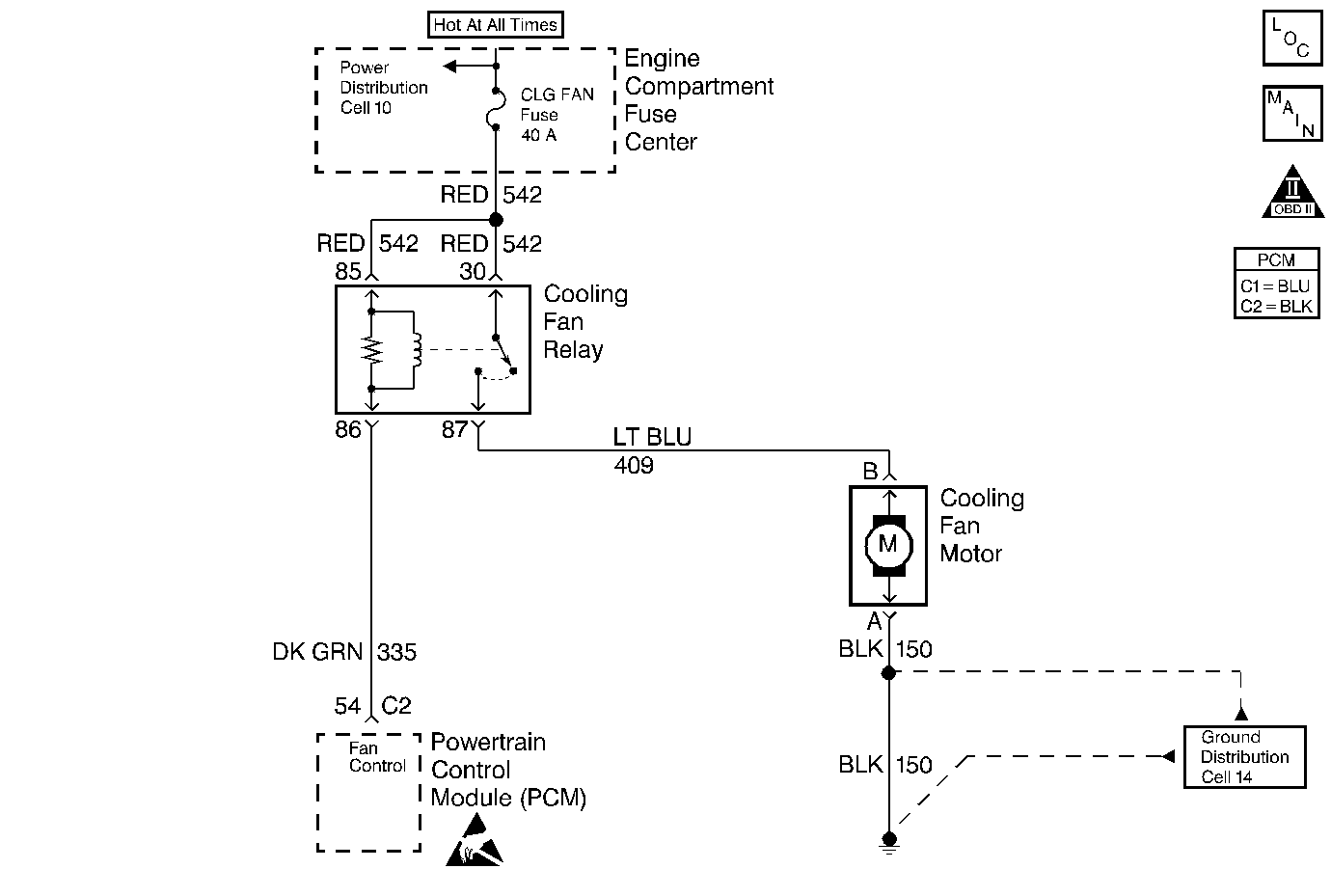
Circuit Description
The electric cooling fan is controlled by the powertrain control module (PCM) through the cooling fan relay based on inputs from the following components:
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor |
| • | The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor |
| • | The A/C selector switch |
| • | The A/C refrigerant pressure sensor |
| • | The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) |
The PCM controls the cooling fan by grounding the cooling fan control circuit which turns ON the cooling fan relay.
The cooling fan relay will be commanded ON when the following conditions are met:
| • | The engine coolant temperature reaches 106°C (223°F) or more. |
| • | The A/C clutch requested. |
| • | The vehicle speed is less than 38 MPH. |
The cooling fan relay will be commanded ON regardless of vehicle speed when the following conditions are met:
| • | A DTC is set that requests the coolant fan to be ON. |
| • | The engine coolant temperature is 151°C (304°F) or more. |
| • | The A/C refrigerant pressure is high. |
The cooling fan may be commanded ON when the engine is not running under a fan run-on conditions described in the electric cooling fan general description portion of the service manual.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | Battery voltage is greater than 9.5 volts. |
| • | Coolant fan fault line detects a malfunction for 6 seconds. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information will be stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers. |
| • | A history DTC is stored. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL will turn OFF after three consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | The MIL/DTCs can be cleared by using the scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the owner complained of an overheating problem, it must be determined if the complaint was due to an actual boil over, or if the Temp light, or temperature gage indicated overheating. |
| • | Check for the proper amount of coolant in the system. |
| • | If the gage, or light, indicates overheating, but no boil over is detected, the gage or light circuit should be checked. The gage accuracy can also be checked by comparing the engine coolant temperature sensor reading using a scan tool with the gage reading. |
| • | If the engine is actually overheating, and the gage indicates overheating, but the cooling fan is not coming ON, the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor may have shifted out of calibration and should be checked. Refer to Temperature vs Resistance . |
| • | If the engine is overheating, and the coolant fan is ON, the cooling system should be checked. Refer to Engine Overheating in Engine Cooling. |
Test Description
Numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the malfunction occurred. The information is then stored on the scan tool for later reference.
-
The cooling system operation and the coolant level should be checked before determining if any electrical conditions are present causing a cooling system malfunction.
-
With the engine OFF, the cooling fan motor should not be commanded ON by the PCM.
-
If the cooling fan motor turns OFF after disconnecting the PCM electrical connectors, the PCM was causing the cooling fan motor to be ON constantly.
-
A test light that illuminates indicates that the cooling fan motor battery feed circuit is shorted to battery voltage. The cooling fan motor will also remain engaged when the cooling fan relay electrical connector is disconnected.
-
Connecting the cooling fan relay battery feed and the cooling fan motor battery feed circuits together bypasses the PCMs control of the cooling fan motor. A cooling fan motor that fails to engage at this point indicates that the malfunction is in the cooling fan motor battery feed circuit, the cooling fan motor or the cooling fan ground circuit.
-
The battery feed is supplied to the cooling fan relay through the same fuse. No voltage on both circuits would indicate that the fuse is open. Locate and repair any shorts that may have caused the fuse to open before replacing the fuse.
-
With the engine stopped and the cooling fan relay commanded ON, the PCM should ground the cooling fan relay control circuit. This will also illuminate the test light.
-
This step determines if the reason the cooling fan motor did not come ON was due to an open battery feed circuit to the cooling fan motor.
-
The replacement PCMs must be reprogrammed and the crankshaft position system variation procedure must be performed. Refer to the latest Techline information for PCM programming and Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn for the Crankshaft Position System Variation Procedure.
-
If no malfunctions have been found at this point, refer to the Diagnostic Aids for additional checks and information.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | Go to | ||
Were any repairs necessary? | -- | |||
Is the cooling fan motor OFF? | 98°C (209°F) | |||
4 | Use the scan tool and command the cooling fan relay ON. Is the cooling fan motor ON? | -- | ||
Is the cooling fan motor OFF? | -- | |||
6 |
Is the test light ON for both terminals? | -- | ||
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
Connect a jumper wire between the cooling fan relay battery feed and cooling fan motor battery feed circuit terminals. Is the cooling fan motor ON? | -- | |||
Repair the open in the battery feed circuit that did not light. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
10 | Repair the short to B+ in the cooling fan motor battery feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Connect the test light to B+ and probe the cooling fan control circuit. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
14 | Repair the short to ground in the cooling fan control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 | Check the terminals to the cooling fan relay and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
16 | Check the cooling fan control circuit for an open or a poor electrical connection and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
17 | Connect the test light to B+ and probe the cooling fan motor ground circuit. Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
18 | Repair the open or a poor electrical connection in the cooling fan motor battery feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
19 | Check for a poor electrical connections at the cooling fan motor electrical connector and repair as necessary. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Was a repair necessary. | -- | ||
20 | Repair the open or a poor electrical connection in the cooling fan motor ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
21 | Replace the cooling fan motor. Refer to Engine Cooling Fan Replacement in Engine Cooling. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
22 | Replace the cooling fan relay. Refer to Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor and Cooling Fan Relays Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||
Does the cooling fan motor turn ON when commanded? | -- | System OK, go to Diagnostic Aids | ||
25 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has ran and passed? | -- | -- | |
26 | Check if any additional DTCs are set. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK, go to Diagnostic Aids |
