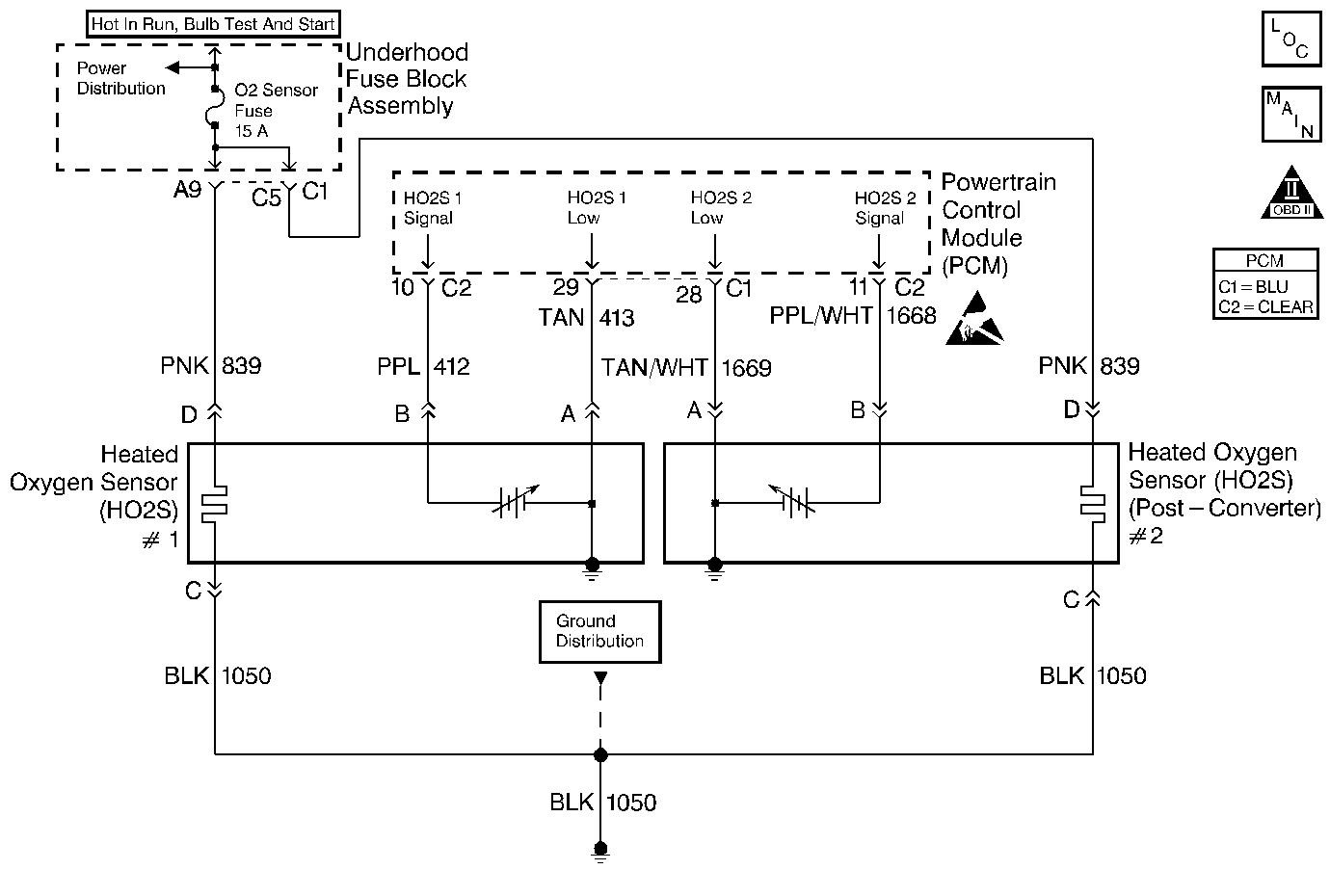
Circuit Description
The PCM supplies a bias voltage of about 450 mV between the HO2S signal and low circuits. When measured with a 10 megohm digital voltmeter, this may display as low as 350 mV. The oxygen sensor varies the voltage within a range of about 800 mV when the exhaust is rich, down through about 50 mV when exhaust is lean. The PCM constantly monitors the HO2S signal during closed loop operation and compensates for a rich or lean condition by decreasing or increasing injector pulse width as necessary. If the HO2S 2 voltage remains excessively high for an extended period of time, DTC P0138 will be set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | No active fuel trim, fuel injector circuit, Misfire, EVAP, EGR, TP, IAT, MAP, ECT, CKP, or MAF sensor DTCs present. |
| • | System voltage is greater than 9 volts. |
| • | Closed loop commanded air/fuel ratio is between 14.4 and 14.9. |
| • | Throttle angle is between 3% and 40%. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
HO2S 2 signal voltage remains above 999 mV during normal closed loop operation.
OR
HO2S 2 signal voltage remains above 200 mV during deceleration fuel mode operation.
Either condition for up to 50 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the PCM stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the PCM records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The PCM writes the conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL Off after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed (current DTC) clears when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC clears after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if this or any other emission related diagnostic does not report any failures. |
| • | Use a scan tool in order to clear the MIL/DTC. |
| • | Interrupting the PCM battery voltage may or may not clear DTCs. This practice is not recommended. Refer to Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Description , Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes. |
Diagnostic Aids
Notice: Use the connector test adapter kit J 35616-A for any test that
requires probing the following items:
• The PCM harness connectors • The electrical center fuse/relay cavities • The component terminals • The component harness connector
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Fuel pressure: An excessively rich fuel mixture can cause a DTC P0138 to be set. |
| Refer to Fuel System Pressure Test . |
| • | Evaporative emissions (EVAP) canister purge: Check for fuel saturation. If full of fuel, check canister control and hoses. |
| Refer to EVAP Control System Diagnosis . |
| • | Fuel Pressure Regulator: Check for a leaking fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by checking the vacuum line to regulator for the presence of fuel. If fuel is present, replace the fuel pressure regulator. Refer to Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement . |
| • | TP Sensor: An intermittent TP sensor output will cause the system to go rich due to a false indication of the engine accelerating. Throttle Angle displayed on a scan tool should increase steadily from 0% to 100% when opening the throttle. If not, check the TP sensor for loose mounting screws. If the TP mounting screws are OK, replace the TP sensor. Refer to Throttle Position Sensor Replacement . |
| • | Shorted Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S): If the HO2S is internally shorted the HO2S voltage displayed on the scan tool will be over 1 volt. Try disconnecting the affected HO2S and jumper the HO2S low circuit to ground with the key ON, engine not running. If the displayed HO2S voltage changes from over 1000 mV to around 450 mV, replace the HO2S. Silicon contamination of the HO2S can also cause a high HO2S voltage to be indicated. This condition is indicated by a powdery white deposit on the portion of the HO2S exposed to the exhaust stream. If contamination is evident, replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . |
| • | Open HO2S Signal or Low Circuit or Malfunctioning HO2S: A poor connection or open in the HO2S signal or low circuit can cause the DTC to set during deceleration fuel mode. An HO2S which is malfunctioning and not allowing a full voltage swing between the rich and lean thresholds can also cause this condition. Operate the vehicle while monitoring the HO2S voltage with a scan tool. If the HO2S voltage is limited within a range between 300mV to 600mV, check the HO2S signal and low circuit wiring and associated terminal connections. If the wiring and connections are OK, replace the affected HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . |
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions .
The heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) require an air reference for proper operation. The air reference is supplied through the HO2S wiring. Inspect the HO2S wires and connections for breaks or contamination. Do not use solder to repair HO2S wiring. Solder will obstruct the air path. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems for proper repair procedures.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
In order to determine if the engine is rich during De-acceleration Fuel Cut-Off (DFCO) operate the vehicle up to highway speed conditions and release the accelerator pedal allowing the vehicle to coast in gear. Monitor the scan tool HO2S voltage and the DFCO parameter. A rich condition will cause HO2S voltage to be above 468 mV during DFCO.
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of un-approved silicon RTV engine gasket material, the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine or coolant consumption. Phosphorus contamination also leaves a white powdery coating on the HO2S. Phosphorus contamination comes from oil consumption. If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
-
This step checks the HO2S High signal circuit for a short to voltage.
-
An HO2S contaminated by silicon will have a white, powdery deposit on the portion of the HO2S that is exposed to the exhaust stream. The usual cause of silica contamination is the use of un-approved silicon RTV engine gasket material, the use of silicon based sprays or fluids within the engine or coolant consumption. Phosphorus contamination also leaves a white powdery coating on the HO2S. Phosphorus contamination comes from oil consumption. If the cause of this contamination is not corrected, the replacement HO2S will also get contaminated.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2 |
Is the HO2S voltage fixed greater than the value specified? | 976 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Was a condition found and repaired? | -- | Refer to Diagnostic Aids. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
4 |
Is the HO2S voltage within the value range specified? | 351 to 551 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
5 | The HO2S is detecting a rich exhaust condition or may be contaminated. Check for one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above or similar engine conditions as necessary. Was a condition found and repaired? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
6 |
Is the voltage measured greater than the value specified? | 20 mV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
7 | Repair the short to voltage in the HO2S High signal circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Important: Before replacing a contaminated HO2S determine and repair the cause of the contamination. Replace the HO2S. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
9 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Important: If a rich engine condition was repaired inspect the engine oil for fuel contamination and replace engine oil as necessary. Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
11 | Review Captured Info using the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
