The maintenance free battery is standard in all vehicles.
The battery is completely sealed except for two small vent holes in the sides.
These vent holes allow the small amount of gas produced in the battery
to escape.
The battery has the three following functions in the electrical system:
| • | Provides a source of energy for cranking the engine |
| • | Acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system |
| • | Provides, for a limited time, the energy when the electrical load
used exceeds the output of the generator. |
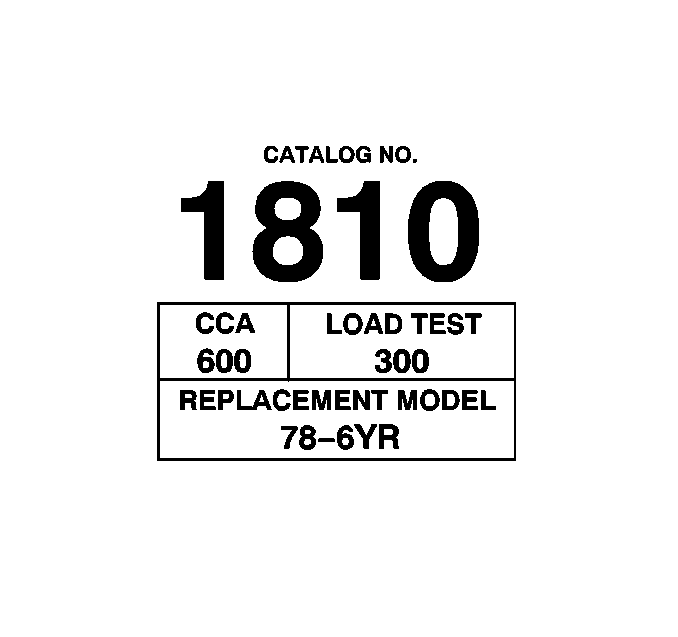
The battery specification label contains information pertinent to servicing
the battery. This information includes the cold cranking amperage, reserve
capacity, the original equipment and replacement part numbers.
Battery Ratings
A battery has two ratings:
| • | Cold cranking amperage (CCA) |
Reserve Capacity
The reserve capacity rating is an estimate of how long the vehicle can
be driven with no generator output, the headlamps turned on, and a minimum
electrical load (most of the accessories turned off). It is the maximum
amount of time (in minutes) it will take a fully charged battery, being
discharged at a constant rate of 25 amperes and constant temperature
of 27°C (80°F), to reach a terminal voltage of 10.5 volts.
Other temperature or current draws, the state of charge, or the condition
of the battery will affect how long the battery will actually last when
the vehicle is being driven without generator output.
Cold Cranking Amperage
Cold cranking amperage is an indication of the ability of the battery
to crank the engine at cold temperatures. This rating is the minimum amperage
that the battery must maintain for 30 seconds at -18°C (0°F),
while maintaining at least 7.2 volts. The actual performance of a battery
will vary with actual temperature.
Electrolyte Freezing
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific gravity, or
the state of charge. The higher the state of charge, the lower the freezing
point. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be kept charged.
A discharged battery can freeze at temperatures as high as -7°C
(20°F). As long as the green dot is visible in the hydrometer,
the freezing point of the battery will be somewhere below -32°C
(-25°F). A fully charged battery will not freeze until the
temperature falls below -54°C (-65°F).
Protection During Vehicle Storage
Certain electronic devices on the vehicle maintain a small continuous
current drain (parasitic load) on the battery, such as a PCM or a VCM. A battery
that is not used for an extended period of time will discharge. Eventually
permanent damage will result. Discharged batteries will also freeze
in cold weather. Refer to Electrolyte Freezing.
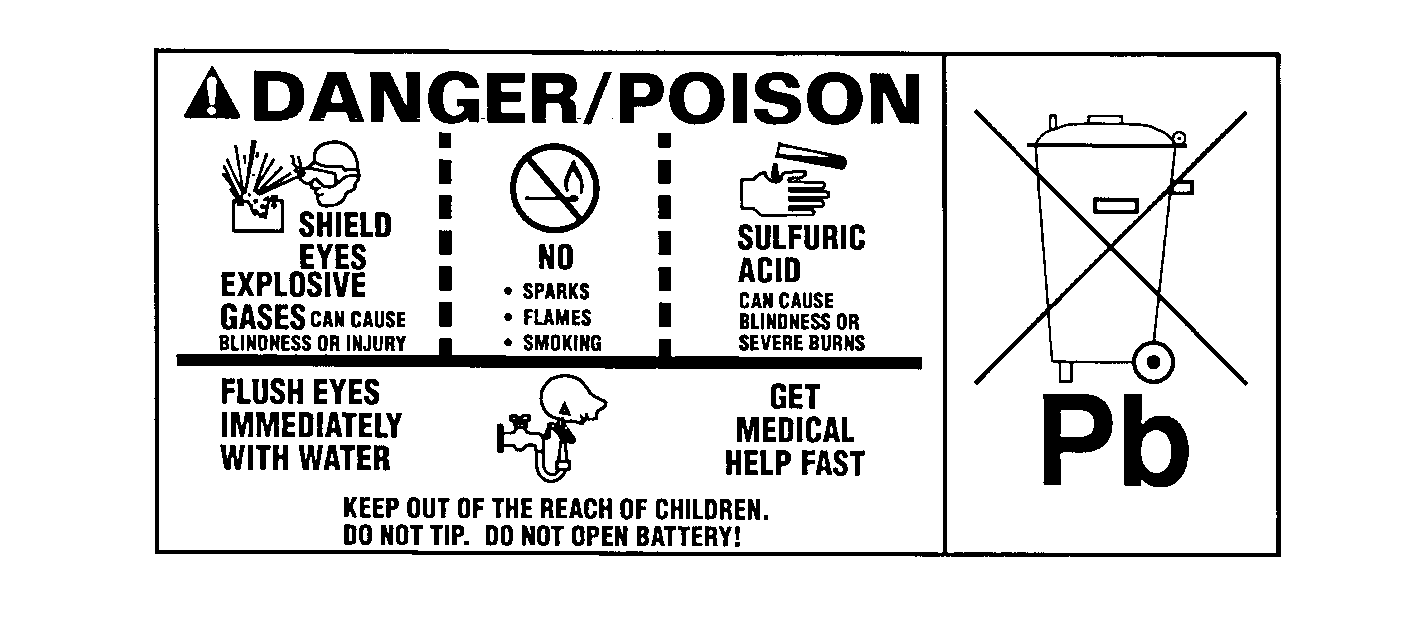
Caution: Batteries produce explosive gases. Batteries contain corrosive acid.
Batteries supply levels of electrical current high enough to cause burns.
Therefore, in order to reduce the risk of personal injury while working
near a battery, observe the following guidelines:
| • | Always shield your eyes. |
| • | Avoid leaning over the battery whenever possible. |
| • | Do not expose the battery to open flames or sparks. |
| • | Do not allow battery acid to contact the eyes or the skin. |
| - | Flush any contacted areas with water immediately and thoroughly. |
Notice: Turn OFF the ignition when connecting or disconnecting the battery cables,
the battery charger or the jumper cables. Failure to do so may
damage the PCM or other electronic components.
Do the following in order to maintain the battery state of charge while
storing the vehicle for more than 30 days:
| • | Ensure that the green dot is visible in the built-in hydrometer. |
| • | Disconnect the negative battery cable to protect the battery from
discharge by parasitic current drains. |
| • | When it is time to reconnect the battery, use the following procedure: |
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners
must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring
replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant
are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or
corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified.
These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage
the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when
installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
| - | Lightly wire brush
any oxidation from the contact face of the battery terminal and the battery
post before reattaching the cable. |
Tighten
Tighten the battery cable bolt to 15 N·m (11 lb ft).
| - | Reset the clock and the push-button tuning radio before the vehicle
is put back into service. |
| • | Maintain a high state of charge when the battery cannot be disconnected. |
| • | Establish a regular schedule for recharging the battery every
20-45 days. |
| - | When a battery is found without a green dot visible in the hydrometer,
promptly recharge the battery. |
| - | To reduce charging time, use a battery charger that can produce
a charging voltage of at least 16 volts. |
| - | Original equipment maintenance free batteries are not damaged
by charging rates of 50 amps or more. |
| - | The battery will not be damaged as long as the battery does not
spew acid from the vents or get hotter than 52°C (125°F). |
| - | Check the battery being charged every 45-60 minutes. |
| - | If gassing or overheating does occur, reduce the rate of charge,
or stop if necessary. |
| - | Avoid overcharging by stopping one hour after the green dot appears
in the hydrometer. |
| • | Maintain a high state of charge when the battery cannot be disconnected. |
| • | Establish a regular schedule for recharging the battery every
20-45 days. |
| • | A battery that has remained in a discharged state for a long period
of time is difficult to recharge or may be permanently damaged. |
Built-in Hydrometer
A built-in temperature compensation hydrometer is molded into the top
of the maintenance free battery. When observing the hydrometer, make sure
the battery top is clean. Use a light in poorly-lit areas.
Under normal operating conditions, on of three indications can be observed:
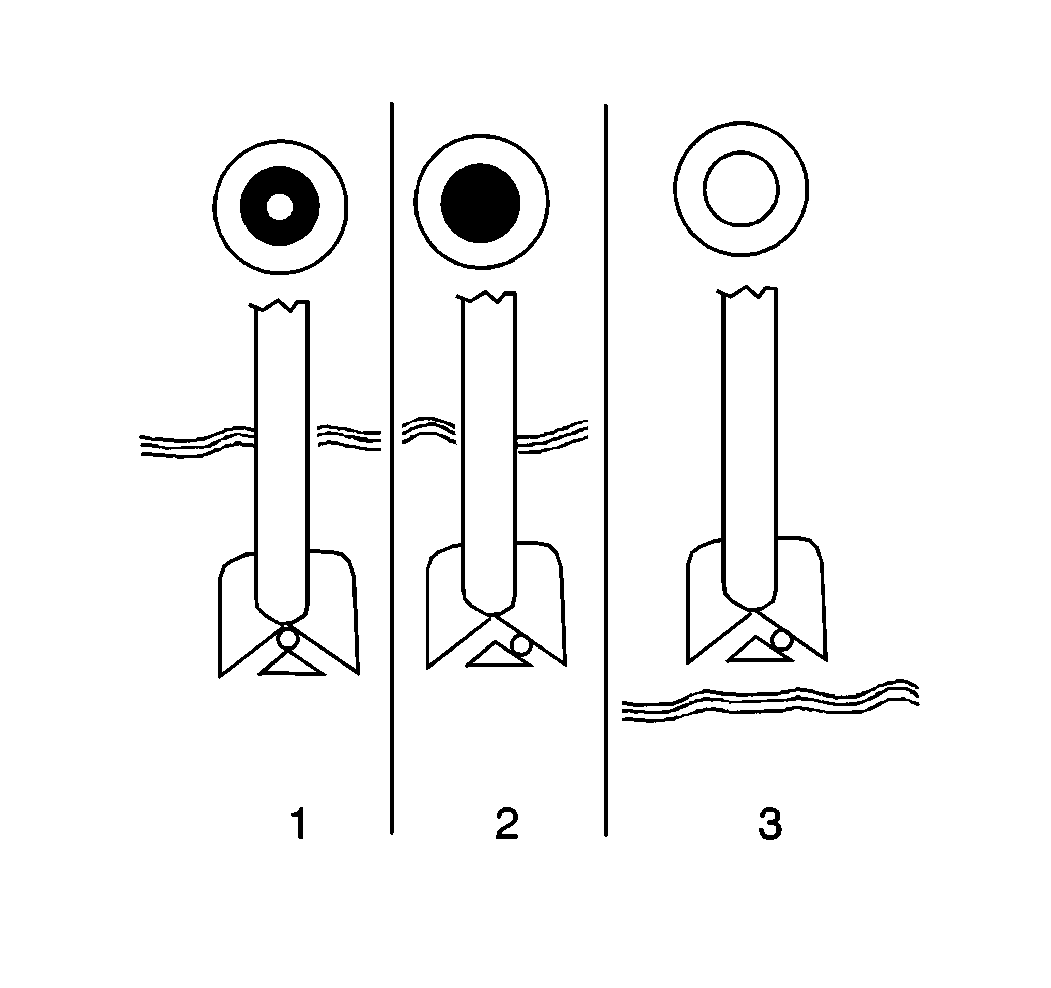
| • | Any green appearance in the hydrometer is interpreted as a green
dot (1). This means the battery is ready for testing. Refer to
Battery Not Operating Properly
. |
| • | A dark dot is visible (2). The green dot is not visible. |
| - | If the green dot is not visible and there is a complaint about
cranking, charge the battery. Refer to
Battery Charging
. |
| • | A clear or yellow dot (3) means that electrolyte level is below
the bottom of the hydrometer and is too low for diagnosis. The yellow dot
may have been caused by one of the following conditions: |
| - | Excessive or prolonged charging |
When you find a battery in this condition, this may indicate high charging
voltages caused my a faulty charging system. Because of this, the charging
and electrical system must be checked. Refer to
Battery Hydrometer Displays Yellow Dot
.
Replace the battery if a cranking complaint exists, and the battery
has a yellow or clear hydrometer. Refer to
Battery Replacement
.



